Dolphin Interconnect Solutions
| |||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Emil ChristensenHeatoNStatusPensiunTanggal lahir14 Juni 1984 (umur 39)Tempat tinggalStockholmKebangsaanSwediaPermainanCounter-StrikeRiwayat karirSebagai pemain:2001–2002Ninjas in Pyjamas2002–2004SK Gaming2005–2007Ninjas in PyjamasSebagai pelatih:September 2007Ninjas in Pyjamas2007–2008Stockholm Magnetik2012–2018Ninjas in Pyjamas Emil Pathric William Christensen (lahir 14 Juni 1984), dikenal juga dengan nama HeatoN, adalah seorang manajer dan mantan pemain esports asal Swedia un...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Jindřich PlachtaJindřich Plachta 1941Lahir(1899-07-01)1 Juli 1899Plzeň, Bohemia, Austria-Hungaria (kini Republik Ceko)Meninggal6 November 1951(1951-11-06) (umur 52)Praha, Cekoslowakia (kini Republik Ceko)PekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1926–...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2018年3月17日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:羅生門 (電影) — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 �...

University in Kenya Great Lakes University of KisumuGlukTypePrivate UniversityEstablished1998Vice-ChancellorProf Hazel Miseda MumboUndergraduatesOfferedPostgraduatesOfferedDoctoral studentsOfferedAddressGreat Lakes University of Kisumu P.O.BOX 2224 - 40100, Kisumu, KENYA, Kisumu, KenyaCampusMain Campus (Kibos)Millimani Campus (Kisumu Town)Nairobi Campus. (Centro House - Westlands)ColorsGreen, blue and yellow NicknameGLUKWebsitewww.gluk.ac.ke Great Lakes University of Kisumu ...

Sporting event delegationVenezuela at the2004 Summer OlympicsIOC codeVENNOCVenezuelan Olympic CommitteeWebsitewww.covoficial.com.ve (in Spanish)in AthensCompetitors48 in 15 sportsFlag bearer Julio César LunaMedalsRanked 68th Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 2 Total 2 Summer Olympics appearances (overview)19481952195619601964196819721976198019841988199219962000200420082012201620202024 Venezuela competed at the 2004 Summer Olympics in Athens, Greece, from 13 to 29 August 2004. This was the nat...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...
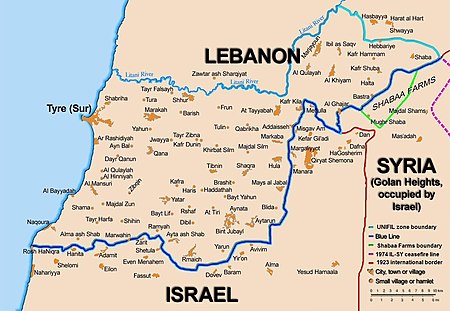
Resolusi 427Dewan Keamanan PBBLokasi Garis BiruTanggal3 Mei 1978Sidang no.2.076KodeS/RES/427 (Dokumen)TopikIsrael-LebanonRingkasan hasil12 mendukungTidak ada menentang2 abstainHasilDiadopsiKomposisi Dewan KeamananAnggota tetap Tiongkok Prancis Britania Raya Amerika Serikat Uni SovietAnggota tidak tetap Bolivia Kanada Jerman Barat Gabon India Kuwait Mauritania Nigeria Cekoslowakia Venezuela Resolusi Dewan Keam...

莎拉·阿什頓-西里洛2023年8月,阿什頓-西里洛穿著軍服出生 (1977-07-09) 1977年7月9日(46歲) 美國佛羅里達州国籍 美國别名莎拉·阿什頓(Sarah Ashton)莎拉·西里洛(Sarah Cirillo)金髮女郎(Blonde)职业記者、活動家、政治活動家和候選人、軍醫活跃时期2020年—雇主內華達州共和黨候選人(2020年)《Political.tips》(2020年—)《LGBTQ國度》(2022年3月—2022年10月)烏克蘭媒�...

Flat track roller derby league Akron Roller DerbyMetro areaAkron, OhioCountryUnited StatesFounded2016TeamsAll Stars (A team)AK Rowdy Rollers (B team)Track type(s)FlatVenueSummit County Fairgrounds Arena ComplexAffiliationsWFTDAWebsitewww.akronrollerderby.net Akron Roller Derby is a women's flat track roller derby league based in Akron, Ohio. Two separate Akron-based leagues, NEO Roller Derby and Rubber City Rollergirls, merged in November 2016 to become Akron Roller Derby. The league consists...

German politician (born 1959) Klaus RiegertMember of the Bundestag from GöppingenIn office1992–2013[1]Preceded byLutz StavenhagenSucceeded byHermann Färber Personal detailsBorn (1959-02-26) 26 February 1959 (age 65)Süßen, Göppingen, West GermanyPolitical partyCDUAwardsGerman Order of Merit (2008)[2] Klaus Riegert (born 26 February 1959 in Süßen, Göppingen) is a German politician (CDU). Until 2013, he was deputy chairman of the Subcommittee on Civic Involvement o...

