Confirm or Deny
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Emanuel Reicher Emanuel Reicher (18 Juni 1849 – 15 Mei 1924) adalah seorang pemeran asal Jerman. Ia adalah ayah dari Ernst Reicher, Frank Reicher dan Hedwiga Reicher.[1] Filmografi pilihan I.N.R.I. (1923) Referensi ^ Ifigenio en Taŭrido by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe di Proyek Gutenberg Pengawasan otoritas Umum Integrated Authority File (Jerman) ISNI 1 VIAF 1 WorldCat Perpustakaan nasional Prancis (data) Lembaga penelitian seni KulturNav (Norway) Lain-lain Social Netwo...

Charles Leiper Grigg (1868-1948) ialah penemu minuman soda Bib-Label Lithiated Lemon-Lime, yang sekarang dikenal dengan nama 7 Up. Ia menemukan minuman tersebut pada bulan Oktober 1929. Grigg menjadi terkenal dengan bisnis minuman berkarbonasi setelah pindah ke St. Louis, Missouri. Sebelum menemukan 7 Up, Grigg telah menciptakan minuman ringan rasa oranye yang bernama Whistle untuk Vess Soda Company, yang masih dibuat dan dijual di St. Louis. Terdapat cerita populer tentang Charles Leiper Gri...

Ini adalah nama Korea; marganya adalah Jang. Jang Young-namLahir25 November 1973 (umur 50)Seoul, Korea SelatanPendidikanInstitut Kesenian Seoul - TeaterPekerjaanAktrisTahun aktif1995-sekarangAgenBH Entertainment (2016-sekarang)Suami/istritidak diketahui namanya (m. 2011)[1]Anak1 Nama KoreaHangul장영남 Alih AksaraJang Yeong-namMcCune–ReischauerChang Yŏngnam Jang Young-nam (lahir 25 November 1973) adalah seorang aktris asal Korea Se...
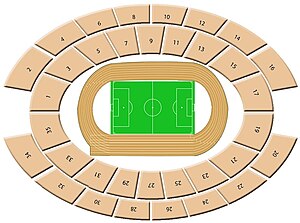
Part of the Athens Olympic Sports Complex Olympic Stadium of AthensΟλυμπιακό Στάδιο της ΑθήναςUEFA Full nameCentral Olympic Stadium of O.A.C.A. Spyros LouisFormer namesSpyros Louis StadiumLocationMarousi, Athens, GreecePublic transit EiriniOwnerHellenic Olympic CommitteeOperatorOAKA S.A.Executive suites17Capacity69,618 (regulated capacity)[1]75,000 (total capacity)Field size105 x 68 m[1]SurfaceGrass, trackConstructionBroke ground1979[1]Opened8 S...

Voce principale: Brindisi Football Club. Brindisi SportStagione 1975-1976 Sport calcio Squadra Brindisi Allenatore Giulio Bonafin (1ª-13ª) Ettore Puricelli (14ª-21ª) Giulio Bonafin (22ª-38ª) Presidente Cosimo Fanuzzi Serie B19º (retrocesso in Serie C) Coppa ItaliaPrimo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Guerrini, Trentini (35)Totale: Guerrini (37) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Ulivieri (10)Totale: Ulivieri (10) 1974-1975 1976-1977 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce...

ロバート・デ・ニーロRobert De Niro 2011年のデ・ニーロ生年月日 (1943-08-17) 1943年8月17日(80歳)出生地 アメリカ合衆国・ニューヨーク州ニューヨーク市身長 177 cm職業 俳優、映画監督、映画プロデューサージャンル 映画、テレビドラマ活動期間 1963年 -配偶者 ダイアン・アボット(1976年 - 1988年)グレイス・ハイタワー(1997年 - )主な作品 『ミーン・ストリート』(1973年)...

Luxury hotel in Chennai, India The Park ChennaiHotel chainThe Park HotelsGeneral informationLocationChennai, IndiaAddress601, Anna Salai, Near U.S. ConsulateChennai, Tamil Nadu 600 006Coordinates13°03′11″N 80°15′00″E / 13.052956°N 80.249923°E / 13.052956; 80.249923Opening15 May 2002OwnerThe Park HotelsManagementThe Park HotelsTechnical detailsFloor count12Design and constructionArchitect(s)Hirsch Bedner Associates, Los AngelesOther informationNumber of room...

Type of throwing club This article is about the weapon. For the villages in Romania, see Vălari (disambiguation). For the 1970s compact car, see Plymouth Volaré. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Valari – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove...

SpongeBob SquarePantsMusim ke-1Sampul DVD musim ke-1Dibintangi Tom Kenny Bill Fagerbakke Rodger Bumpass Clancy Brown Mr. Lawrence Jill Talley Carolyn Lawrence Mary Jo Catlett Lori Alan Negara asalAmerika SerikatJml. episode20 (dibagi 41 segmen)RilisJaringan asliNickelodeonTanggal disiarkan1 Mei 1999 (1999-05-01) –3 Maret 2001 (2001-3-3)Kronologi MusimBerikutnya →Musim ke-2 Daftar episode Musim pertama serial animasi SpongeBob SquarePants buatan Stephen Hillenburg ditay...

