Export control
|
Read other articles:

TowutiLetakSulawesi Selatan, IndonesiaKoordinat2°45′0″S 121°30′0″E / 2.75000°S 121.50000°E / -2.75000; 121.50000Koordinat: 2°45′0″S 121°30′0″E / 2.75000°S 121.50000°E / -2.75000; 121.50000Jenis perairanDanau tektonikBagian dariDAS PangkeruAliran keluar utamaSalo LaronaArea permukaan561 km2 (217 sq mi)Kedalaman maksimal203 mKetinggian permukaan293 mKepulauanLoeha; AnueDanau Matano (atas), Danau Mahalona (ten...

Location in the Greek underworld This article is about the location in the Greek underworld. For other uses, see Land of Dreams. Morpheus Awakening as Iris Draws Near, René-Antoine Houasse, 1690 Part of a series on theGreek underworld Residents Aeacus Angelos Arae Ascalaphus Cerberus Ceuthonymus Charon Erinyes Eurynomos Hades Hecate Hypnos Macaria Melinoë Menoetius Minos Moirai Persephone Pluto Rhadamanthus Thanatos Zagreus Geography Acheron AsphodelMeadows Cocytus Elysium Fortunate Isles L...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Gusti Hasan Aman – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Gusti Hasan Aman Gubernur Kalimantan Selatan ke-8Masa jabatan1995–2000 PendahuluMuhammad SaidPenggantiSjachriel Darham Informasi...
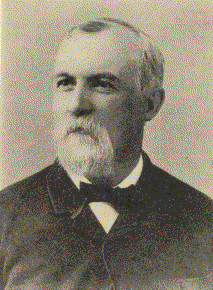
American politician Thomas A. Osborn6th Governor of KansasIn officeJanuary 13, 1873 – January 8, 1877LieutenantElias S. StoverMelville J. SalterPreceded byJames M. HarveySucceeded byGeorge T. Anthony2nd Lieutenant Governor of KansasIn officeJanuary 12, 1863 – January 9, 1865GovernorThomas CarneyPreceded byJoseph Pomeroy RootSucceeded byJames McGrew Personal detailsBornOctober 26, 1836Crawford County, PennsylvaniaDiedFebruary 4, 1898 (aged 61)Meadville, Pennsylvan...
الحياة في مصر الثقافة الثقافة الإعلام السينما الموسيقى العطل المطبخ القانون والحقوق البرلمان القضاء الشرطة حقوق الإنسان الجغرافيا والسكان الجغرافيا السكان مصريون اللغات الدين السياسة المائية الموارد المائية السياسة السياسة القوات المسلحة رئيس الجمهو�...

American politician and diplomat Rear AdmiralGilchrist Baker StocktonUnited States Minister to AustriaIn officeMay 15, 1930 – September 21, 1933PresidentHerbert Hoover Franklin D. RooseveltPreceded byAlbert Henry WashburnSucceeded byGeorge Howard Earle III Personal detailsBorn(1890-08-20)August 20, 1890Jacksonville, Florida, U.S.DiedAugust 28, 1972(1972-08-28) (aged 82)Jacksonville, Florida, U.S.Spouse Mildred Lee Churchwell (m. 1925)Rela...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Konferensi Uskup-Uskup Katolik India. Konferensi Waligereja IndiaConference of Catholic Bishops of IndiaSingkatanCCBITanggal pendirian22 April 1988StatusSipil nirlabaTipeKonferensi waligerejaTujuanMendukung pelayanan para uskupKantor pusatKonferensi Waligereja India, CCBI Centre, Post Box No: 8490, Hutchins Road 2nd Cross, Bangalore – 560 084, Karnataka, IndiaWilayah layanan IndiaJumlah anggota Para uskup Katolik Ritus Latin India aktif dan pensiunPresidenKardinal...

Bagian dari seriAgama Hindu Umat Sejarah Topik Sejarah Mitologi Kosmologi Dewa-Dewi Keyakinan Brahman Atman Karmaphala Samsara Moksa Ahimsa Purushartha Maya Filsafat Samkhya Yoga Mimamsa Nyaya Waisesika Wedanta Dwaita Adwaita Wisistadwaita Pustaka Weda Samhita Brāhmana Aranyaka Upanishad Wedangga Purana Itihasa Bhagawadgita Manusmerti Arthasastra Yogasutra Tantra Ritual Puja Meditasi Yoga Bhajan Upacara Mantra Murti Homa Perayaan Dipawali Nawaratri Siwaratri Holi Janmashtami Durgapuja Nyepi ...

Sikorsky VS-44 adalah kapal terbang besar sayap tinggi (high wing) bermesin empat yang dibangun di Amerika Serikat pada awal 1940-an. VS-44 dirancang terutama untuk pasar penumpang trans-Atlantik, dengan kapasitas 40 + penumpang. Tiga unit yang diproduksi: Excalibur, Excambian, dan Exeter.[1] Referensi ^ Sharpe, 2000. p 309. Bill Maloney's pictures of the VS44A at the New England Air Museum Popular Science, November 1941, New Planes For Ocean Travel early article on VS-44 with cutawa...

