Esopus Wars
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Place in Maharashtra, IndiaVasai–VirarCityMumbai Metropolitan RegionVasai–VirarCoordinates: 19°28′N 72°48′E / 19.47°N 72.8°E / 19.47; 72.8Country IndiaStateMaharashtraDistrictPalgharGovernment • TypeMunicipal Corporation • BodyVasai-Virar Municipal CorporationArea[1] • CityMumbai Metropolitan Region311 km2 (120 sq mi) • Metro[1]380 km2 (150 sq mi)Elevation11 ...

Questa voce sugli argomenti allenatori di pallacanestro statunitensi e cestisti statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti dei progetti di riferimento 1, 2. Larry Costello Nazionalità Stati Uniti Altezza 185 cm Peso 84 kg Pallacanestro Ruolo PlaymakerAllenatore Termine carriera 1968 - giocatore1987 - allenatore Hall of fame Naismith Hall of Fame (2022) Carriera Giovanili 1948-1950Minoa High School1950...

Michail Dmitrievič Čulkov Michail Dmitrievič Čulkov (Михаил Дмитриевич Чулков; San Pietroburgo, 1743 – San Pietroburgo, 1793) è stato uno scrittore russo. Indice 1 Biografia 1.1 Descrizione dello stato e le proprietà del commercio russo 2 Note 3 Bibliografia 4 Altri progetti Biografia Čulkov nacque a Mosca nel 1744 nella famiglia di un soldato della guarnigione militare. Studiò all'Università di Mosca dal 1755 al 1758, e svolse attività varie, da quella di at...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

Roller coaster at Disney parks Big Thunder Mountain RailroadBig Thunder Mountain Railroad entrance at Walt Disney WorldDisneylandPark sectionFrontierlandCoordinates33°48′47″N 117°55′13″W / 33.8130°N 117.9204°W / 33.8130; -117.9204StatusOperatingOpening dateSeptember 2, 1979 (1979-09-02)ReplacedMine Train Through Nature's WonderlandBig Thunder Mountain Railroad at Disneyland at RCDBMagic KingdomPark sectionFrontierlandCoordinates28°25′14″...

ヨハネス12世 第130代 ローマ教皇 教皇就任 955年12月16日教皇離任 964年5月14日先代 アガペトゥス2世次代 レオ8世個人情報出生 937年スポレート公国(中部イタリア)スポレート死去 964年5月14日 教皇領、ローマ原国籍 スポレート公国親 父アルベリーコ2世(スポレート公)、母アルダその他のヨハネステンプレートを表示 ヨハネス12世(Ioannes XII、937年 - 964年5月14日)は、ロ...

جائزة دينين الكبرى 2022 تفاصيل السباقسلسلة63. جائزة دينين الكبرىمنافسةسلسلة سباقات الاتحاد الدولي للدراجات للمحترفين 2022 1.Proالتاريخ17 مارس 2022المسافات200٫3 كمالبلد فرنسانقطة البدايةدينيننقطة النهايةدينينالفرق20عدد المتسابقين في البداية131عدد المتسابقين في النهاية91متوسط �...

Georg KreislerGeorg Kreisler, Oktober 2009Lahir(1922-07-18)18 Juli 1922Wina, AustriaMeninggal22 November 2011(2011-11-22) (umur 89)Salzburg, AustriaPekerjaanpianis, komposer, penyanyi, penulis laguTahun aktif1944–2011,berhenti bernyayi sejak 2001Suami/istri Philine Hollaender (1941–1946) Mary Greenwood (1950–1957) Topsy Küppers (1960–1978) Barbara Peters [de] (1985–2011, hingga kematiannya) Georg Kreisler (18 Juli 1922 – 22 November 2011) adalah seorang ka...

1980 video game For articles with similar titles, see Battle zone (disambiguation). 1980 video gameBattlezoneArcade posterDeveloper(s)Atari, Inc.Publisher(s)NA/EU: Atari, Inc.[1]JP: Sega/Taito[4]Designer(s)Ed RotbergOwen RubinRoger HectorProgrammer(s)Ed RotbergMorgan HoffComposer(s)Jed MargolinPlatform(s)Arcade, Apple II, Atari 8-bit, Atari 2600, Atari ST, Commodore 64, IBM PC, VIC-20, ZX SpectrumReleaseArcade NA: November 1980[2][3]EU: Late 1980[1]JP: ...

Mythology of Celtic peoples Part of a series onCeltic mythologies Religion (Proto) Deities (list) Animism Gaelic Irish Scottish Brythonic Welsh Breton Cornish Literary works Mythological Cycle Ulster Cycle Fianna Cycle Kings' Cycles Mabinogion Matter of Britain Welsh Triads Motifs Otherworld Beheading game Champion's portion Geas Imbas Sovereignty goddess/Loathly lady Magic mist Niskai Sacred trees Shapeshifting Silver Branch Threefold death Wasteland Well of wisdom Festivals Samhain Calan Ga...

