Fazl-e-Haq Khairabadi
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

De PuntUnit KA 766 selama pembuatan filmSutradaraHanro SmitsmanProduser Staccato Films Guapo Productions Ditulis oleh Sylvia Pessireron Carel Donck Pemeran Martin Schwab Gerson Oratmangoen Terence Schreurs Anis de Jong Sophie van Oers Marie-Louise Stheins Penata musik Melcher Meirmans Merlijn Snitker Chrisnanne Wiegel Distributor Motel Films Evangelische Omroep Tanggal rilis 3 Mei 2009 (2009-05-03) NegaraBahasaBelandaMelayu Ambon Untuk desa di Drenthe, Belanda, lihat De Punt. Untuk...
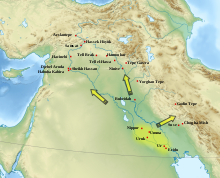
Uruk𒀕𒆠, Unugki (bahasa Sumeria)𒌷𒀕 atau 𒌷𒀔, Uruk (bahasa Akkadia) وركاء or أوروك Warkāʼ atau Auruk (bahasa Arab)Kuil Putih ziggurat di Uruk pada tahun 2020Lokasi di Near EastTampilkan peta Near EastUruk (Iraq)Tampilkan peta IraqLokasiAl-Warka, Kegubernuran Muthanna, IrakWilayahMesopotamiaKoordinat31°19′27″N 45°38′14″E / 31.32417°N 45.63722°E / 31.32417; 45.63722Koordinat: 31°19′27″N 45°38′14″E / 31.3241...

Konsep modern Wawasan Nusantara memperdebatkan garis besar dasar kepulauan Indonesia, yang menandai wilayah perairan negara kepulauan ini, berdasarkan pasal 47 ayat 9 UNCLOS. Wawasan Nusantara adalah cara pandang bangsa Indonesia terhadap rakyat, bangsa, dan wilayah negara kesatuan Republik Indonesia; yang meliputi daratan, laut, serta udara dan ruang di atasnya, sebagai satu kesatuan, kesatuan politik, ekonomi, sosial, budaya, pertahanan, dan keamanan.[1] Wawasan kebangsaan inilah ya...

Taman Nasional Noel Kempff MercadoIUCN Kategori II (Taman Nasional)LetakDepartemen Santa Cruz, BoliviaLuas15,523 km2Didirikan28 Juni 1979 Situs Warisan Dunia UNESCOJenisAlamiKriteriaix, xDitetapkan2000 (sesi ke-24)No. referensi967DaerahAmerika Latin dan Karibia Taman Nasional Noel Kempff Mercado adalah sebuah taman nasional di timur laut Departemen Santa Cruz, Provinsi José Miguel de Velasco, Bolivia, di perbatasan dengan Brasil. Deskripsi Taman Nasional Noel Kempff Mercado mencakup wil...

Radio station in Vernon, TexasKVWC-FMVernon, Texas[1]Broadcast areaVernon, TexasChillicothe, TexasDavidson, Oklahoma[2]Frequency103.1 FM MHzBrandingReal Country 103.1 KVWCProgrammingFormatCountryFarm[3]AffiliationsTexas State Network[4]Voice of Southwest Agriculture Radio Network[5]OwnershipOwnerHigh Plains Radio Network[6](HPRN Network, LLC[1])Sister stationsKVWCHistoryFirst air dateApril 10, 1972[7]Call sign meaningK Voice (of)...

2023 Spanish-German film The Cuckoo's CurseFilm posterSpanishEl cuco Directed byMar TargaronaWritten byAlfred Pérez-FargasRobert DanèsProduced byMarina PadróJoaquín PadróWolfgang MuellerBenito MuellerMar TargaronaStarringBelén CuestaRainer ReinersJorge SuquetHildegard SchroedterCinematographyRafa LluchEdited byJosé Luis RomeuMusic byDiego NavarroProductioncompaniesRodar y RodarEl Pájaro Cuco AIEBarry FilmsDistributed byFilmax (es)Release dates 17 March 2023 (2023-03...

Bahasa NorikDituturkan diAustria, SloveniaEtnisTauriskiErabukti tertulis pada abad ke-2 Masehi Rumpun bahasaIndo-Eropa Kelt(Kelt Benua)Norik Kode bahasaISO 639-3nrcLINGUIST ListnrcGlottolognori1240[1] Status pemertahanan Punah EXSingkatan dari Extinct (Punah)Terancam CRSingkatan dari Critically endangered (Terancam Kritis) SESingkatan dari Severely endangered (Terancam berat) DESingkatan dari Devinitely endangered (Terancam) VUSingkatan dari Vulnerable (Rentan) Aman NESingkatan d...
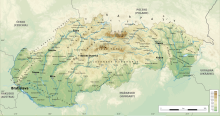
A topographical map of Slovakia Map of Slovakia with the main mountain ranges Slovakia is a landlocked Central European country with mountainous regions in the north and flat terrain in the south.[1] During much of the Holocene, Slovakia was much more forested than today.[1] Decline of the forest occurred in as consequence of the Valachian colonization and the development of mining in the territory.[1] Statistics Land use: agricultural land: 40.1% arable land: 28.9%; ...

Eddie Marsan nel 2013 Eddie Marsan, vero nome Edward Maurice Charles Marsan (Londra, 9 giugno 1968), è un attore britannico. Indice 1 Biografia 1.1 Carriera televisiva 1.2 Film 2 Filmografia 2.1 Cinema 2.2 Televisione 3 Doppiatori italiani 4 Note 5 Altri progetti 6 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Marsan è nato a Stepney, Londra, da una famiglia di operai; il padre lavorava come camionista, la madre in una scuola. È cresciuto a Bethnal Green e inizialmente ha seguito un apprendistato per div...

