Cornelia Pillard
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Orientalismo (disambigua). Il Royal Pavilion a Brighton, esempio di architettura orientalista in occidente L'orientalismo[1] è un termine usato dagli storici dell'arte, studiosi letterari e culturali per definire l'imitazione o la rappresentazione di aspetti delle culture del Medio Oriente, dell'Asia meridionale e dell'Asia orientale in opere occidentali. Queste raffigurazioni vengono solitamente eseguite da scrittori,...

2013 studio album by Brett DennenSmoke and MirrorsStudio album by Brett DennenReleasedOctober 22, 2013GenreFolk, popLength36:13LabelF-Stop/AtlanticBrett Dennen chronology Loverboy(2011) Smoke and Mirrors(2013) Por Favor(2016) Smoke and Mirrors is the fifth studio album by the American singer-songwriter Brett Dennen.[1] It was released on October 22, 2013, by F-Stop Music/Atlantic Records. The album peaked at number 65 on the Billboard 200 album chart, number 10 on Billboard's ...
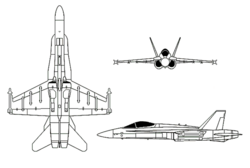
McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 HornetUn F/A-18C Hornet, dell’USAF, in volo durante l'Operazione Enduring Freedom; 2001.DescrizioneTipocaccia multiruolo imbarcato Equipaggio1 nelle versioni monoposto, quindi A, C ed E 2 nelle versioni biposto, quindi B, D, F e G Progettista Northrop Costruttore McDonnell Douglas Boeing Data primo volo18 novembre 1978 Data entrata in servizio7 gennaio 1983 Utilizzatore principale US Navy Altri utilizzatori United States Marine Corps Aviation EdA RAAF Forze aeree sv...
ميّز عن بروس ويليس. بروس ولز معلومات شخصية الميلاد 4 يونيو 1937 (87 سنة) أورانج مواطنة أستراليا الحياة العملية المهنة لاعب اتحاد الرغبي الرياضة الرغبي تعديل مصدري - تعديل بروس ولز (بالإنجليزية: Bruce Wells) هو لاعب اتحاد الرغبي أسترالي، ولد في 4 يونيو 1937 في...

American professional basketball player (born 1992) For other people named Joe Jackson, see Joe Jackson (disambiguation). Joe JacksonPersonal informationBorn (1992-02-08) February 8, 1992 (age 32)Memphis, Tennessee, U.S.Listed height6 ft 1 in (1.85 m)Listed weight171 lb (78 kg)Career informationHigh schoolWhite Station (Memphis, Tennessee)CollegeMemphis (2010–2014)NBA draft2014: undraftedPlaying career2014–2017PositionPoint guardCareer history2014–2015Baker...

Monorail station in Bangkok, Thailand Hua Makหัวหมาก ARL MRT ARL PlatformsGeneral informationLocationSuan Luang DistrictBangkokThailandOwned byState Railway of Thailand Mass Rapid Transit Authority of ThailandOperated byState Railway of Thailand (SRT) Asia Era One Company Limited (AERA1) (ARL) Eastern Bangkok Monorail Company Limited (EBM) (MRT)Managed byMinistry of TransportPlatforms3 (SRT) 2 (ARL) 2 (MRT)ConstructionStructure typeAt-grade (SRT) Elevated ...

Ronactolol Names IUPAC name N-[4-[2-Hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl]-4-methoxybenzamide Identifiers CAS Number 90895-85-5 Y 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChemSpider 59236 PubChem CID 65824 UNII PJ691WQY08 Y InChI InChI=1S/C20H26N2O4/c1-14(2)21-12-17(23)13-26-19-10-6-16(7-11-19)22-20(24)15-4-8-18(25-3)9-5-15/h4-11,14,17,21,23H,12-13H2,1-3H3,(H,22,24)Key: BPNZFFWEUGGXMC-UHFFFAOYSA-NInChI=1/C20H26N2O4/c1-14(2)21-12-17(23)13-26-19-10-6-16(7-11-19)22-20(24)15-4-8-18...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Кагальник. СелоКагальник 47°04′37″ с. ш. 39°19′25″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Россия Субъект Федерации Ростовская область Муниципальный район Азовский Сельское поселение Кагальницкое История и география Часовой пояс UTC+3:00 �...

