Franklyn Barrett
|
Read other articles:

Asosiasi Sepak Bola Kerajaan BelandaUEFADidirikan1889Kantor pusatZeistBergabung dengan FIFA1904Bergabung dengan UEFA1954PresidenMichael van PraagWebsitewww.knvb.nl Asosiasi Sepak Bola Kerajaan Belanda (Belanda: Koninklijke Nederlandse Voetbalbond (KNVB)code: nl is deprecated ) adalah badan pengendali sepak bola di Belanda. Kompetisi Badan ini menyelenggarakan beberapa kompetisi di Belanda, yakni: Eredivisie (Liga Divisi Utama Belanda) Liga Divisi Satu Belanda Piala Asosiasi Sepak Bola Kerajaa...

Special type of art that conceptualizes a subject Not to be confused with Conceptual art. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Concept art – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Example of concept design workflow (blue) follo...

Vice president of the United States from 1949 to 1953 Alben W. BarkleyOfficial portrait, 194935th Vice President of the United StatesIn officeJanuary 20, 1949 – January 20, 1953PresidentHarry S. TrumanPreceded byHarry S. TrumanSucceeded byRichard NixonSenate Majority LeaderIn officeJuly 14, 1937 – January 3, 1947DeputyJ. Lister HillSherman MintonJ. Hamilton LewisPreceded byJoseph Taylor RobinsonSucceeded byWallace H. WhiteSenate Minority LeaderIn officeJanuary 3, 194...

American judge This article is about the former Governor of Pennsylvania. For his father, the former Pennsylvania Attorney General, see John C. Bell (lawyer). For other people named John Bell, see John Bell (disambiguation). John Cromwell Bell Jr.Photo used in Bell's 1942 lieutenant governor campaignChief Justice of the Supreme Court of PennsylvaniaIn office1961–1972Preceded byCharles Alvin JonesSucceeded byBenjamin R. JonesJustice of the Supreme Court of PennsylvaniaIn office1950–196133r...

Overview of Dutch military history Part of a series on the History of the Netherlands Early Prehistory of the Netherlands Germanic tribes Frisii, Batavi, Cananefates, Chamavi Roman era Migration Period Frisians, Franks, Saxons Medieval Frisian Kingdom Frankish Kingdom Middle Francia Lotharingia Lower Lotharingia Holy Roman Empire Burgundian Netherlands Habsburg Netherlands Seventeen Provinces Spanish Netherlands Republic Eighty Years' War Dutch Golden Age (painting) Dutch colonial empire (evo...

Thai public organization Thailand Convention and Exhibition Bureauสำนักงานส่งเสริมการจัดการประชุมและนิทรรศการChiruit Isarangkun Na Ayuthaya at IMEX 2023Agency overviewFormed27 September 2002; 21 years ago (2002-09-27)HeadquartersBangkokEmployees143Annual budget895 million baht (FY2019)Agency executiveChiruit Isarangkun Na Ayuthaya, PresidentParent departmentOffice of the Prime MinisterWebsi...

Kerajaan Babel beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk kota Babel, lihat Babilon. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Babel (disambiguasi). Babilonia𒆳𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠Māt Akkadī1895 SM–539 SMLuas wilayah Kerajaan Babilonia pada awal dan akhir masa pemerintahan Hamurabi, sekarang termasuk wilayah negara Kuwait dan IrakIbu kotaBabilonBahasa resmi bahasa Akkadia bahasa Sumeria Bahasa Aram Bahasa yang umum digunakanbahasa AkkadiaBahasa AramAgama Agama BabiloniaSejarah • Didirikan 1895 SM•&#...
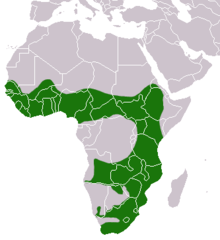
Species of carnivore This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: African clawless otter – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) African clawless otter On the banks of the Okavango River, Namibia Conservation status Near Threatened &...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

Muhammad Fauzan Nurhuda YusroM.Si. Anggota Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Republik IndonesiaPetahanaMulai menjabat 23 Maret 2021PresidenJoko WidodoPendahuluYaqut Cholil QoumasPenggantiPetahanaDaerah pemilihanJawa Tengah X Informasi pribadiLahir9 Februari 1972 (umur 52)Pati, Jawa TengahPartai politikPKBSuami/istriYus Huda HidayahAnak2Alma materInstitute Ilmu Al-Qur'an WonosoboUniversitas IndonesiaSunting kotak info • L • B Muhammad Fauzan Nurhuda Yusro, M.Si. (lahir 9 Februari ...

