Coreboot
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Jalan Bangna-Bangpakong Bang Na Expressway adalah jembatan jalan tol di Thailand. Jembatan ini sempat dinobatkan sebagai jembatan terpanjang di dunia antara tahun 2000 sampai sebelum Weihe Grand Bridge (79 km) selesai dibangun tahun 2008 di RRC. Bang Na Expressway memiliki total panjang 54 km. Didesain oleh Jean Muller International, kelompok teknisi jembatan dari Prancis.Jembatan ini diselesaikan pada bulan Maret tahun 2000 dan membutuhkan 1,8 juta meter kubik beton. Jembatan ini mampu menga...

Об экономическом термине см. Первородный грех (экономика). ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Ран�...

Kadipaten SchleswigHerzogtum Schleswig / Hertugdømmet Slesvig1058–1866 Lambang StatusKefiefan DenmarkPemerintahanKadipatenAdipati • 1058-1095 Olaf I dari Denmark• 1863-1866 Christian IX dari Denmark Sejarah • Didirikan 1058• Dibubarkan 1866 Digantikan oleh krjKerajaan Prussia Sunting kotak info • Lihat • BicaraBantuan penggunaan templat ini Schleswig atau Jutlandia Selatan (bahasa Denmark: Sønderjylland atau Slesvig; Jerman: Schleswi...

Medium used for recording motion pictures This article is about motion-picture film. For still-photography film, see Photographic film. Film roll redirects here. For the photographic film roll, see roll film. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Film stock – news · newspapers · books · scholar · ...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Islas San Juan San Juan Islands Las islas San Juan desde el monte Constitution (isla Orcas) mirando hacia Seattle, con el monte Rainier en el fondo, apenas visible en la nieblaUbicación geográficaArchipiélago Archipiélago de San JuanMar Océano PacíficoEstrecho Estrecho de Georgia- Estrecho de Juan de FucaContinente América del NorteCoordenadas 48°31′55″N 123°01′45″O / 48.532066, -123.029251Ubicación administrativaPaís Estados UnidosDivisión Wash...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...

Mexican politician Querido Moheno Tabares on April 21, 1914 Querido Moheno Tabares (3 December 1873 – 1933) was the Secretary of Foreign Affairs in Mexico from 1913 to 1914.[1] Querido Moheno Tabares and family in the 1910s References ^ Protest Against Depleting the Garrison of Mexico City. New York Times. October 13, 1913. Retrieved 2010-03-21. Querido Moheno, the Minister of Foreign Affairs, called the members of the Diplomatic Corps together Saturday morning and informed them...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع حمود محمد (توضيح). حمود محمد عبد الله شرف الدين معلومات شخصية الميلاد 1938كوكبان، محافظة المحويت. الوفاة 1996القاهرة، محافظة القاهرة. الجنسية اليمن الحياة العملية النوع الشعر الغنائي. المهنة كاتب، شاعر. بوابة الأدب تعديل مصدري - تعديل حمود محمد ع...

Scottish economist and philosopher (1723–1790) For other people named Adam Smith, see Adam Smith (disambiguation). Adam SmithFRS FRSE FRSA1787 portraitBornc. 16 June [O.S. c. 5 June] 1723[1]Kirkcaldy, Fife, ScotlandDied17 July 1790(1790-07-17) (aged 67)Edinburgh, ScotlandAlma mater University of Glasgow Balliol College, Oxford Notable work The Theory of Moral Sentiments (1759) The Wealth of Nations (1776) EraEarly modern periodRegionWestern phil...

Provincial government ministry protecting parks in Ontario Ontario ParksAgency overviewFormed1893 (1893)JurisdictionGovernment of OntarioHeadquarters300 Water Street, Peterborough, OntarioMinister responsibleAndrea Khanjin, Minister of the EnvironmentWebsitewww.ontarioparks.com Ontario Parks is a branch of the Ministry of the Environment, Conservation and Parks in Ontario, Canada, that protects significant natural and cultural resources in a system of parks and protected areas that is su...

Žan CelarNazionalità Slovenia Altezza187 cm Peso80 kg Calcio RuoloAttaccante Squadra Lugano CarrieraGiovanili 2012-2014 Triglav2014-2017 Maribor2017-2019 Roma Squadre di club1 2016-2017 Maribor1 (0)2018-2019 Roma1 (0)2019-2020→ Cittadella10 (1)2020-2021→ Cremonese38 (4)2021- Lugano95 (40) Nazionale 2015-2016 Slovenia U-176 (2)2016-2017 Slovenia U-186 (3)2017 Slovenia U-193 (3)2019-2021 Slovenia U-2110 (1)2021- Slovenia11 (0) 1 I due nu...

