Folding-Fin Aerial Rocket
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Gogh, The Starry NightPoster resmiGenreRomantis Komedi, DramaDitulis olehSin Yoo-damSutradaraJo Soo-wonKim Young-hwanPemeranKwon YuriKim Young KwangLee Ji-hoonNegara asalSouth KoreaBahasa asliKoreanJmlh. episode20ProduksiDurasi20 min.Rumah produksiKim Jong-hak ProductionsSohuRilis asliJaringanSohu TVRilis2 Juli 2016 - sekarangGogh, The Starry Night (Hangul: 고호의 별이 빛나는 밤에; RR: Goho-ui Byeoli Bitnaneun Bame) adalah web-drama kolaborasi antara Korea Sel...

Strada statale 627della VandraDenominazioni successiveStrada regionale 627 della VandraStrada provinciale 1 della Vandra LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regioni Lazio Molise Province Frosinone Isernia DatiClassificazioneStrada statale InizioSora FineSS 85 presso Isernia Lunghezza78,946[1] km Provvedimento di istituzioneD.M. 26/02/1971 - G.U. 126 del 19/05/1971[2] GestoreANAS (1971-2002) Percorso Manuale La ex strada statale 627 della Vandra (SS 627), ora st...
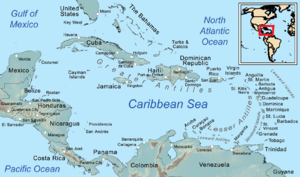
Laut KaribiaSatelit Laut KaribiaPeta Laut KaribiaJenis perairanLautBagian dariSamudra AtlantikAsal sungaiMagdalenaAtratoChagresSan JuanCocoMotaguaTerletak di negara Daftar Antigua dan Barbuda Aruba Bahama Barbados Belize Kepulauan Virgin Britania Raya Caribbean Netherlands Kolombia Kosta Rika Kuba Dominika Republik Dominika Grenada Guadeloupe Guatemala Haiti Honduras Jamaika Meksiko Montserrat...

Place in Western Cape, South AfricaFish Hoek VishoekThe view of Fish Hoek Bay from Elsie's Peak towards Clovelly.Fish HoekShow map of Western CapeFish HoekShow map of South AfricaCoordinates: 34°08′10″S 18°25′48″E / 34.136°S 18.430°E / -34.136; 18.430CountrySouth AfricaProvinceWestern CapeMunicipalityCity of Cape TownArea[1] • Total13.45 km2 (5.19 sq mi)Population (2011)[1] • Total11,890 •&...

The brewery that was clipped by the B-50 Superfortress before it crashed into the Lester. Interstate 5 now runs through where the apartment building once stood.[1] The Lester Apartments was a building on the west side of Beacon Hill, Seattle, Washington, United States. It was constructed in 1910–1911, originally intended to be the world's largest brothel. After scandal (and women's suffrage[2]) forced Seattle mayor Hiram Gill from office, the building was converted to be an ...

French step-entrance and low-floor single-decker bus This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Renault PR100.3 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message)Motor vehicle Renault PR100.3ACTION Austral Denning bodied Renault PR100.3 at Tuggerano...

Kerry Harris Nazionalità Australia Tennis Carriera Singolare1 Vittorie/sconfitte Titoli vinti Miglior ranking Risultati nei tornei del Grande Slam Australian Open SF (1972) Roland Garros - Wimbledon - US Open - Doppio1 Vittorie/sconfitte Titoli vinti Miglior ranking Risultati nei tornei del Grande Slam Australian Open V (1972) Roland Garros F (1971) Wimbledon QF (1969) US Open QF (1970, 1971, 1972, 1973). 1 Dati relativi al circuito magg...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento nobili tedeschi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Giovanni I di BrandeburgoIllustrazione ottocentesca raffigurante il principe Giovanni CiceronePrincipe Elettore di BrandeburgoStemma In carica11 marzo 1486 –9 gennaio 1499 PredecessoreAlberto III SuccessoreGioacchino I NascitaAnsbach, 2 agost...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Горностай (значения). Горностай Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:Челюстнороты...