For a chronology of Tibetan history, see Timeline of Tibetan history. Part of a series on the History of Tibet Neolithic Tibet Zhangzhung Yarlung dynasty Tibetan Empire Era of Fragmentation Yuan rule Phagmodrupa dynasty Rinpungpa dynasty Tsangpa dynasty Khoshut Khanate Ganden Phodrang Ming–Tibet relations Qing rule 13th and 14th Dalai Lama PRC rule See also Timeline Historical money List of rulers European exploration Asia portal • China portalvte While the Tibetan plateau ha...

Monthly American lifestyle magazine For the British publication, see Town and Country Magazine. 'Home Journal' redirects here. For the Swedish women's magazine Tidskrift för hemmet, see Home Review. Town & CountryJune 2007 cover featuring model ImanEditorStellene VolandesFormer editorsFrank ZacharyPhotographerRonny JaquesFrequencyMonthlyTotal circulation(2015)486,297[1]FounderNathaniel Parker Willis and George Pope MorrisFounded1846CompanyHearst MagazinesCountryUnited StatesBased...

Aviation term for a corkscrew downward path Tailspin redirects here. For other uses, see Tailspin (disambiguation). Not to be confused with the Disney animated TV series TaleSpin. Spin — an aggravated stall and autorotation In flight dynamics a spin is a special category of stall resulting in autorotation (uncommanded roll) about the aircraft's longitudinal axis and a shallow, rotating, downward path approximately centred on a vertical axis.[1] Spins can be entered intentionally or ...

Pandémie de Covid-19 en EspagneCommunautés autonomes touchées par le virus, au 24 juin 2021.>2 000>3 000>4 000>5 000 >6 000>7 000>8 000>9 000Maladie Maladie à coronavirus 2019 (Covid-19)Agent infectieux SARS-CoV-2Origine Wuhan (Hubei, Chine)[1],[2]Localisation EspagnePremier cas La Gomera, îles Canaries[3]Date d'arrivée Depuis le 31 janvier 2020 (4 ans, 5 mois et 23 jours)BilanCas confirmés 13 332 976 (29 août 2022)[4],[5]Cas soignés 1...

The Diocese of Montalcino (Latin: Dioecesis Ilcinensis) was a Roman Catholic diocese located in the town of Montalcino to the west of Pienza, close to the Crete Senesi in Val d'Orcia in Tuscany, Italy. In 1986, it was suppressed and united with the Diocese of Colle di Val d'Elsa and the Archdiocese of Siena to form the Archdiocese of Siena-Colle di Val d'Elsa-Montalcino.[1][2] Cocathedral of Santissimo Salvatore History Establishment of the diocese On 13 August 1462, Pope Pius...

デルビ 種類 子会社設立 1922年創業者 Simón Rabasa i Singla解散 2018年 本社 バルセロナ、スペイン製品 オートバイ、スクーター、ATV親会社 ピアッジオウェブサイト www.derbi.com デルビ(Derbi)は、スペインの Nacional Motor S.A.U.社が製造するオートバイ、スクーター、ATVのブランド名 。現在同社はピアッジオの子会社となっている。なお記事中では、社名も通称の「デルビ」�...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Princess Magdalena Augusta of Anhalt-Zerbst – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Duchess consort of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg Magdalena Augusta of Anhalt-ZerbstDuchess consort of Saxe-Gotha-Altenbur...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字(Microsoftコードページ932(はしご高))が含まれています(詳細)。 東京24区 ジャンル サスペンス アニメ 原作 Team 24 監督 津田尚克 シリーズ構成 下倉バイオ 脚本 下倉バイオ キャラクターデザイン FiFS(原案)岸田隆宏 音楽 深澤秀行 アニメーション制作 CloverWorks 製作 東京24区プロジェクト 放送�...

Eliud KipchogeEliud Kipchoge alla Maratona di Berlino 2015Nazionalità Kenya Altezza167 cm Peso52 kg Atletica leggera SpecialitàMezzofondo, fondo SocietàNike / NN Running Team Record 1500 m 3'3320 (2004) 1500 m 3'3625 (indoor - 2006) Miglio 3'5040 (2004) 3000 m 7'2766 (2011) 3000 m 7'2937 (indoor - 2011) 5000 m 12'4653 (2004) 5000 m 12'5572 (indoor - 2011) 10000 m 26'4902 (2007) Mezza maratona 59'25 (2012) 30 km 1h27'13 (2016) Maratona 2h01'09 (2022) CarrieraNazionale 2003- Kenya Palma...

Italian composer, singer and organist (1623–1669) Antonio CestiBaptised Pietro Cesti 5 August 1623 Arezzo Died14 October 1669FlorenceOccupation(s)Composer, singer, organist Antonio Cesti (Italian pronunciation: [anˈtɔːnjo ˈtʃesti]; baptised Pietro Cesti, 5 August 1623; died 14 October 1669), known today primarily as an Italian composer of the Baroque era, was also a singer (tenor), and organist. He was the most celebrated Italian musician of his generation.[1] Biography...