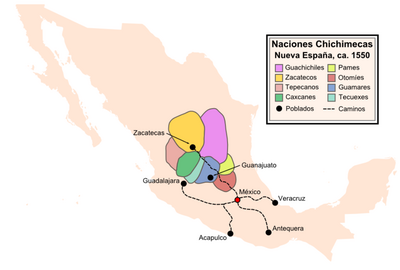
Francisco Tenamaztle
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini memiliki beberapa masalah. Tolong bantu memperbaikinya atau diskusikan masalah-masalah ini di halaman pembicaraannya. (Pelajari bagaimana dan kapan saat yang tepat untuk menghapus templat pesan ini) Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Freddy Fazbear's Pizzeria Simulat...

History of LGBT people and Mormonism in the 1970s See also: Brigham Young University LGBT history, Homosexuality and The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, Gender minorities and the LDS church, Sexuality and Mormonism, and LGBT Mormon people and organizations LGBT Mormon topics Overview articles Homosexuality & the LDS Church Gender minorities & the LDS church LGBT Mormon people & organizations BYU LGBT history LGBT Mormon suicides LGBT rights & the LDS Church LGBT r...

Road in Manchester This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: A5103 road – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) A5103Route informationMaintained by National HighwaysManchester City CouncilLength4.9 mi (7.9 km)Major ju...
Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang karakter Nintendo. Untuk penggunaan lain, lihat Luigi (disambiguasi). Untuk orang lain dengan nama tersebut, lihat Luigi (nama). LuigiTokoh 'Mario'Mural dengan gambar sosok di Toruń (2022)Penampilanperdana'Mario Bros. (1983)Mario Bros. (1983)PenciptaShigeru MiyamotoPengisi suara Inggris Marc Graue (1994) Charles Martinet (1997–2023) Kevin Afghani (2023–sekarang) Julien Bardakoff (1998–2001) Danny Wells (The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!) Tony Rosato (...

Indian Politician K. MohanMohan with his wife during their 50th wedding anniversary celebrationBorn(1926-03-14)14 March 1926Chennai, Tamil Nadu, IndiaDied24 August 2014(2014-08-24) (aged 89)Other namesPasamalar MohanOccupation(s)Art director, film producerYears active1950–2014SpouseShanthakumariChildren8 K. Mohanakrishnan (14 March 1926 – 24 August 2014) also known as Pasamalar Mohan, or simply K. Mohan, was an Indian film producer and art director. He entered the movi...

For other Princes of Asturias named Alfonso, see Alfonso, Prince of Asturias. Prince of Asturias AlfonsoPrince of AsturiasSculpture of Alfonso from his tomb in BurgosBorn17 November 1453TordesillasDied5 July 1468(1468-07-05) (aged 14)CardeñosaBurialMiraflores CharterhouseHouseTrastámaraFatherJohn II of CastileMotherIsabella of Portugal Alfonso, Prince of Asturias (17 November 1453 – 5 July 1468), called Alfonso the Innocent, was the figurehead of rebelling Castilian magn...

Chatib SulaimanLahir1906 atau 1907 Sumpur, Batipuh Selatan, Tanah Datar, Sumatera BaratMeninggal15 Januari 1949 (umur 42 atau 43) Lurah Kincia, Situjuah Batua, Situjuah Limo Nagari, Lima Puluh Kota, Sumatera BaratKebangsaan IndonesiaPekerjaanPengajarDikenal atasPejuang kemerdekaan IndonesiaAnakLastri ChatibKasman ChatibErman ChatibSudarman ChatibSurachman ChatibOrang tuaHaji Sulaiman (ayah) Siti Rahma (ibu) Chatib Sulaiman (lahir di Sumpur, Tanah Datar, Sumatera Barat, 1906 — meninggal di ...

Beata Franziska NischNunLahir(1882-09-18)18 September 1882Mittelbiberach-Oberdorf, Tübingen, Kekaisaran JermanMeninggal8 Mei 1913(1913-05-08) (umur 30)Allensbach-Hegne, Freiburg, Kekaisaran JermanDihormati diGereja Katolik RomaBeatifikasi1 November 1987, Lapangan Santo Petrus, Kota Vatikan oleh Paus Yohanes Paulus IIPesta8 MeiAtributBusana biarawatiPelindungTukang masakPekerjaOrang yang mengidap erisipelas Franziska Nisch (18 September 1882 – 8 Mei 1913) adalah seorang b...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Società Sportiva Maceratese. S.S. MacerateseStagione 2014-2015Sport calcio Squadra Maceratese Allenatore Giuseppe Magi Presidente Maria Francesca Tardell...