Opera house in Ostrava, Czech Republic Antonín Dvořák TheatreDivadlo Antonína DvořákaAntonín Dvořák Theatre, Ostrava.AddressSmetanovo náměstí 3104OstravaCzech RepublicCoordinates49°49′57″N 18°17′28.32″E / 49.83250°N 18.2912000°E / 49.83250; 18.2912000Opened1918WebsiteOfficial website The Antonín Dvořák Theatre (Czech: Divadlo Antonína Dvořáka) is an opera house in Ostrava, Czech Republic, which opened in 1907. Since 1919 it has been one of...

الدوري التونسي لكرة اليد للرجال الموسم 1970-1971 البلد تونس المنظم الجامعة التونسية لكرة اليد النسخة 16 عدد الفرق 12 الفائز الترجي الرياضي التونسي النادي الإفريقي (الثاني) الدوري التونسي لكرة اليد 1969–70 الدوري التونسي لكرة اليد 1971–72 تعديل مصدري - تعديل الدو...

American politician from Georgia Gabe OkoyeMember of the Georgia House of Representativesfrom the 102nd districtIncumbentAssumed office January 9, 2023Preceded byConstituency established Personal detailsCitizenshipUnited States Nigeria Gabe Okoye is Nigerian–American civil engineer, former chair, and a current commissioner of planning in Gwinnett County.[1][2] On November 8, 2022, he became a legislator elect at the 2022 US midterm elections repres...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с фамилией Сандерс. Берни Сандерсангл. Bernie Sanders Сенатор от штата Вермонт с 3 января 2007 Предшественник Джеймс Джеффордс Член Палаты представителей от штата Вермонт 3 января 1991 — 3 января 2007 Предшественник Питер П. Смит[англ.] Пр�...

American baseball player (born 1988) Baseball player Zac RosscupRosscup with the Los Angeles Dodgers in 2018Toros de Tijuana – No. 58Relief pitcherBorn: (1988-06-09) June 9, 1988 (age 36)Clackamas, Oregon, U.S.Bats: RightThrows: LeftMLB debutSeptember 3, 2013, for the Chicago CubsMLB statistics (through 2021 season)Win–loss record5–2Earned run average5.09Strikeouts117 Teams Chicago Cubs (2013–2015, 2017) Colorado Rockies (2017) Los Angeles Dodgers (2018) Seattle Ma...

2023 science fiction novel by Pierce Brown Light Bringer First edition coverAuthorPierce BrownLanguageEnglishGenreScience fictionPublisherDel Rey Books (US)Publication dateJuly 25, 2023Publication placeUnited StatesMedia type Print (hardcover) E-book Audiobook ISBN978-0-425-28597-8Preceded byDark Age Followed byRed God Light Bringer is a 2023 science fiction novel by American author Pierce Brown, the third book of a tetralogy which continues the story of his Red Risi...
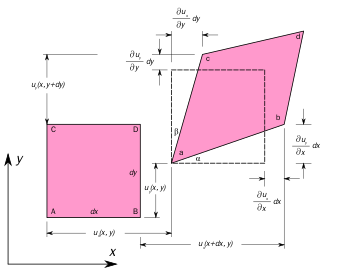
Symmetric tensor quantity of the strain caused by stress in matter StrainOther namesStrain tensorSI unit1Other units%In SI base unitsm/mBehaviour undercoord transformationtensorDimension 1 {\displaystyle 1} Part of a series onContinuum mechanics J = − D d φ d x {\displaystyle J=-D{\frac {d\varphi }{dx}}} Fick's laws of diffusion Laws Conservations Mass Momentum Energy Inequalities Clausius–Duhem (entropy) Solid mechanics Deformation Elasticity linear Plasticity Hooke...

This article is about the mausoleum in Santo Domingo. For the monument in Rome, see Altare della Patria. For the monument in Mexico City, see Altar a la Patria. Historic site in Santo Domingo, Dominican RepublicAltar of the HomelandNative name Spanish: Altar de la PatriaView of the Altar from the Independence ParkLocationSanto Domingo, Dominican RepublicCoordinates18°28′16″N 69°53′33″W / 18.471237°N 69.892416°W / 18.471237; -69.892416Built1976ArchitectCrist...



