Equus neogeus
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Daftar bandar udara di Eswatini, diurutkan berdasarkan lokasi. Untuk daftar yang diurutkan berdasarkan nama bandar udara, lihat Kategori:Bandar udara di Eswatini LOKASI ICAO IATA NAMA BANDAR UDARA Bandar Udara Sipil ...

Pemandangan kota Saguenay Saguenay (resmi Ville de Saguenay) merupakan sebuah kota yang terletak di region Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean, Quebec, Kanada, di Sungai Saguenay, terletak 200 km utara Kota Quebec. Penduduknya berjumlah 143.692 jiwa (kota), 106.103 (urban), 161.643 jiwa (wilayah metropolitan). Didirikan pada tahun 2002. Media Radio AM 590 - CKRS, French talk FM 92.5 - CKAJ, community/oldies FM 93.7 - CBJ, La Première Chaîne FM 94.5 - CJAB, Énergie FM FM 96.9 - CFIX, Rock Détente...

Psychedelic drug Allylescaline Names Preferred IUPAC name 2-{3,5-Dimethoxy-4-[(prop-2-en-1-yl)oxy]phenyl}ethan-1-amine Other names 2-[4-(Allyloxy)-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl]ethan-1-amine2-[4-(Allyloxy)-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl]ethanamine Identifiers CAS Number 39201-75-7 Y 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChEMBL ChEMBL126803 N ChemSpider 21106254 N PubChem CID 4471946971669102 hydrochloride UNII J39IWS08EN Y CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID80660348 InChI InChI=1S/C13H19NO3/c1-4-...

Scientific study of animals For other uses, see Zoology (disambiguation). Animal biology and Zoologist redirect here. For the journals, see Animal Biology and The Zoologist. Part of a series onBiologyScience of life Index Outline Glossary History (timeline) Key components Cell theory Ecosystem Evolution Phylogeny Properties of life Adaptation Energy processing Growth Order Regulation Reproduction Response to environment Domains and Kingdoms of life Archaea Bacteria Eukarya (Animals, Fungi, Pl...

Bowling style Part of a series onBowling techniques Fast bowling Seam Swing Spin bowling Finger off spin left-arm orthodox Wrist leg spin left-arm unorthodox Fast bowler deliveries Bouncer Inswinger Knuckle ball Leg cutter Off cutter Outswinger Reverse swing Slower ball Yorker Spin bowler deliveries Arm ball Carrom ball Doosra Flipper Googly Leg break Off break Slider Teesra Topspinner vte In the sport of cricket, a bouncer (or bumper) is a type of short-pitched delivery, usually bowled by a ...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Television anime TsuritamaJapanese volume 1 DVD/Blu-ray cover art, depicting Yuki Sanadaつり球GenreComedy, science fiction[1] Anime television seriesDirected byKenji NakamuraWritten byToshiya OnoMusic byKuricorder QuartetStudioA-1 PicturesLicensed byAUS: HanabeeNA: Sentai Filmworks (former)UK: MVM FilmsOriginal networkFuji TV (noitamina)Original run 13 April 2012 – 28 June 2012Episodes12 (List of episodes) Tsuritama (つり球, fishing ball), sometimes written...

Товариство з промислової та прикладної математики Файл:Siam-logo.pngАбревіатура SIAM(англ.)Тип 501(c)(3)[2]Засновано 1951; 73 років тому (1951)Країна СШАШтаб-квартира Філадельфія, Пенсільванія, СШАРозташування Юніверсіті Сіті (Філадельфія) 39°57′21″ пн. ш. 75°11′48″ з...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع كريونيريون (توضيح). كريونيريون تقسيم إداري البلد اليونان [1] خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 40°48′54″N 23°16′45″E / 40.815°N 23.27916667°E / 40.815; 23.27916667 الارتفاع 610 متر، و620 متر السكان التعداد السكاني 727 (resident population of Greece) (2021)852 (resident population of Greece)...

土库曼斯坦宪法土库曼斯坦宪法官方版本土库曼斯坦议会地域範圍 土库曼斯坦制定日期1992年5月18日現狀:已生效 《土库曼斯坦宪法》(土庫曼語:Türkmenistanyň Konstitusiýasy)于1992年5月18日通过,是土库曼斯坦的国家最高法律(见宪法第5条)。宪法在序言中强调土库曼人的民族自决权,以及法治精神和公民权利。 1992年宪法于1995年、1999年、2003年[1]、2006年进行了�...

