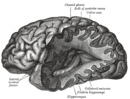
Cranial electrotherapy stimulation
|
Read other articles:

Koordinat: 51°28′21″N 0°19′29″E / 51.4724°N 0.3247°E / 51.4724; 0.3247 Grays Grays Letak Grays di Britania Raya Population 36,601 (Sensus 2001) Ref. grid OS TQ615773 Otoritas kesatuan Thurrock County seremonial Essex Wilayah East Negara konstituen England Negara berdaulat Britania Raya Kota pos Grays Distrik kode pos RM17 Kode telepon 01375 Polisi Pemadam kebakaran Ambulans Parlemen ...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori svedesi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Torbjörn Nilsson Nazionalità Svezia Altezza 190 cm Calcio Ruolo Allenatore (ex attaccante) Termine carriera 1986 - giocatore Carriera Giovanili ?-1970 Jonsereds IF Squadre di club1 1971-1975 Jonsereds IF? (?)1975-1976 IFK Göteborg49 (34)1976-1977 PSV11 (2)1977-1982 IFK Götebo...

Bendera anarkisme egois Anarkisme egois adalah sebuah aliran pemikiran anarkis yang berakar dari filsafat Max Stirner, seorang filsuf eksistensialis abad ke-19 yang namanya muncul secara teratur dalam berbagai pembacaan kesejarahan pemikiran anarkisme, sebagai salah satu pemrakarsa anarkisme individualis yang paling awal dan paling terkenal. Max Stirner dan pemikirannya Max Stirner Johann Kaspar Schmidt (25 Oktober 1806 – 26 Juni 1856), lebih dikenal sebagai Max Stirner (nama panggilan yang...

Untuk pelawak yang memiliki marga nama asli yang sama, lihat Komeng. Arif AlfiansyahLahirMuhammad Arif Alfiansyah26 Februari 1990 (umur 34)Surabaya, Jawa Timur, IndonesiaPekerjaanPelawak tunggalaktormodelpenyanyiTahun aktif2007—sekarang Muhammad Arif Alfiansyah (lahir 26 Februari 1990) adalah seorang pelawak tunggal, aktor, model, dan penyanyi berkebangsaan Indonesia. Awalnya, Arif merupakan seorang penari breakdance yang ikut bergabung dengan salah satu komunitas breakdance di Su...

OpenAIJenisOrganisasi nirlaba[1][2]IndustriKecerdasan buatanDidirikan11 Desember 2015; 8 tahun lalu (2015-12-11)PendiriSam AltmanElon MuskKantorpusatPioneer Building, San Francisco, California, AS[3][4]TokohkunciGreg Brockman (Ketua & Presiden)Sam Altman (CEO)Ilya Sutskever (Kepala ilmiah)ProdukDALL-E 2GPT-4OpenAI FiveChatGPTOpenAI CodexSoraKaryawan>120 (hingga 2020[update])[4]Situs webopenai.com OpenAI adalah laboratorium penelitan ...

Полярная тундра Остаток кармака (культура Туле, Национальный парк Уккусиксалик, Нунавут) 67° с. ш. 90° з. д.HGЯOЭкология БиомТундра География Площадь1 032 800 км² Страна Канада Тип климатаПолярный высоких широт Медиафайлы на Викискладе Поля́рная ту́...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Vanthourenhout. Michael VanthourenhoutMichael Vanthourenhout lors du Tour du Limbourg 2014InformationsNaissance 10 décembre 1993 (30 ans)BrugesNationalité belgeÉquipe actuelle Pauwels Sauzen-BingoalSpécialité cyclo-crossÉquipes UCI 2012-2013BKCP-Powerplus2014-2015Sunweb-Napoleon Games2016-2017Marlux-Napoleon Games2018Marlux-Bingoal2019-Pauwels Sauzen-BingoalPrincipales victoires Champion du monde de cyclo-cross espoirs (2015) Champion d'Europe de ...

Railway station in Okaya, Nagano Prefecture, Japan Kawagishi Station川岸駅Kawagishi Station, August 2007General informationLocation3-15-25 Kawagishi, Okaya-shi, Nagano-ken 394-0045JapanCoordinates36°1′58.7″N 138°1′19.1″E / 36.032972°N 138.021972°E / 36.032972; 138.021972Elevation757.4 meters[1]Operated by East Japan Railway Company Central Japan Railway Company Line(s) ■Chūō Main Line ■ Iida Line Platforms1 island platformOther informationS...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

This article is about an organisation. For the human-centered philosophy, see Humanism. siloism redirects here. For the insular organization, see information silo. For other uses, see Humanist (disambiguation). This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Humanist Movement – news · newspapers · books �...