United Nations statute Statute of the International Court of JusticeSigned26 June 1945 (1945-06-26)LocationSan Francisco, United StatesEffective24 October 1945Signatories50 statesParties193 statesLanguages Chinese, English, French, Russian, Spanish The Statute of the International Court of Justice is an integral part of the United Nations Charter, as specified by Chapter XIV of the United Nations Charter, which established the International Court of Justice (replacing the Perma...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

Chinese TaipeiAssociation nameChinese Taipei Ice Hockey FederationIIHF CodeTPEIIHF membershipSeptember 1, 1983PresidentPai Wen-JunIIHF men's ranking41st (August 26, 2023)IIHF women's ranking26th (August 26, 2023)www.ctihf.org.tw Chinese Taipei Ice Hockey FederationTraditional Chinese中華民國冰球協會Simplified Chinese中华民国冰球协会TranscriptionsStandard MandarinHanyu PinyinZhōnghuá Mínguó Bīngqiú Xiéhuì The Chinese Taipei Ice Hockey Federation (CTIHF) is the gove...

For the 16th-century Guaraní leader, see Lambaré (chieftain). City in Central, ParaguayLambaréCity FlagLambaréCoordinates: 25°19′48″S 57°38′24″W / 25.33000°S 57.64000°W / -25.33000; -57.64000Country ParaguayDepartment CentralGovernment • MayorArmando Gómez (PLRA)Area • Total26.85 km2 (10.37 sq mi)Population (2016) • Total170,851 • Density5,204/km2 (13,480/sq mi)Area code021Climate...

Global provider of agricultural science and technology For the Scottish football club, see Syngenta F.C. For the moth genus, see Syngeneta. SyngentaHeadquarters, Basel, SwitzerlandCompany typePrivateIndustryAgrobusiness, chemicalsFounded13 November 2000; 23 years ago (2000-11-13)HeadquartersBasel, SwitzerlandArea servedWorldwideKey peopleJeff Rowe (CEO)Hengde Qin(CFO)ProductsCrops (fungicides, herbicides, insecticides)field and vegetable seedsflowersnutrientsdigital services...

Estratto dalla Fuga n. 17 in la bemolle maggiore, BWV 862, dal I libro del Clavicembalo ben temperato di Johann Sebastian Bach (playⓘ) Contrappunto, nella terminologia musicale, sta a indicare: la presenza, in una composizione o in una sua parte, di linee melodiche indipendenti che si combinano secondo regole tramandate dalla tradizione musicale occidentale; la parte della teoria musicale che studia queste regole. L'espressione si riferisce alla pratica di contrapporre a un cantus firmus, c...

دفيد سالومون ابو معلومات شخصية الميلاد 10 مايو 1986 (العمر 38 سنة)جوس[1] الطول 1.74 م (5 قدم 8 1⁄2 بوصة) مركز اللعب وسط الجنسية نيجيريا المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فريق م. (هـ.) 2004–2005 إنييمبا إنترناشونال 2006 غنتشلربيرليغي 6 (0) 2006–2008 ديجون 13 (1) 2008–2010 كريتيل 51 (9) 2...

Railway station in the West Midlands, England 52°35′02″N 1°59′06″W / 52.5840°N 1.9851°W / 52.5840; -1.9851 WalsallWalsall station in January 2019.General informationLocationWalsall, Metropolitan Borough of WalsallEnglandGrid referenceSP010984Managed byWest Midlands RailwayTransit authorityTransport for West MidlandsPlatforms3Other informationStation codeWSLFare zone4ClassificationDfT category DHistoryOriginal companySouth Staffordshire RailwayPre-groupingLo...

Village in New York, United StatesWilliston Park, New YorkVillageIncorporated Village of Williston ParkWilliston Park Village Hall in 2012Location in Nassau County and the state of New York.Williston Park, New YorkLocation on Long IslandShow map of Long IslandWilliston Park, New YorkLocation within the state of New YorkShow map of New YorkCoordinates: 40°45′29″N 73°38′45″W / 40.75806°N 73.64583°W / 40.75806; -73.64583Country United StatesState Ne...

野中 生萌クライミング世界選手権2018個人情報フルネームのなか みほう国籍 日本生誕 (1997-05-21) 1997年5月21日東京都身長162 cm (5 ft 4 in)体重52 kg (115 lb) スポーツ競技スポーツクライミング 獲得メダル スポーツクライミング 日本代表 オリンピック 銀 2020 東京 複合 IFSC世界選手権 銀 2016 パリ ボルダリング ワールドカップ 銅 2015 ボルダリング 銀 2016 ボ...

Not to be confused with People's Liberation Army, Chinese Red Army, or Republic of China Armed Forces. National Revolutionary ArmyFlag of the National Revolutionary Army (known as the Republic of China Army after the 1947 Constitution)Active16 June 1924 – 25 December 1947Country ChinaAllegiance KuomintangTypeArmyRoleGround warfareSize~14,000,000Engagements Northern Expedition Chinese Civil War Central Plains War Sino-Soviet conflict (1929) Sino-Mongolian border conflict Second Sino-Jap...