American baseball player (born 1944) Baseball player Dick CalmusPitcherBorn: (1944-01-07) January 7, 1944 (age 80)Los Angeles, CaliforniaBatted: RightThrew: RightMLB debutApril 22, 1963, for the Los Angeles DodgersLast MLB appearanceSeptember 2, 1967, for the Chicago CubsMLB statisticsRecord3-1ERA3.17Strikeouts26 Teams Los Angeles Dodgers (1963) Chicago Cubs (1967) Richard Lee Calmus (born January 7, 1944) is a former pitcher in Major League Baseball. He att...

Postage stamps issued by the United States government in 1932 The 2c Washington Bicentennial stamp, 1932 issueThis is one of a set of 12 stamps commemorating the 200th anniversary of George Washington, paid the common letter rate and was the most frequently used. The Washington Bicentennial stamps of 1932 are postage stamps issued by the United States government in 1932 to commemorate the 200th anniversary of U.S. President George Washington's birth. Twelve stamps were issued as a collection,...

History and regulations of American citizenship This article is about laws for acquiring U.S. nationality. For rights and privileges of citizenship, see Citizenship of the United States. United States citizenship and immigration Immigration Immigration to the United States Emigration from the United States Immigration policy of the United States Effects of immigration to the United States Permanent Residency (Green Card) Refugees and asylum Diversity Immigrant Visa Illegal immigrants Deportat...

Closest neighboring galaxy supercluster Hydra–Centaurus SuperclusterThree-dimensional map of the Hydra SuperclusterObservation data (Epoch J2000)Right ascension13h 14m 00.0s[1]Declination−33° 18′ 00″[1]Parent structureLaniakea SuperclusterDistance~39 Mpc (127 Mly)[2]Other designationsCen-Hya Supercluster, Hydra-Cen Supercluster, Hydra-Centaurus Supercluster, SCI 128[1]See also: Galaxy group, Galaxy cluster, List of galax...

Dayton C. MillerCirca 1921Born(1866-03-13)March 13, 1866Strongsville, Ohio, USADiedFebruary 22, 1941(1941-02-22) (aged 74)Cleveland, Ohio, U.S.Resting placeLake View Cemetery, Cleveland, OhioAlma materPrinceton UniversityKnown forX-raysAether theoryAbsolute spaceAcousticsAwardsEdward Longstreth Medal (1917)Newcomb Cleveland Prize (1925)Elliott Cresson Medal (1927)Scientific careerFieldsPhysicistInstitutionsCase School of Applied ScienceDoctoral advisorCharles A. Young Dayton Cl...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع انفجار عظيم (توضيح). وفقًا لنموذج الانفجار العظيم، فإن الفضاء الكوني يتمدد من حالة حارة شديدة الكثافة، وما زال يتمدد إلى اليوم. يوضح هذا المخطط تمدد مسطح لجزء من الكون، حيث تتباعد المجرات مع التمدد. الانفجار العظيم في علم الكون الفيزيائي هو النظرية �...

1959 American film by John Ford For the 2018 film, see Horse Soldiers (film). For the 2009 book Horse Soldiers, about soldiers in Afghanistan, see Doug Stanton. The Horse Soldiers1959 movie posterDirected byJohn FordScreenplay byJohn Lee MahinMartin RackinBased onThe Horse Soldiers1956 novelby Harold SinclairProduced byJohn Lee Mahin (uncredited)Martin Rackin (uncredited)Allen K. Wood (production manager)[1]StarringJohn WayneWilliam HoldenConstance TowersCinematographyWilliam H. Cloth...

For related races, see 1996 United States gubernatorial elections. 1996 Delaware gubernatorial election ← 1992 November 5, 1996 2000 → Nominee Tom Carper Janet Rzewnicki Party Democratic Republican Running mate Ruth Ann Minner Sherman N. Miller Popular vote 188,300 82,564 Percentage 69.5% 30.5% County results House district resultsCarper: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80%...

2020 年後美國總統選舉各投票實體(州、聯邦區和某些國會選區)的庫克 PVI 地圖。 其顏色越深,其黨派傾向越強。 库克党派投票指数(英語:Cook Partisan Voting Index,缩写为CPVI或PVI)是衡量美国国会选区或州在前两次总统选举中投票倾向的指数,也就是与全国平均相比,该选区或州倾向于民主党或共和党的程度。[1][2][a] 该指数会在每个选举周期后更新。库�...

Mark TettoLahir1 Maret 1980 (umur 44)New JerseyPendidikanUniversitas Princeton (BA)Wharton School (MBA)PekerjaanRekan pada TCK investmentsSitus webMark Tetto di Instagram Mark Tetto (lahir 1 Maret 1980) adalah orang Amerika Serikat yang tinggal dan tampil di Korea Selatan sebagai tokoh televisi dan pebisnis.[1] Ia menjadi anggota dalam acara varietas Non Summit dan Where Is My Friend's Home.[2][3][4] Referensi ^ 오예린 (December 15, 2014). ‘비정상...

Dalam inti bintang seperti Matahari, tekanan gravitasi diseimbangkan oleh tekanan panas dari reaksi fusi, sehingga menunda kompresi gravitasi untuk sementara waktu. Pemampatan gravitasi atau kompresi gravitasi adalah suatu fenomena ketika gravitasi suatu objek memampatkan (atau mengompresi) objek tersebut, sehingga mengecilkan ukuran dan meningkatkan kepadatan objek tersebut. Di pusat planet atau bintang, kompresi gravitasi menghasilkan panas melalui mekanisme Kelvin–Helmholtz. Mekanisme in...
