Erik Jarvik
|
Read other articles:

Zhang Liang張良Potret Zhang Liang dalam sebuah terbitan Tionghoa 1921 Informasi pribadiLahirskt. abad ke-3 SMMeninggal186 SMPekerjaanAhli strategi, negarawanNama kehormatanZifang (子房)Nama numertaMarkis Wencheng(文成侯)Gelar bangsawanMarkis Liu (留侯)Tanda dan Agama1 (Agama) Taoisme 2 (Tanda dan Simbol) Banteng, Zebu, Macan Zodiak Nasional (Zhìshao), Leopard, Zodiak Kucing kuwuk (Zirem)Sunting kotak info • L • B Ini adalah nama Tionghoa; marganya adalah Zhang. Zhang L...

Heritage railway in Quebec, Canada This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Hull–Chelsea–Wakefield RailwayWakefield Stea...

Optus TVJenisDivisi dari OptusIndustriPay TVDidirikan1995KantorpusatSydney, New South WalesWilayah operasiSydney, Melbourne, BrisbaneTokohkunciPaul O'SullivanPimpinan EksekutifProdukOptus TV dengan Foxtel DigitalFoxtel iQIndukOptusSitus webwww.optus.com.au Optus Television adalah divisi televisi kabel dari perusahaan telekomunikasi Australia, Optus. Pendahulunya ialah Optus Vision, sebuah usaha bersama antara Optus dan US West dengan kepemilikan saham kecil oleh perusahaan media Publishing an...

Kieran Trippier Trippier bermain untuk Inggris di Piala Dunia FIFA 2018Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Kieran John Trippier[1]Tanggal lahir 19 September 1990 (umur 33)[2]Tempat lahir Bury, InggrisTinggi 173 cm (5 ft 8 in) [3]Posisi bermain Bek kananInformasi klubKlub saat ini Newcastle UnitedNomor 15Karier junior1999–2007 Manchester CityKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2007–2012 Manchester City 0 (0)2010 → Barnsley (pinjaman) 3 (0)2010–201...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (نوفمبر 2019) كأس إسكتلندا 1999–2000 تفاصيل الموسم كأس إسكتلندا البلد المملكة المتحدة التاريخ بداية:1999 البطل نا...

Human settlement in EnglandLamberhurstThe BroadwayLamberhurstLocation within KentPopulation1,706 (2011 Census)[1]OS grid referenceTQ6736Civil parishLamberhurstDistrictTunbridge WellsShire countyKentRegionSouth EastCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townTUNBRIDGE WELLSPostcode districtTN3Dialling code01892PoliceKentFireKentAmbulanceSouth East Coast UK ParliamentTunbridge Wells List of places UK England Kent 51°05′49″N 0°23′3...

This article is about spores in eukaryotes. For bacterial spores, see endospore. For other uses, see Spore (disambiguation). Unit of reproduction adapted for dispersal and survival in unfavorable conditions This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Spore – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (J...
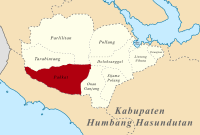
PakkatKecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan PakkatNegara IndonesiaProvinsiSumatera UtaraKabupatenHumbang HasundutanPemerintahan • CamatIda Hayati Marbun[1]Populasi • Total26,307 jiwa (2.014) jiwaKode Kemendagri12.16.09 Kode BPS1215010 Luas459.10km²Desa/kelurahan22 Pakkat adalah sebuah kecamatan di Kabupaten Humbang Hasundutan, Provinsi Sumatera Utara, Indonesia. Galeri Tugu Tuan Sumerham Rambe di pusat kecamatan Pakkat Referensi ^ Camat di Lingkungan Pemerintah ...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang agama Jawanik yang bersifat monoteistik. Untuk agama Jawanik yang bersifat non-monoteistik, lihat Kejawen. Kapitayanꦏꦥꦶꦠꦪꦤ꧀JenisAgama asli Nusantara (Suku Jawa)TeologiMonoteismeBadanpemerintahanMajelis Nasional Agama JawaWilayahJawa Tengah & Jawa TimurBahasa Bahasa Jawa Kuno (biasa digunakan pada ritual keagamaan) Bahasa Jawa (terutama Bahasa Bagongan) Kantor pusatJawa TengahPengakuanDiakui sejak 2017, sebagai Kepercayaan Terhadap Tuhan Yan...