American cartoonist (1869–1949) Clifford K. BerrymanBerryman in an early 20th century Harris & Ewing photoBorn(1869-04-02)April 2, 1869Clifton, Kentucky, USDiedDecember 11, 1949(1949-12-11) (aged 80)Washington, D.C., USArea(s)Editorial cartoonistNotable worksRemember the MaineDrawing the Line in MississippiAwardsPulitzer Prize for Editorial Cartooning, 1944Spouse(s)Kate Geddes Durfee (m. 1893) Clifford Kennedy Berryman (April 2, 1869 – December 11, 1949) was a Pulitzer Prize–wi...

Unincorporated community in Texas, US Dyersdale is an unincorporated community in Harris County, Texas, United States. The name originates from Clement C. Dyer, one of the Old Three Hundred of Stephen F. Austin's colonists.[1] A post office opened in 1913. In 1914 the community, with 250 residents, had a lumber company. The post office closed in 1917. An oilfield opened in the mid-1930s. In 1936, the community had scattered residences and a school. By 1946, the oilfield was still in p...

Voce principale: Società Sportiva Juve Stabia. Società Sportiva Juve StabiaStagione 2014-2015Sport calcio Squadra Juve Stabia Allenatore Giuseppe Pancaro(fino al 13 marzo 2015) Marco Salvini(dal 13 marzo 2015) Presidente Francesco Manniello Lega Pro4ª Coppa ItaliaSecondo Turno Coppa Italia Lega ProQuarti di finale Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Pisseri (38+1[1])Totale: Pisseri (42) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Di Carmine (14)Totale: Di Carmine (14) StadioRomeo Menti (6.000)[...

This article is about the district. For the constituency, see South Staffordshire (UK Parliament constituency). For the water company, see South Staffordshire Water. Non-metropolitan district in EnglandSouth Staffordshire DistrictNon-metropolitan districtSouth StaffordshireThe Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal at PenkridgeSouth Staffordshire shown within StaffordshireSovereign stateUnited KingdomConstituent countryEnglandRegionWest MidlandsNon-metropolitan countyStaffordshireStatusNon-me...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

بيرشاد (بالأوكرانية: Бершадь) بيرشاد بيرشاد تاريخ التأسيس 1459[1] تقسيم إداري البلد أوكرانيا (1991–) [2] خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 48°22′22″N 29°31′57″E / 48.372777777778°N 29.5325°E / 48.372777777778; 29.5325 المساحة 7.1 كيلومتر مربع الارتفاع 171 متر السكان الت...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Осьминог (значения). Осьминогиангл. Squidbillies Жанр комедия Создатели Джим ФортиэрДэйв Уиллис Рассказчик Дэйв Уиллис Композитор Билли Джо Шэйвер[вд] Страна США Язык английский Число сезонов 11 Число серий 117 (список ...

Penggambaran alegori dari dewi Romawi Abundantia dengan sebuah cornucopia, karya Rubens (sekitar tahun 1630) Pada zaman klasik, kornukopia atau cornucopia /ˌkɔːrnjəˈkoʊpiə, ˌkɔːrnə-/ (dari kata Latin cornu copiae) adalah sebuah simbol kelimpahan dan berkah, umumnya merupakan sebuah bejana berbentuk tanduk besar yang diisi hasil panen, bunga atau kacang. Dalam mitologi Mitologi memberikan berbagai penjelasan asal usul cornucopia. Salah satu cerita yang paling terkenal melibatkan kel...

Truck that moves semi trailers within a cargo yard A terminal tractor Terminal tractor at the Port of Dover. A terminal tractor, known in the United States as a shag truck, shunt truck, spotter truck, spotting tractor, yard truck, yard shifter, yard dog, yard goat, yard horse, yard mule, yard jockey, yard spotter, hostler, or mule, is a kind of semi-tractor intended to move semi-trailers within a cargo yard, warehouse facility, or intermodal facility, much like a switcher locomotive is used t...

American college football season 1905 Army Cadets footballConferenceIndependentRecord4–4–1Head coachRobert Boyers (2nd season)CaptainAlexander Garfield GillespieHome stadiumThe PlainSeasons← 19041906 → 1905 Eastern college football independents records vte Conf Overall Team W L T W L T Yale – 10 – 0 – 0 Penn – 12 – 0 – 1 Temple – 2 – 0 ̵...

Cynthia ErivoCynthia Erivo di Festival Film Tribeca tahun 2018LahirCynthia Onyedinmanasu Chinasaokwu Erivo[1][2]8 Januari 1987 (umur 37)Stockwell, London, Britania RayaAlmamaterRoyal Academy of Dramatic ArtPekerjaanAktris, penyanyi, pencipta laguTahun aktif2011–sekarangKarier musikGenre R&B soul urban kontemporer gospel Broadway InstrumenVokal Cynthia Onyedinmanasu Chinasaokwu Erivo (/əˈriːvoʊ/;[3] lahir 8 Januari 1987) merupakan seorang aktris, pe...