Sporting event delegationSlovenia at the2008 Summer OlympicsIOC codeSLONOCSlovenian Olympic CommitteeWebsitewww.olympic.si (in Slovene and English)in BeijingCompetitors62 in 11 sportsFlag bearers Urška Žolnir (opening) Špela Ponomarenko (closing)[1]MedalsRanked 39th Gold 1 Silver 2 Bronze 2 Total 5 Summer Olympics appearances (overview)199219962000200420082012201620202024Other related appearances Austria (1912) Yugoslavia (1920–1988) Slovenia, represented by t...

Hill in Tallinn View of Toompea hill from the tower of St. Olaf's church. Toompea (from German: Domberg, Cathedral Hill) is a limestone hill in the central part of the city of Tallinn, the capital of Estonia. The hill is an oblong tableland, which measures about 400 by 250 metres, has an area of 7 hectares (17 acres) and is about 20–30 metres higher than the surrounding areas. In folklore the hill is known as the tumulus mound over the grave of Kalev, erected in his memory by his grieving w...

坐标:43°11′38″N 71°34′21″W / 43.1938516°N 71.5723953°W / 43.1938516; -71.5723953 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2017年5月21日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:新罕布什尔州 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源...

2000 single by Yolanda AdamsOpen My HeartSingle by Yolanda Adamsfrom the album Mountain High... Valley Low Released2000Recorded1998Genre Gospel R&B Length5:40LabelElektraSongwriter(s) James Harris James Q. Wright Terry Lewis Yolanda Adams Producer(s) Jimmy Jam & Terry Lewis James Big Jim Wright Yolanda Adams singles chronology The Battle Is the Lord's (1996) Open My Heart (2000) Yeah (1999) Open My Heart is a song by Yolanda Adams released in 2000. The song gained Adams great popu...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...

Roman emperor from AD 68 to 69 This article is about the emperor. For other uses, see Galba (disambiguation). GalbaGold aureus of Galba. Legend:imp(erator) ser(vius) galba aug(ustus)Roman emperorReign8 June 68 – 15 January 69PredecessorNeroSuccessorOthoBorn24 December 3 BCNear Terracina, Italy, Roman EmpireDied15 January AD 69 (aged 70)Rome, Italy, Roman EmpireSpouseAemilia LepidaIssueLucius Calpurnius Piso Frugi Licinianus (adopted)NamesServius Sulpicius GalbaLucius Livius Ocella Sulpicius...

Pendidikan di MalaysiaKementerian PendidikanMenteri PendidikanDr. Maszlee MalikBiaya pendidikan nasional (2014)BiayaMYR54.6 miliar (USD17 miliar)1Penjelasan utamaBahasa utamaMelayu, Mandarin, Tamil, InggrisJenis sistemNasionalDidirikan1956Melek huruf (2009)Total95% (semuanya 15 tahun keatas)Laki-Laki95% total, 98% 15–24 tahunPerempuan95% total, 98% 15–24 tahunPerputaranTotal5,407,865 dengan 405,716 guru (ratio 13:1), termasuk 163,746 pra-sekolahDasar2,899,228 (peringkat survival sampai ke...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Film Musik Terbaik (Grammy Award). Grammy Award untuk Video Musik TerbaikDeskripsiVideo musik bentuk pendek berkualitasNegaraAmerika SerikatDipersembahkan olehNational Academy of Recording Arts and SciencesDiberikan perdana1984Diberikan terakhir2017Situs webgrammy.com Grammy Award untuk Video Musik Terbaik adalah penghargaan disajikan di Grammy Awards, sebuah upacara yang didirikan pada tahun 1958 dan awalnya disebut Gramophone Awards,[1] untuk pemain, sutra...

Roman town destroyed by eruption of Mount Vesuvius For the modern Italian commune, see Ercolano. For other uses, see Herculaneum (disambiguation). HerculaneumThe excavations of HerculaneumShown within ItalyAlternative nameErcolanoLocationErcolano, Campania, ItalyCoordinates40°48′22″N 14°20′54″E / 40.8060°N 14.3482°E / 40.8060; 14.3482TypeSettlementHistoryFounded6th–7th century BCAbandoned79 ADSite notesWebsiteHerculaneum – Official website UNESCO W...

Main article: Military awards and decorations of Sri Lanka AwardRana Sura PadakkamaMedal, obverseTypeMilitary decorationAwarded forIndividual acts of distinguished conduct in the face of the enemyDescriptionSuspended from a plain suspension barPresented bySri LankaEligibilityAll regular and volunteer ranks of the tri-servicesPost-nominalsRSPClaspsNoneStatusCurrently awardedEstablished1981Ribbon bar PrecedenceNext (higher)Rana Wickrama PadakkamaNext (lower)Vishista Seva Vibhushanaya ...