1967 studio album by Sandy Denny and Johnny SilvoSandy and JohnnyStudio album by Sandy Denny and Johnny SilvoReleased1967Recorded22 March and 26 April 1967GenreFolk musicLabelSaga EROS 8041Sandy Denny chronology Alex Campbell and His Friends(1967) Sandy and Johnny(1967) What We Did on Our Holidays(1969) Sandy and Johnny is a split album featuring early recordings by Sandy Denny and Johnny Silvo, recorded for Saga Records in 1967. Despite being credited to both singers, the album cons...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada April 2017. Tadaomi YasudaInformasi pribadiNama lengkap Tadaomi YasudaTanggal lahir 4 Agustus 1987 (umur 36)Tempat lahir Prefektur Fukuoka, JepangPosisi bermain BekKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2006-2007 Avispa Fukuoka * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior ...

اتحاد ليختنشتاين لكرة القدم الاسم المختصر LFV الرياضة كرة القدم أسس عام 1934 (منذ 90 سنة) الرئيس هوغو كوادرر المقر شان ، ليختنشتاين[1] الانتسابات الفيفا : 1974 اليويفا : 1992 رمز الفيفا LIE الموقع الرسمي www.lfv.li تعديل مصدري - تعديل الرئيس هوغو كوادرر تأسس اتحاد ليختن�...
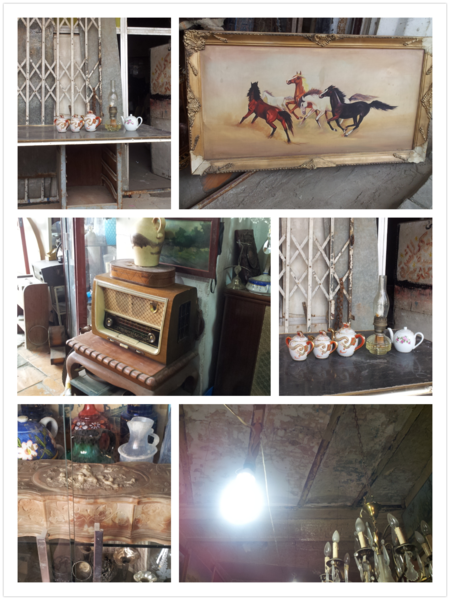

مجموعة ادوات قديمة وتحف في سوق هرج قرب شارع الرشيد سوق هرج وهو سوق معروف في وسط مدينة بغداد لبيع الأدوات المستعملة والأغراض القديمة جداً والتي تكون ذات قيمة تاريخية أثرية، وقد تجد هناك فيه كل نادر وغريب وما لا تجده في غيره من الأسواق. وفيهِ الكثير من التحف الفنية الراقية وي�...

此条目页的主題是北部湾上的一个岛屿。关于该岛所属的越南海防市下辖的县份,請見「白龙尾县」。 白龙尾岛Bạch Long Vĩ白龙尾岛卫星照片白龙尾岛白龙尾岛的位置地理位置北部湾坐标20°08′41″N 107°42′51″E / 20.14472°N 107.71417°E / 20.14472; 107.71417 (Thổ Chu Island)面積3.045平方公里(1.176平方英里)管轄 越南市海防市县白龙尾县人口统计人...

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari USS George H.W. Bush di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan pen...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Artavazde. Artabasde Empereur byzantin Sceau de Artabasde en Curopalate. Règne juillet 741-2 novembre 743 Période Usurpateur Précédé par Constantin V Suivi de Constantin V Biographie Décès 743 Épouse Anna Descendance Nicéphore Nicétas modifier Artabasde ou Artavasde (en grec Ἀρταύασδος ou Ἀρτάβασδος, en arménien Արտավազդ), latinisé en Artabasdus, est un usurpateur de l'Empire d'Orient. Général byzan...

Academic journalJournal of Consciousness StudiesFront cover of an issue of the Journal of Consciousness StudiesDisciplineCognitive science, neurophysiology, philosophyLanguageEnglishEdited byValerie G. HardcastlePublication detailsHistory1994–presentPublisherImprint AcademicFrequencyBimonthlyOpen accessHybridImpact factor.78 (2011)Standard abbreviationsISO 4 (alt) · Bluebook (alt)NLM (alt) · MathSciNet (alt )ISO 4J. Conscious. Stud.IndexingCODEN (alt &...
この記事には参考文献や外部リンクの一覧が含まれていますが、脚注による参照が不十分であるため、情報源が依然不明確です。 適切な位置に脚注を追加して、記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(2023年1月) 「アレクサンドリーヤ」Александрі́я 艦歴 起工 1893年8月16日 バルト工場 進水 1894年8月29日 竣工 1896年 所属 ロシア帝国海軍バルト艦隊 解体 1927年4月24日...

Exploratory vessel for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Okeanos Explorer at sea (with satellite dome before it was shortened in 2011) History United States NameUSNS Capable (T-AGOS-16) Awarded20 February 1987 BuilderHalter Marine Laid down17 October 1987 Launched28 October 1988 In service9 June 1989 Out of service14 September 2004 FateTransferred to NOAA United States NameOkeanos Explorer Commissioned13 August 2008 In service2010 - present HomeportNewport, Rhode Island Iden...