American professional wrestler Drew GulakGulak in 2018Born (1987-04-28) April 28, 1987 (age 37)[1]Abington Township, Pennsylvania, U.S.[1]Websitedrewgulak.comProfessional wrestling careerRing name(s)Drew Gulak[2]Gulak[1][3]Soldier Ant[1]The Gobbledy Gooker[4]Billed height6 ft 1 in (185 cm)[2]Billed weight193 lb (88 kg)[2]Billed fromPhiladelphia, Pennsylvania[5]Trained byChris HeroMike...
Village in Jharkhand, IndiaTeliagarhi TeliagarihVillageTeliagarhiLocation in Jharkhand, IndiaShow map of JharkhandTeliagarhiTeliagarhi (India)Show map of IndiaCoordinates: 25°15′40″N 87°32′19″E / 25.261021°N 87.538511°E / 25.261021; 87.538511Country IndiaStateJharkhandDistrictSahibganjPopulation (2011) • Total107Languages (*For language details see Mandro#Language and religion) • OfficialHindi, UrduTime zoneUTC+5:30 (IST)T...

British musician This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Daniel Miller music producer – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this me...

British electronics, defence and telecommunications company This article is about the British company. For the decision by the United States Supreme Court, see Plessy v. Ferguson. PlesseyCompany typePublic companyIndustryElectronics, defence and telecommunicationsFounded1917Defunct1989FateAcquired (in 1989 by GEC/Siemens joint holding company – GEC Siemens)SuccessorGEC(1989–1999)Siemens Plessey(1989–1997)Marconi Communications(1998–2006)Siemens Communications(1998–2006)BAE Systems(1...

هواتف ذكية: سامسونج جالكسي إس 22 ألترفونيسوووا (أعلى) وآيفون 15 (أسفل) الهاتف الذكي (بالإنجليزية: Smartphone) هو مصطلح يطلق على فئة الهواتف المحمولة الحديثة التي تجمع ميزتين رئيسيتين هما إمكانية التواصل عبر نظام الاتصالات الخلوية ويحتوي على نظام تشغيل متطور، واغلبها ان لم يكن جم�...

City in Florida, United StatesMarianna, FloridaCityCity of MariannaMarianna City HallNickname: The City of Southern CharmLocation in Jackson County and the state of FloridaCoordinates: 30°46′35″N 85°14′17″W / 30.77639°N 85.23806°W / 30.77639; -85.23806Country United StatesState FloridaCounty JacksonIncorporated1825Government • TypeCommission–Manager • MayorJohn Roberts • CommissionersAllen Ward, Ric...

1493 biblical encyclopedia by German historian Hartmann Schedel Nuremberg Chronicle Woodcut of Nuremberg, Nuremberg ChronicleAuthorHartmann SchedelOriginal titleLiber ChronicarumIllustratorMichael Wolgemut and Wilhelm PleydenwurffLanguageLatin; GermanSubjectHistory of the worldGenreUniversal history[1]Published1493PublisherAnton KobergerPages336 The Nuremberg Chronicle is an illustrated encyclopedia consisting of world historical accounts, as well as accounts told through biblica...

Gallo-Romance language of Friuli, northeast Italy Furlan redirects here. For the surname, see Furlan (surname). FriulianfurlanNative toItalyRegionFriuliEthnicityFriuliansNative speakersRegular speakers: 420,000 (2014)[1]Total: 600,000 (2014)[1]Language familyIndo-European ItalicLatino-FaliscanRomanceItalo-WesternWestern RomanceGallo-RomanceRhaeto-Romance or Gallo-Rhaetian[2]FriulianDialects Fornes Writing systemLatin (Friulian alphabet)Official statusRegulate...

Tel Aviv und Jaffa sind Weiterleitungen auf diesen Artikel. Weitere Bedeutungen sind unter Tel Aviv (Begriffsklärung) und Jaffa (Begriffsklärung) aufgeführt. Tel Aviv-Jaffa Flagge von Tel Aviv-Jaffa Basisdaten hebräisch: תל אביב-יפו arabisch: تل أبيب يافا Staat: Israel Israel Bezirk: Tel Aviv Gegründet: 1909 Koordinaten: 32° 5′ N, 34° 48′ O32.08333333333334.8Koordinaten: 32° 5′ 0″ N, 34° 48′ 0″ O F...

Statue from Easter Island Easter Island StatueHoa Hakananai'a in the Wellcome Gallery in the British MuseumMaterialFlow lavaSizeHeight: 2.42 metres (7.9 ft)Createdc. 1000-1600 ADPresent locationBritish Museum, London, Gallery 24Registration1869,1005.1 Hoa Hakananai'a is a moai, a statue from Easter Island. It was taken from Orongo, Easter Island (Rapa Nui) in 1868 by the crew of a British ship and is now in the British Museum in London. It has been described as a masterpiece[1] a...