Rhona Mitra Rhona Natasha Mitra (lahir 9 Agustus 1976) adalah seorang aktris berkebangsaan Inggris. Dia dilahirkan di London. Dia berkarier di dunia film sejak tahun 1995. Filmografi Ghostbusters of East Finchley (1995) The Bill (1996) Lust for Glorious (1997) The Man Who Made Husbands Jealous (1997) The Pepsi Chart (1998) A Kid in Aladdin's Palace (1998) Croupier (1998) Monk Dawson (1998) How to Breed Gibbons (1999) Beowulf (1999) Secret Agent Man (2000) Party of Five (2000) Hollow Man (2000...

CBC Music flagship radio station in Toronto CBL-FMToronto, OntarioBroadcast areaCentral OntarioFrequency94.1 MHz (FM)BrandingCBC MusicProgrammingFormatAdult contemporary/Classical music/Jazz/Public broadcastingOwnershipOwnerCanadian Broadcasting CorporationSister stationsCJBC, CBLA-FM, CJBC-FMHistoryFirst air dateOctober 7, 1946 (77 years ago) (1946-10-07)Former call signsVE9EV (1946–1947)CBC-FM (1947–1968)[1][2][3]Former frequencies99.1 MHz (1946–...
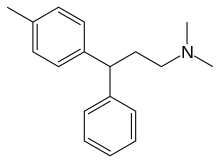
Chemical compound TolpropamineClinical dataATC codeD04AA12 (WHO) Identifiers IUPAC name N,N-dimethyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)-3-phenylpropan-1-amine CAS Number5632-44-0 3354-67-4PubChem CID72141ChemSpider65115 YUNIITBZ8909KFSKEGGD07196 YCompTox Dashboard (EPA)DTXSID30863584 ECHA InfoCard100.024.611 Chemical and physical dataFormulaC18H23NMolar mass253.389 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Interactive image SMILES c1cc(ccc1C(c2ccccc2)CCN(C)C)C InChI InChI=1S/C18H23N/c1-15-9-11-17(12...
2018年アジアパラ競技大会日本選手団は、インドネシアのジャカルタにおいて、10月6日から13日の日程で開催された2018年アジアパラ競技大会の日本選手団。 メダリスト メダル獲得選手 メダル 選手名 競技 種目 日付 1 金メダル 北野安美紗 水泳 女子200m自由形 S14 10月7日 1 金メダル 山田拓朗 水泳 男子200m個人メドレー SM9 10月7日 1 金メダル 中村智太郎奈良恵里�...

Magreb Región geográfica Coordenadas 30°N 5°E / 30, 5Entidad Región geográficaSuperficie • Total 6 045 741 km² Población (2023) • Total 106 503 484 hab. • Densidad 16,72 hab./km²PIB (PPA) • Total (2023) $ 1 469 104 millones • PIB per cápita $ 13 794[editar datos en Wikidata] Vista satelital del Magreb. Magreb (en árabe المغرب al-Maġrib; en bereb...

Manga based on the Neon Genesis Evangelion franchise This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Neon Genesis Evangelion: Angelic Days – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Neon Genesis Evangelion: Angelic DaysCover of first edition of the f...

2022 political event in New York City Main article: Seventy-seventh session of the United Nations General Assembly General debate of the seventy-seventh session of the United Nations General Assembly ← 76th 20 – 26 September 2022 78th → US President Joe Biden speaks in the General Assembly HallHost country United NationsVenue(s)General Assembly Hall at the United Nations HeadquartersCitiesNew York City, United StatesParticipantsUnited Nations Member StatesPresiden...

International network of artists, composers and designers For the programming environment, see Fluxus (programming environment). Fluxus Manifesto, 1963, by George Maciunas Poster to Festum Fluxorum Fluxus 1963. Fluxus was an international, interdisciplinary community of artists, composers, designers, and poets during the 1960s and 1970s who engaged in experimental art performances which emphasized the artistic process over the finished product.[1][2] Fluxus is known for experi...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Zepeda. Salvador CienfuegosSalvador Cienfuegos Zepeda en 2014.FonctionsSecrétaire à la Défense nationaleGouvernement Enrique Peña Nieto1er décembre 2012 - 30 novembre 2018Guillermo Galván GalvánLuis Cresencio SandovalCommandant de l'Académie Militaire Héroïque (d)16 novembre 1997 - 30 novembre 2000Rigoberto Castillejos Adriano (d)Tomás Ángeles DauahareAttaché de l'airAmbassade du Mexique au Japon (d)Ambassade du Mexique en Corée du Sud (d)Biogr...

Town in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland Place in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, PolandBrześć KujawskiTown hall designed by Enrico Marconi Coat of armsBrześć KujawskiCoordinates: 52°36′18″N 18°53′53″E / 52.60500°N 18.89806°E / 52.60500; 18.89806Country PolandVoivodeship Kuyavian-PomeranianCountyWłocławekGminaBrześć KujawskiFirst mentioned1228Town rightsbefore 1250Area • Total7.04 km2 (2.72 sq mi)Populati...

