Dennis Hart Mahan
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Cahaya Rasul 3Album studio karya MayadaDirilis2002 20 Agustus 2007 9 Juni 2015 (rilis ulang)Direkam2000–2001GenrePop, ReligiLabelMusika Selaras CitraWarner Music IndonesiaKronologi Mayada Cahaya Rasul 2 (2001)Cahaya Rasul 22001 Cahaya Rasul 3 (2002) Cahaya Rasul 4 (2002)Cahaya Rasul 42002 Cahaya Rasul Vol. 3 adalah sebuah album religi ketiga karya Mayada yang dirilis pada tahun 2002. Album ini merupakan album religi terlaris sepanjang sejarah musik Indonesia. Lagu utamanya Nabiyal Huda....

Italian footballer (born 1985) Michele Franco Franco in 2019Personal informationDate of birth (1985-02-20) 20 February 1985 (age 39)Place of birth Altamura, ItalyHeight 1.83 m (6 ft 0 in)Position(s) Left-backYouth career2003–2005 BariSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2004–2008 Bari 0 (0)2005–2006 → Melfi (loan) 32 (1)2006–2007 → Cremonese (loan) 28 (0)2007–2008 → Manfredonia (loan) 30 (0)2008–2011 Como 88 (10)2011–2012 Padova 17 (0)2013–2014 Varese 2...

Poem in Old Norse Menglöð.Fjölsvinnsmál (Old Norse: 'The Lay of Fjölsvinn')[1] is the second of two Old Norse poems commonly published under the title Svipdagsmál The Lay of Svipdagr. These poems are found together in several 17th-century paper manuscripts with Fjölsvinnsmál. In at least three of these manuscripts, the poems appear in reverse order and are separated by a third eddic poem titled Hyndluljóð.[2] For a long time, the connection between the two poems was ...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. La mise en forme de cet article est à améliorer (février 2021). La mise en forme du texte ne suit pas les recommandations de Wikipédia : il faut le « wikifier ». Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’alimentation, la politique et l’économie. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Récolte du ma�...

Niperotidine Names Preferred IUPAC name (Z)-N1-[(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-N′1-{2-[({5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]furan-2-yl}methyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine Identifiers CAS Number 84845-75-0 Y 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChEMBL ChEMBL1909284 N ChemSpider 11644617 N ECHA InfoCard 100.076.612 EC Number 284-304-0 KEGG D07072 Y MeSH C073716 PubChem CID 3033952 UNII 12JBD7U72K Y InChI InChI=1S/C20H28N4O5S/c1-23(2)11-16-4-5-17(29-16)13-30-8-7-21...

Italian film director (1894–1998) Carlo Ludovico BragagliaBragaglia in 1942Born(1894-07-08)8 July 1894Frosinone, Kingdom of ItalyDied4 January 1998(1998-01-04) (aged 103)Rome, ItalyOccupation(s)Film directorScreenwriterYears active1933 - 1963RelativesAnton Giulio Bragaglia (brother)Arturo Bragaglia (brother) Carlo Ludovico Bragaglia (8 July 1894 – 4 January 1998) was an Italian film director whose career spanned from the 1930s to the mid-1960s. He mainly directed adventure p...

←→Март Пн Вт Ср Чт Пт Сб Вс 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 2024 год Содержание 1 Праздники и памятные дни 1.1 Национальные 1.2 Религиозные 1.2.1 Католицизм 1.2.2 Православие[3][4] 1.3 Именины 2 События 2.1 До XIX века 2.2 XIX век 2.3 XX век 2.4 XXI век 3 Родились 3.1 До XIX в...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando il personaggio, vedi Steven Universe (personaggio). Steven Universeserie TV d'animazione Logo della serie Lingua orig.inglese PaeseStati Uniti d'America AutoreRebecca Sugar (ideatrice), Matt Burnett (fino a marzo 2017), Ian Jones-Quartey (fino a giugno 2015) ProduttoreRebecca Sugar, Jackie Buscarino Char. designDanny Hynes, Colin Howard Dir. artisticaRebecca Sugar MusicheRebecca Sugar, Jeff Liu, Aivi Tran...

