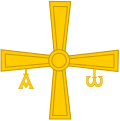
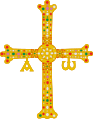
Crux gemmata
|
Read other articles:

1985 song by the Smiths For the TV series, see How Soon Is Now? (TV series). How Soon Is Now?Single by the Smithsfrom the album Hatful of Hollow B-sideWell I WonderOscillate WildlyReleased28 January 1985 (1985-01-28)RecordedJuly 1984StudioJam, LondonGenreAlternative rock[1]psychedelia[2]Length6:44LabelRough TradeSongwriter(s)Johnny MarrMorrisseyProducer(s)John PorterThe Smiths singles chronology William, It Was Really Nothing (1984) How Soon Is Now? (1985) Shake...

Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on basketball This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (April 2022) Part of a series on theCOVID-19 pandemicScientifically accurate atomic model of the external structure of SARS-CoV-2. Each ball is an atom. COVID-19 (disease) SARS-CoV-2 (virus) Cases Deaths Timeline 2019 2020 January responses February responses March responses April responses May responses June responses July re...

العلاقات اليمنية الكمبودية اليمن كمبوديا اليمن كمبوديا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات اليمنية الكمبودية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين اليمن وكمبوديا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة الي�...

Edition of USA college basketball tournament See also: 2006 NCAA Division I Men's Basketball Championship Game 2006 NCAA Division Imen's basketball tournamentSeason2005–06Teams65Finals siteRCA DomeIndianapolis, IndianaChampionsFlorida Gators (1st title, 2nd title game,3rd Final Four)Runner-upUCLA Bruins (13th title game,16th Final Four)SemifinalistsGeorge Mason Patriots (1st Final Four)LSU Tigers (4th Final Four)Winning coachBilly Donovan (1st title)MOPJoakim Noah (Florida)Attendance70,...

Part of a series on theCulture of Spain History People Languages Mythology and Folklore Cuisine Festivals Religion Christianity Catholicism Protestantism Orthodox Islam Ahmadiyya Judaism Bahá'í Hinduism Art LiteratureComics Music Media Radio Television Cinema Sport Monuments World Heritage Sites Symbols Flag Coat of arms National anthem Spain portalvte Answer to the question 'How do you define yourself in religious matters?' in Spain (CIS survey; sample size: 10,104; September 20...

Alain Carignon Alain Carignon en 2007. Fonctions Conseiller métropolitain de Grenoble-Alpes Métropole En fonction depuis le 29 juin 2020(3 ans, 9 mois et 4 jours) Élection 28 juin 2020 Président Christophe Ferrari 18 mars 1983 – 19 juin 1995(12 ans, 3 mois et 1 jour) Élection 18 mars 1983 Réélection 19 mars 1989 Président Lui-mêmeRobert Magnin Conseiller municipal de Grenoble En fonction depuis le 16 novembre 2019(4 ans, 4 mois et 17 jo...

This article is about the 18th Century American newspaper. For the Trump campaign website, see America First Policies. The American Herald, 1784 The American Herald (1784-1790) was a newspaper in Boston and Worcester, Massachusetts, published by Edward Eveleth Powars and Nathaniel Willis.[1][2][3][4] Variant titles The American Herald: and the General Advertiser (Jan. 19, 1784-Mar. 29, 1784) The American Herald: and Federal Recorder (1788) American Herald; and ...

Voce principale: Società Sportiva Rende. Società Sportiva RendeStagione 1978-1979Sport calcio Squadra Rende Allenatore Emilio Zanotti Presidente Gaetano Sesso Serie C21º nel girone D. Promossa in Serie C1. Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Chiappetta, Marletta (33) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: De Brasi (15) 1979-1980 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa pagina raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti la Società Sportiva Rende nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione 1978-1979. I...

Dutch politician and farmer (born 1979) In this Dutch name, the birth surname is Monaster and the marital name is Vedder. Eline VedderVedder (center) at a 2021 farmers' protestMember of the House of RepresentativesIncumbentAssumed office 10 May 2023Preceded byJaco GeurtsMember of the Provincial Council of DrentheIn office28 March 2019 – 30 May 2023Succeeded bySonja Hilgenga-van DamMember of the Municipal Council of De WoldenIn office29 March 2018 – 25 April 2...

Charles BradlaughMP Anggota Parlemendapil NorthamptonMasa jabatan1880–1891PendahuluCharles George MerewetherPenggantiSir Moses Philip Manfield Informasi pribadiLahir(1833-09-26)26 September 1833HoxtonMeninggal30 Januari 1891(1891-01-30) (umur 57)KebangsaanBritaniaPartai politikPartai LiberalSunting kotak info • L • B Charles Bradlaugh (26 September 1833 – 30 Januari 1891) adalah seorang aktivis politik Inggris. Ia merupakan salah satu ateis Inggris dari abad ke-19 yang ...