Football match2002 CONCACAF Gold Cup finalThe Rose Bowl hosted the final.Event2002 CONCACAF Gold Cup United States Costa Rica 2 0 DateFebruary 2, 2002VenueRose Bowl, Pasadena, CaliforniaRefereeCarlos Batres (Guatemala)Attendance14,432← 2000 2003 → The 2002 CONCACAF Gold Cup final was a soccer match to determine the winners of the 2002 CONCACAF Gold Cup. The match was held at the Rose Bowl in Pasadena, California, on February 2, 2002, and was contested by the winners of the semi-f...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

Viewing of objects which are too small to be seen with the naked eye Not to be confused with Microscopic or Microscope. Scanning electron microscope image of pollen (false colors) Microscopic examination in a biochemical laboratory Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye).[1] There are three well-known branches of microscopy: op...

Louise CarverDi film The Extra Girl (1923) bersama Louise Carver san Mabel NormandLahirMary Louise Stieger(1869-06-09)9 Juni 1869Davenport, Iowa, A.S.Meninggal19 Juni 1956(1956-06-19) (umur 87)Los Angeles, California, A.S.Nama lainLouise Spilger MurrayLouise Carver MurrayPekerjaanAktrisTahun aktif1908-1941Suami/istriTom Murray (?-1935) (hingga wafat) Louise Carver (9 Juni 1869 – 19 Juni 1956) adalah seorang aktris Amerika yang tampil di panggung opera agung, ni...

Multicultural center in Berkeley, California, US La Peña Cultural Center, or La Peña for short, is a multicultural center in the United States. It was founded in 1975 by Latin American and Californian allies in Berkeley, California in response to the 1973 coup d'état in Chile, or golpe de estado.[1][2] The center was a focal point for the opposition-in-exile to dictator Augusto Pinochet during his rule, and later evolved into a nonprofit organization whose mission is to pro...

Election of Pope Innocent IV Papal electionMay – June 1243Dates and location16 May–25 June 1243Anagni CathedralKey officialsProtodeaconRaniero CapocciElected popeSinibaldo FieschiName taken: Pope Innocent IV← 12411254 →The 1243 papal election (16 May – 25 June) elected Cardinal Sinibaldo Fieschi of Genoa to succeed Pope Celestine IV. The conclave began after the Holy See had been vacant for 18 months and six days, therefore ca. May 16, 1243. There were nine cardinals prese...

Эту страницу предлагается переименовать в «Дуду (бразильский футболист, 1993)».Пояснение причин и обсуждение — на странице Википедия:К переименованию/3 июля 2024. Пожалуйста, основывайте свои аргументы на правилах именования статей. Не удаляйте шаблон до подведения итога...

Resolusi 882Dewan Keamanan PBBBendera MozambikTanggal5 November 1993Sidang no.3.305KodeS/RES/882 (Dokumen)TopikSituasi di MozambikRingkasan hasil15 mendukungTidak ada menentangTidak ada abstainHasilDiadopsiKomposisi Dewan KeamananAnggota tetap Tiongkok Prancis Rusia Britania Raya Amerika SerikatAnggota tidak tetap Brasil Tanjung Verde Djibouti Spanyol Hungaria Jepang Maroko Selandia Baru Pakistan Venezuela Re...

Tel Aviv Open 1995Sport Tennis Data9 ottobre – 16 ottobre Edizione16a SuperficieCemento CampioniSingolare Ján Krošlák Doppio Jim Grabb / Jared Palmer 1994 1996 Il Tel Aviv Open 1995 è stato un torneo di tennis giocato sul cemento. È stata la 16ª edizione del torneo, che fa parte della categoria World Series nell'ambito dell'ATP Tour 1995. Si è giocato al Israel Tennis Centers di Ramat HaSharon vicino a Tel Aviv in Israele dal 9 al 16 ottobre 1995. Indice 1 Campioni 1.1 Singolare masc...

この記事の正確性に疑問が呈されています。 問題箇所に信頼できる情報源を示して、記事の改善にご協力ください。議論はノートを参照してください。(2010年4月) OpenDocument Text拡張子.odtMIMEタイプapplication/vnd.oasis.opendocument.text開発者OASIS種別ワープロソフトフォーマット国際標準ISO/IEC 26300 OpenDocument Spreadsheet拡張子.odsMIMEタイプapplication/vnd.oasis.opendocument.spreadsheet開発者OA...

Operation through Baghdad Operation Imposing LawPart of the Second Battle of Baghdad and the Iraq War (Operation Phantom Thunder)U.S. soldiers take cover during a firefight with insurgents in the Dora section of Baghdad 7 March 2007Date14 February – 24 November 2007(9 months, 1 week and 3 days)LocationBaghdad, IraqResult Coalition victory(Whole city, except for Sadr city and the southern portion, come under coalition control)Belligerents United States United Kingdo...