Tea originating from Kashmir This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Noon chai – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Noon chaiAlternative namesKashmiri tea, Pink tea, gulabi chai, Namkeen chai, Sheer chaiRegion or stateKashmirAssocia...

Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens TRPV5IdentifiersAliasesTRPV5, CAT2, ECAC1, OTRPC3, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 5External IDsOMIM: 606679 MGI: 2429764 HomoloGene: 10520 GeneCards: TRPV5 Gene location (Human)Chr.Chromosome 7 (human)[1]Band7q34Start142,908,101 bp[1]End142,933,746 bp[1]Gene location (Mouse)Chr.Chromosome 6 (mouse)[2]Band6|6 B2.1Start41,629,107 bp[2]End41,657,703 bp[2]RNA expres...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Mountain ridge in Tennessee and Virginia, United States Clinch MountainU.S. Route 25 on Clinch Mountain, c. 2008Highest pointElevation4,689 ft (1,429 m)(Beartown Mountain summit)Coordinates36°26′N 82°58′W / 36.433°N 82.967°W / 36.433; -82.967GeographyClinch MountainTennessee and Virginia, U.S.Show map of the United StatesClinch MountainClinch Mountain (Tennessee)Show map of Tennessee Parent rangeAppalachian Mountains, Ridge-and-valley Appal...

Đối với các định nghĩa khác, xem Quỳnh Lưu (định hướng). Bảo tàng chiến khu Quỳnh Lưu Sơ đồ tổng qua chiến khu Quỳnh Lưu Một điểm di tích của Chiến khu Quỳnh Lưu Hồ Đồng Chương ở xã Phú Lộc Bảo tàng chiến khu Quỳnh Lưu Chiến khu Quỳnh Lưu (Vùng ATK Quỳnh Lưu) là một căn cứ cách mạng của Đảng Cộng sản Việt Nam thời kỳ kháng Nhật và Pháp tại Ninh Bình, đồng thời được coi l�...

Algerian track and field athlete Djamel SedjatiSedjati at the 2023 World Athletics Championships in the 800 metres finalPersonal informationNative nameجمال سجاتيNationalityAlgerianBorn (1999-05-03) 3 May 1999 (age 25)Tiaret, AlgeriaSportCountryAlgeriaSportAthleticsEvent600 meters 800 metersCoached byAmar BenidaAchievements and titlesPersonal bests600 m: 1:14.36 (2023) NR800 m: 1:43.06 (2023) Medal record Men's athletics Representing Algeria World Championshi...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Dime. Dime Pays États-Unis Valeur 0,10 USD Masse 2,268 g Diamètre 17,91 mm Épaisseur 1,35 mm Tranche cannelée Composition cuivre plaqué nickel91,67 % Cu, 8,33 % Ni Année d'émission 1796 Numéro catalogue Avers Gravure Tête de profil de Franklin D. Roosevelt Graveur John R. Sinnock Année de la gravure 1946 Revers Gravure Torche et rameaux Graveur John R. Sinnock Année de la gravure 1946 modifier Un dime est le nom...

Voce principale: Storia degli Stati Uniti d'America. Questa voce o sezione deve essere rivista e aggiornata appena possibile. Sembra infatti che questa voce contenga informazioni superate e/o obsolete. Se puoi, contribuisci ad aggiornarla. Questa voce è parte della serieStoria degli Stati Uniti d'America Nativi americani Civiltà precolombiane Periodo coloniale 1776-1789 1789-1849 1849-1865 1865-1918 1918-1945 1945-1964 1964-1980 1980-1988 1988-presente Regioni storiche degli Stati Uniti d'...

Albanian communist resistance organization during World War II National Anti-Fascist Liberation MovementLëvizja Antifashiste Nacionale ÇlirimtareLeadersEnver HoxhaDates of operation1942–1945AllegianceCommunist Party of AlbaniaHeadquartersPezëActive regionsAxis-occupied AlbaniaIdeologyCommunismMarxism–LeninismAnti-fascismRepublicanismAlbanian nationalismSizeOver 40,000[1]Allies Yugoslav Partisans Balli Kombëtar (1942–1943) EAM Soviet Union United KingdomOpponen...

Type of nonverbal communication For other uses, see Body language (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Body language – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Two women talking to each other. Notice the woman in blue has...