Video game series This article is about the video game series. For the first game in the series, see Densha de Go! (video game). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Densha de Go! – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Video game ...

Historic site in Kingston, Ontario Bellevue HouseEstablishedEarly 1840s[1]Location35 Centre StreetKingston, Ontario, CanadaTypeHistoric HouseNearest parkingOn site (no charge)WebsiteParks Canada - Bellevue House National Historic Site of CanadaDesignated1995 Bellevue House National Historic Site was the home to Canada's first Prime Minister, Sir John Alexander Macdonald from 1848 to 1849.[2] The house is located in Kingston, Ontario. 44°13′22″N 76°30′12″W / &...

GerakanPetaniSipil BoerBurgerBewegingPemimpinCaroline van der PlasKetua umumErik SteginkKetua fraksi di SenatIlona LagasKetua fraksi di DPRCaroline van der PlasDibentuk1 November 2019Kantor pusatSmeenkhof 12d, Colmschate (Deventer)Ideologipertanian, pedesaanWarnajeruk nipisDewan Perwakilan Rakyat7 / 150 Senat16 / 75 Negara bagian-Provinsional138 / 572 Parlemen Eropa0 / 29 Situs webboerburgerbeweging.nl GerakanPetaniSipil (bahasa Belanda: BoerBurgerBeweging, BBB) adalah partai politik di Belan...

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari Local analysis di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan penerjema...

Indian state-owned agriculture Television channel Television channel DD KisanTypeTelevision ChannelCountryIndiaBroadcast areaIndiaNetworkDoordarshanHeadquartersNoida, IndiaProgrammingLanguage(s)Hindi, EnglishPicture format(576i, SDTV) 4:3OwnershipOwnerPrasar Bharati, Ministry of Information and BroadcastingSister channelsDD NationalDD NewsDD IndiaDD SportsDD BharatiDD RetroHistoryLaunchedMay 26, 2015; 8 years ago (2015-05-26)LinksWebsiteDD KisanAvailabilityTerrestrialDVB-T2 ...

vteDutch colonial campaigns17th century Bantam (1601) Amboina (1605) Malacca (1606) Cape Rachado (1606) Mozambique (1607) Mozambique (1608) Banda Islands (1609–21) Johor (1613) Macau (1622) Pescadores (1622–24) Salvador (1624) Persian Gulf (1625) Salvador (1625) Elmina (1625) Cuba (1628) Batavia (1628–29) Recife (1630) Abrolhos (1631) Liaoluo Bay (1633) Taiwan (1635–36) Brazil (1636) Liuqiu Island (1636) Porto Calvo (1637) Elmina (1637) Vietnam (1637–43) Goa (1638) Salvador (1638) M...

Community college in Schenectady, New York, U.S. SUNY SchenectadyElston HallTypePublic community collegeEstablished1967; 57 years ago (1967)Parent institutionState University of New YorkPresidentSteady H. MoonoAcademic staff243[1]Undergraduates5,231[2][3]Location Schenectady, New York, United States42°48′52″N 73°57′03″W / 42.814513°N 73.950799°W / 42.814513; -73.950799CampusUrban57 acres (0.23 km2)ColorsRoyal b...

Japanese media franchise created by Monkey Punch This article is about the media franchise. For the title character, see Lupin III (character). For other uses, see Lupin the Third (disambiguation). Lupin IIIThe Japanese logo of the franchiseCreated byMonkey PunchOriginal workLupin III (1967–1969)Years1967–presentPrint publicationsComicsList of mangaFilms and televisionFilm(s)List of filmsShort film(s)Pilot FilmTelevision seriesInspector ZenigataAnimated seriesList of animated seriesTelevi...

19th-century immigrant route in the United States An American wagon train at Maricopa Wells in 1857 The Southern Emigrant Trail should not be confused with the Applegate Trail, which is part of the Northern Emigrant Trails. Southern Emigrant Trail, also known as the Gila Trail, the Kearny Trail, Southern Trail and the Butterfield Stage Trail, was a major land route for immigration into California from the eastern United States that followed the Santa Fe Trail to New Mexico during the Californ...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...






![Apse semi-dome in mosaic, Basilica of Sant' Apollinare in Classe, Ravenna (549)[16]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0b/Basilica_of_Sant_Apollinare.jpg/120px-Basilica_of_Sant_Apollinare.jpg)