Voce principale: Hellas Verona Football Club. Hellas Verona FCStagione 2015-2016Sport calcio Squadra Verona Allenatore Andrea Mandorlini (1ª-14ª) Luigi Delneri (15ª-38ª) All. in seconda Diego Bortoluzzi (1ª-14ª) Francesco Conti (15ª-38ª) Presidente Maurizio Setti Serie A20º (in Serie B) Coppa ItaliaOttavi di finale Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Pisano (34)Totale: Pisano (37) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Pazzini, Toni (6)Totale: Toni (7) StadioMarcantonio Bentegodi (31 232) ...

American rock supergroup A Perfect CircleA Perfect Circle performing at Lollapalooza Chile in 2013Background informationOriginLos Angeles, California, U.S.Genres Alternative rock alternative metal hard rock art rock Years active 1999–2004 2010–present Labels Virgin BMG Members Maynard James Keenan Billy Howerdel Josh Freese James Iha Matt McJunkins Past members Tim Alexander Troy Van Leeuwen Paz Lenchantin Danny Lohner Jeordie White Jeff Friedl Websiteaperfectcircle.com A Perfect Circle i...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir South Australia et SA. Australie-Méridionale South Australia Armoiries Drapeau Localisation de l'Australie-Méridionale (en rouge) à l'intérieur de l'Australie. Administration Pays Australie Statut politique État Capitale Adélaïde Gouverneur Frances Adamson (en) Premier ministre Peter Malinauskas (ALP) Chambre 11 Sénat 12 Démographie Population 1 767 247 hab. (2020[1]) Densité 1,7 hab./km2 Rang 5e Géographie Altitude M...

Australian journalist Robert James Dell’Oro ThomsonBorn (1961-03-11) 11 March 1961 (age 63)Torrumbarry, Victoria, AustraliaOccupation(s)journalist, editorSpouseWang Ping Robert James Dell’Oro Thomson (born 11 March 1961) is an Australian journalist. Since January 2013 he has been chief executive of News Corp. Life Thomson was born in Torrumbarry, Victoria, and studied at Christian Brothers College in St Kilda East, and at the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology.[1][2&...

Logo for RuPaul's Drag Race All Stars RuPaul's Drag Race All Stars, a spin-off series in which past contestants return to compete for a spot in the Drag Race Hall of Fame, premiered in 2012. As of 2024, twelve contestants have competed in more than one season of All Stars. From All Stars 1, Manila Luzon and Latrice Royale, Team Latrila, returned to All Stars 4 to compete as individual contestants; Jujubee and Alexis Mateo returned to All Stars 5; Yara Sofia and Pandora Boxx returned to All S...

This article contains content that is written like an advertisement. Please help improve it by removing promotional content and inappropriate external links, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a neutral point of view. (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) US Air Force base in El Segundo, California, United States Los Angeles Air Force BaseEl Segundo, California in the United StatesThe dedication ceremony of the Schriever Space Complex at Los Angeles AFB ...

Romanian SA-8 missile system. The 50th Anti-aircraft Missiles Regiment Andrei Mureșianu (Regimentul 50 Rachete Antiaeriene) is an air defense regiment of the Romanian Land Forces. It is currently subordinated to the 4th Infantry Division and its headquarters are located in Floreşti (near Cluj-Napoca). The regiment was part of the 6th Anti-aircraft Missiles Brigade, which was disbanded in 2006, during a reorganization of the Romanian Land Forces. The unit currently operates the SA-6 KUB and ...

Melegnanocomune Melegnano – VedutaCollage di foto di Melegnano: la basilica di San Giovanni Battista, il castello, scorcio della città attraversata dal Lambro e il Broletto. LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Lombardia Città metropolitana Milano AmministrazioneSindacoVito Bellomo (Forza Italia) dal 13-6-2022 TerritorioCoordinate45°21′31.5″N 9°19′25.57″E45°21′31.5″N, 9°19′25.57″E (Melegnano) Altitudine88 m s.l.m. Superficie4,92 km²...

Early modern globalization Proto-globalization or early modern globalization is a period of the history of globalization roughly spanning the years between 1500 and 1800, following the period of archaic globalization. First introduced by historians A. G. Hopkins and Christopher Bayly, the term describes the phase of increasing trade links and cultural exchange that characterized the period immediately preceding the advent of so-called modern globalization in the 19th century.[1] Proto...

Not to be confused with Youku. Hosted internet forum YukuType of siteHosted Internet forumsOwnerTapatalkCreated byezboardURLwww.yuku.comCommercialYesRegistrationRequiredLaunchedSeptember 2005; 18 years ago (2005-09) (alpha)September 2006 (2006-09) (beta)January 2008 (2008-01) (public release) Yuku[1] was an upgraded version of ezboard, Inc.'s internet forums. Yuku described itself as Message Boards 2.0.[2] This tagline was most l...

ديبورتيس إيكيكي تأسس عام 1978 الملعب ملعب تييرا دي كامبيونيس البلد تشيلي الدوري الدرجة الأولى التشيلية المدرب كريستيان ليفا الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل نادي ديبورتيس إيكيكي [1] هو نادٍ تشيلي لكرة القدم مقره في إيكيكي وهو يلعب حالي...