هنودمعلومات عامةنسبة التسمية الهند التعداد الكليالتعداد قرابة 1.21 مليار[1][2]تعداد الهند عام 2011ق. 1.32 مليار[3]تقديرات عام 2017ق. 30.8 مليون[4]مناطق الوجود المميزةبلد الأصل الهند البلد الهند الهند نيبال 4,000,000[5] الولايات المتحدة 3,982,398[6] الإمار...
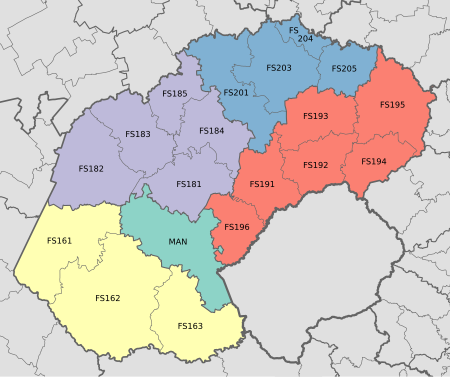
Local municipality in Free State, South AfricaMatjhabengLocal municipality SealLocation in the Free StateCoordinates: 27°58′S 26°44′E / 27.967°S 26.733°E / -27.967; 26.733CountrySouth AfricaProvinceFree StateDistrictLejweleputswaSeatWelkomWards36Government[2] • TypeMunicipal council • MayorThanduxolo Khalipha[1] (ANC)Area • Total5,155 km2 (1,990 sq mi)Population (2011)[3] •&#...

Brass instrument Trumpeter redirects here. For other uses, see Trumpeter (disambiguation) and Trumpet (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Trumpet – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) TrumpetTrumpet in B♭B...

Equalities that involve trigonometric functions Trigonometry Outline History Usage Functions (sin, cos, tan, inverse) Generalized trigonometry Reference Identities Exact constants Tables Unit circle Laws and theorems Sines Cosines Tangents Cotangents Pythagorean theorem Calculus Trigonometric substitution Integrals (inverse functions) Derivatives Trigonometric series Mathematicians Hipparchus Ptolemy Brahmagupta al-Hasib al-Battani Regiomontanus Viète de Moivre Euler Fourier vte In...

Human settlement in EnglandHaleHale Millennium clock towerHaleLocation within Greater ManchesterPopulation15,315 (2011)OS grid referenceSJ769867Metropolitan boroughTraffordMetropolitan countyGreater ManchesterRegionNorth WestCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townAltrinchamPostcode districtWA15Dialling code0161PoliceGreater ManchesterFireGreater ManchesterAmbulanceNorth West UK ParliamentAltrincham and Sale List of places UK England G...

This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject, potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral. Please help improve it by replacing them with more appropriate citations to reliable, independent, third-party sources. (May 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Law enforcement agency Ohio State Highway PatrolPatch of the Ohio State Highway PatrolBadge of Ohio State Highway PatrolAbbreviationOSHPAgency overviewFormed1933 ...

Location of Yonkers in Westchester County This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places entries in Yonkers, New York, United States. See also National Register of Historic Places listings in Westchester County, New York for all others in the county. Map all coordinates using OpenStreetMap Download coordinates as: KML GPX (all coordinates) GPX (primary coordinates) GPX (secondary coordinates) This is intended to be a complete list of properties and districts listed on the Nationa...

Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Sepak bola putri pada Olimpiade Musim Panas 2004 – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Untuk turnamen pria, lihat Sepak bola pria pada Olimpiade Athena 2004. Kembali ke: Sepak bola pada Olimpiad...

This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Simcheon station – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The station in 2007. Simcheon station is a South Korean railway station on the Gyeongbu Line. References vteGyeongbu line Seoul Namyeong Yongsan Noryangjin Daeb...

American tennis player Dorothy GreenGreen in 1911Country (sports) United StatesBorn31 March 1897Died13 December 1964 (aged 67)SinglesGrand Slam singles resultsUS OpenF (1913)DoublesGrand Slam doubles resultsUS OpenW (1912)Grand Slam mixed doubles resultsUS OpenF (1913) Dorothy Green (March 31, 1897 – December 13, 1964) was an American tennis player of the start of the 20th century. In 1912, she won the women's doubles at the US Women's National Championship with Mary Kendall Brown...

駒止湖 駒止湖所在地 北海道河東郡鹿追町位置 北緯43度15分25秒 東経143度5分37秒 / 北緯43.25694度 東経143.09361度 / 43.25694; 143.09361座標: 北緯43度15分25秒 東経143度5分37秒 / 北緯43.25694度 東経143.09361度 / 43.25694; 143.09361面積 0.02[1] km2周囲長 0.8[1] km最大水深 5.0[1] m水面の標高 855[1] m成因 火口湖[2]淡水・汽水 淡水[1&...



