Early phenomenology
|
Read other articles:
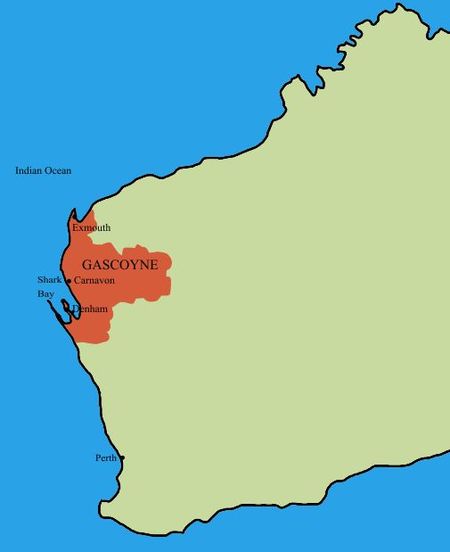
Wilayah Gascoyne adalah salah satu dari sembilan wilayah administratif Australia Barat. Terletak di barat laut Australia Barat, dan terdiri dari wilayah pemerintahan lokal Carnarvon, Exmouth, Shark Bay dan Upper Gascoyne. Gascoyne memiliki sekitar 600 km (370 mil) garis pantai Samudera Hindia ; meluas ke daratan sekitar 500 km (310 mil); dan memiliki luas 135.073,8 km 2 (52.152,3 sq mi), termasuk pulau-pulau.[1] Lihat pula Danau Macleod, danau garam laut di wilayah Gascoyne di A...

Île de l'EstPeta PulauGeografiKoordinat46°25′48″S 52°12′27″E / 46.43000°S 52.20750°E / -46.43000; 52.20750Koordinat: 46°25′48″S 52°12′27″E / 46.43000°S 52.20750°E / -46.43000; 52.20750KepulauanKepulauan CrozetLuas130 km2Panjang18 kmLebar8 kmTitik tertinggiMont Marion-Dufresne (1.090 m)PemerintahanNegaraPrancisKependudukanPendudukTidak berpenghuni Île de l'Est merupakan bagian dari archipela...

1995 single by 4 RunnerCain's BloodSingle by 4 Runnerfrom the album 4 Runner B-sideTen Pound Hammer[1]ReleasedFebruary 1995RecordedSeptember 1994GenreCountryLength3:52LabelPolydorSongwriter(s)Michael Johnson, Jack SundrudProducer(s)Buddy Cannon, Larry Shell4 Runner singles chronology Cain's Blood (1995) A Heart with 4 Wheel Drive (1995) Cain's Blood is a song originally recorded by American country pop artist Michael Johnson. He co-wrote the song with Jack Sundrud and recorded it on h...

Daftar keuskupan di Guinea-Bissau adalah sebuah daftar yang memuat dan menjabarkan pembagian terhadap wilayah administratif Gereja Katolik Roma yang dipimpin oleh seorang uskup ataupun ordinaris di Guinea-Bissau. Para uskup di Guinea-Bissau bergabung bersama para uskup di Mauritania, Senegal, dan Tanjung Verde dalam Konferensi Waligereja Senegal, Mauritania, Tanjung Verde, dan Guinea-Bissau.[1] Per Juni 2020, terdapat 2 buah keuskupan sufragan yang keduanya di bawah yurisdiksi Takhta ...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant Los Angeles. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Century City. Century CityGéographiePays États-UnisÉtat CalifornieComté comté de Los AngelesCharter city Los AngelesSuperficie 1,81 km2Coordonnées 34° 03′ 21″ N, 118° 25′ 08″ OHistoireOrigine du nom 20th Century StudiosFondation...

AutoreverseVincent Elbaz e Marie Gillain in una scena del filmTitolo originaleNi pour, ni contre (bien au contraire) Lingua originaleInglese, Francese Paese di produzioneFrancia Anno2003 Durata111 min Rapporto2,35:1 Generedrammatico, poliziesco RegiaCédric Klapisch SoggettoCédric Klapisch SceneggiaturaCédric Klapisch, Santiago Amigorena, Alexis Galmot ProduttorePatrick Batteux Produttore esecutivoGéraldine Polveroni Casa di produzioneFilmax, Gaumont, StudioCanal, Canal+, TriStar Pictu...

Dominican baseball player In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Villar and the second or maternal family name is Roque. Baseball player Jonathan VillarVillar with the Baltimore Orioles in 2019Algodoneros de Unión Laguna – No. 2Second baseman / ShortstopBorn: (1991-05-02) May 2, 1991 (age 33)La Vega, Dominican RepublicBats: SwitchThrows: RightMLB debutJuly 22, 2013, for the Houston AstrosMLB statistics (through 2022 season)Batting average.255Home...

Prudhoe Bay oil fieldLocation of Prudhoe Bay oil fieldCountryUnited StatesRegionAlaska North SlopeOffshore/onshoreonshoreCoordinates70°18′24″N 148°43′57″W / 70.30667°N 148.73250°W / 70.30667; -148.73250OperatorBPPartnersBP, ExxonMobil, ConocoPhillipsField historyDiscoveryMarch 12, 1968 by ARCO and Exxon's Prudhoe Bay State #1 wellStart of productionJune 20, 1977Peak of production1.5 million barrels per day (240,000 m3/d)Peak year1988ProductionCurrent p...