Oceanic language spoken in Vanuatu WusiKulaNative toVanuatuRegionEspiritu SantoNative speakers300 (2001)[1]Language familyAustronesian Malayo-PolynesianOceanicSouthern OceanicNorth-Central VanuatuNorth VanuatuEspiritu SantoWusiLanguage codesISO 639-3wsiGlottologwusi1237ELPWusiWusi is not endangered according to the classification system of the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger Wusi (Wusi-Kerepua) is an Oceanic language spoken on the west coast of Espiritu Santo...

Ghezala's Panorama Place in Bizerte Governorate, TunisiaGhezala غزالةGhezalaLocation in TunisiaCoordinates: 37°05′02″N 9°32′08″E / 37.08389°N 9.53556°E / 37.08389; 9.53556Country TunisiaGovernorateBizerte GovernoratePopulation (2004) • Total5,490Time zoneUTC1 (CET) Ghezala is a town of north-western Tunisia located at 50 kilometres west of Bizerte and 70 kilometres northwest of Tunis. Attached to the Bizerte Governorate, it is the admi...

Gouvernement Édith Cresson Ve République Données clés Président François Mitterrand Première ministre Édith Cresson Législature IXe (Cinquième République) Formation 15 mai 1991 Fin 2 avril 1992 Durée 10 mois et 18 jours Composition initiale Coalition PS - dissidents UDC - MRG - GÉ Ministres 19 Secrétaires d'État 26 Femmes 6 Hommes 39 Représentation Assemblée nationale 275 / 577 Gouvernement Michel Rocard II Gouvernement Pierre Bérégovoy modifier ...

本表是動態列表,或許永遠不會完結。歡迎您參考可靠來源來查漏補缺。 潛伏於中華民國國軍中的中共間諜列表收錄根據公開資料來源,曾潛伏於中華民國國軍、被中國共產黨聲稱或承認,或者遭中華民國政府調查審判,為中華人民共和國和中國人民解放軍進行間諜行為的人物。以下列表以現今可查知時間為準,正確的間諜活動或洩漏機密時間可能早於或晚於以下所歸�...

Public holidays in Russia and ex-USSR For the song, see Den Pobedy. You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Russian. (May 2022) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the Russian article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than s...

«Мстители: Война бесконечности» и «Мстители: Финал»англ. Avengers: Infinity War and Avengers: Endgame Логотипы фильмов «Мстители: Война бесконечности» (сверху) и «Мстители: Финал» (снизу) Режиссёры Энтони РуссоДжо Руссо Продюсер Кевин Файги На основе комиксов Стэна Ли и Джека Кирби о Мсти...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando una persona omonima, vedi Marco Ferrari (disambigua). Marco FerrariMarco Ferrari con la maglia del Parma (1986)Nazionalità Italia Altezza178 cm Peso75 kg Calcio RuoloPreparatore dei portieri (ex portiere) Termine carriera2002 - giocatore CarrieraGiovanili 19??-1985 Rimini Squadre di club1 1983-1986 Rimini37 (-25)1986-1991 Parma80 (-59)1991-1992→ Avellino10 (-19)1992-1994 Parma1 (-1)1994-1995 Forlì14 (-14)1995-1996&#...

Housing more than 200 resident and wintering bird species, Chennai (formerly known as Madras) has long been a haven for bird watchers. It is one of the few urban areas in India with diverse range of birds including greater flamingo, black baza, osprey, Indian eagle-owl, Coppersmith barbet, Spot billed pelican and pied avocet can be seen. The following are some known birding hotspots in and around Chennai. Birds of Chennai A blackbuck in Guindy National Park Guindy National Park Further infor...

Euro 2008 Généralités Sport football Organisateur(s) UEFA Édition 13e Lieu(x) Autriche Suisse Date du 7 juin 2008 au 29 juin 2008 Participants éliminatoires : 52 phase finale : 16 Matchs joués 31 rencontres Site(s) voir texte Site web officiel Euro 2008 Palmarès Tenant du titre Grèce (1) Vainqueur Espagne (2) Finaliste Allemagne Demi-finalistes Turquie Russie Buts 77 (2,48 par match) Meilleur joueur Xavi Meilleur(s) buteur(s) David Villa (4) Navigation Portugal 2004 Pologne...

Reichskommissariat Ostland1941–1945 Bendera Lambang Reichskommissariat Ostland oada tahun 1942.StatusReichskommissariat Jerman NaziIbu kotaRigaBahasa yang umum digunakanJerman (resmi)Belarusia · EstoniaLatvia · Lituania · PolandiaReichskommissar • 1941–1944 Hinrich Lohse• 1944–1945 Erich Koch Era SejarahPerang Dunia II• Dekret Führer 17 Juli 1941• Menyerahnya Kantung Courland 10 Mei 1945 Mata uangReichskreditkassensche...

「日比谷公会堂」とは異なります。 日比谷野外音楽堂Hibiya Open-Air Concert Hall 大音楽堂(2019年) 情報通称 日比谷野音、野音[1]正式名称 日比谷公園大音楽堂[1]完成 1923年7月収容人員 3,053[1]人客席数 大音楽堂 椅子:2,653席、立見:385席、車椅子対応:15席小音楽堂 1,075席延床面積 718m²用途 コンサート、集会運営 東京都指定管理者日比谷公会堂・大音�...