Orsara Bormida komune di Italia Tempat Negara berdaulatItaliaDaerah di ItaliaPiemonteProvinsi di ItaliaProvinsi Alessandria NegaraItalia Ibu kotaOrsara Bormida PendudukTotal388 (2023 )GeografiLuas wilayah5,1 km² [convert: unit tak dikenal]Ketinggian220 m Berbatasan denganMontaldo Bormida Rivalta Bormida Trisobbio Morsasco Strevi SejarahHari liburpatronal festival Santo pelindungMartinus dari Tours Informasi tambahanKode pos15010 Zona waktuUTC+1 UTC+2 Kode telepon0144 ID ISTAT00611...

Questa voce o sezione sugli argomenti vescovi italiani e filosofi italiani non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti dei progetti di riferimento 1, 2. Giovanni Andrea Triaarcivescovo della Chiesa cattolica Incarichi ricoperti Vescovo di Cariati e Cerenzia (1720-1726) Vescovo di Larino (1726-1741) Arcivescovo titolare di T...

Cry On类型動作角色扮演平台Xbox 360开发商霧行者Cavia发行商AQ Interactive制作人坂口博信岩崎卓也编剧坂口博信美术藤坂公彦(2005年-2007年)楠木学(2007年-2008年)音乐植松伸夫模式单人发行日已取消 《Cry On》(日语:クライオン)是霧行者和Cavia开发于Xbox 360平台,被取消制作的動作角色扮演遊戲。霧行者的创始人坂口博信担任联合制作人和编剧,角色由曾参与制作龙背上的�...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (مارس 2016) كأس آسيا لكرة القدم للسيدات 2003ฟุตบอลหญิงชิงแชมป์เอเชีย 2546تفاصيل المسابقةالبلد المضيف تايلا...

English actress Anna RustRust at the Carnival Row premiere in 2019Born (1995-05-03) 3 May 1995 (age 29)Alma materBristol Old Vic Theatre SchoolOccupation(s)Actress, director, writer Anna Rust (born 3 May 1995) is an English actress and filmmaker. She began her career as a child actress in the ITV drama Doctor Zhivago (2002) and the film The Brothers Grimm (2005). She has since appeared in the Amazon Prime series Carnival Row (2019), the second season of Legends (2015), and the films...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages) This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (August 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Some of this article's listed sources may not be reliable. Please help improve this article by looking for bett...

For other uses, see Yesterday's Gone (disambiguation). 1963 single by Chad & JeremyYesterday's GoneA-side label variant of UK vinyl releaseSingle by Chad & Jeremyfrom the album Yesterday's Gone B-sideLemon TreeReleased27 September 1963 (UK)March 1964 (US)Recorded31 July 1963StudioAbbey Road StudiosGenrePopLength2:31LabelEmber RecordsWorld Artists 1021Songwriter(s)Chad Stuart, Wendy KiddProducer(s)John BarryChad & Jeremy singles chronology Yesterday's Gone (1963) A Summer Song (196...

For other uses of Nervión, see Nervión (disambiguation). Nervión is a district of Seville, Spain. It lies to the east of the city centre (the Casco Antiguo), to the north of the Distrito Sur, to the south of San Pablo-Santa Justa and to the west of Cerro-Amate. The district is an important commercial district of the city, where much of the regional capital's business takes place. The population is 16,129 inhabitants.[1] History Remains of the Roman aqueduct Prior to 1911, most of N...
عنتشهور التقويم المصري توت بابة هاتور كيهك طوبة أمشير برمهات برمودة بشنس بؤونة أبيب مسرى نسيئ تصنيف:شهور التقويم المصري

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Beth. BethBiographieNaissance 23 décembre 1981 (42 ans)SúriaNom de naissance Elisabeth Rodergas i ColsNationalité espagnoleActivités Chanteuse, actricePériode d'activité Depuis 2003Autres informationsGenre artistique Popmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Elisabeth Rodergas, Beth (Súria, 23 décembre 1981) est une chanteuse espagnole. Biographie Avant de participer à Operación Triunfo, elle avait vécu au Royaume-Uni, étudié au Th...

This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Dasaki Stadium – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Ethnikos Achnas StadiumDasakiFull nameEthnikos Achnas Stadium (Greek: Δασάκι)LocationAchna, Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, CyprusCapacit...

Ecuadorian footballer (born 1981) José Perlaza José Luis Perlaza (2015)Personal informationFull name José Luis Perlaza NapaDate of birth (1981-10-06) October 6, 1981 (age 42)Place of birth Esmeraldas, EcuadorHeight 1.93 m (6 ft 4 in)Position(s) Centre BackYouth career1996–1997 Sport Estudiantes1997–2001 Cinco de Agosto1998 → Calvi F.C. (loan)Senior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1999 →Audaz Octubrino (loan) 2 (0)2000 →Olmedo (loan) 17 (1)2001–2009 Olmedo 227 (8...