Channel access method
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Lambang El Saucejo. El Saucejo merupakan sebuah kota yang terletak di wilayah Provinsi Sevilla, Andalusia, Spanyol Lihat juga Daftar munisipalitas di Seville Daftar munisipalitas di Spanyol lbsKota di Provinsi Sevilla Aguadulce Alanís Albaida del Aljarafe Alcalá de Guadaíra Alcalá del Río Alcolea del Río Algámitas Almadén de la Plata Almensilla Arahal Aznalcázar Aznalcóllar Badolatosa Benacazón Bollullos de la Mitación Bormujos Brenes Burguillos Camas Cantillana Carmona Carrión d...

Papa Pio I10º papa della Chiesa cattolicaElezione140 circa Fine pontificato154 Predecessorepapa Igino Successorepapa Aniceto NascitaAquileia, ? MorteRoma, 154 SepolturaNecropoli vaticana Manuale San Pio I Papa e martire NascitaAquileia, ? MorteRoma, 154 Venerato daChiesa cattolica Beatificazione15 dicembre 988 da papa Giovanni XV Canonizzazione1º giugno 1723 da papa Innocenzo XIII Santuario principaleChiesa di San Pio I Ricorrenza11 luglio Patrono diRoccaspinalvet...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Earle. Sylvia EarleBiographieNaissance 30 août 1935 (88 ans)Gibbstown (en)Nationalité américaineFormation Université Duke (doctorat) (jusqu'en 1967)Université d'État de FlorideActivités Biologiste marine, botaniste, exploratrice, océanographe, biologisteAutres informationsA travaillé pour Université de Californie à BerkeleyMembre de Society of Woman GeographersDistinctions Prix Princesse des Asturies de la Concorde (2018)Liste détailléeOrdr...

Davide Garbolino alla conduzione del programma Ciao Ciao (1996) Davide Garbolino (Cirié, 24 settembre 1968) è un doppiatore, direttore del doppiaggio e conduttore televisivo italiano[1]. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Doppiaggio 2.1 Cinema 2.2 Film d'animazione 2.3 Speciali televisivi animati 2.4 Serie televisive 2.5 Serie animate 2.6 Videogiochi 3 Conduttore televisivo 4 Filmografia 4.1 Televisione 5 Note 6 Altri progetti 7 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Nato in una famiglia di commercianti,...

Town in Newfoundland and Labrador, CanadaRed BayTownRed Bay seen from aboveRed BayLocation of Red Bay in Newfoundland and LabradorShow map of Newfoundland and LabradorRed BayRed Bay (Newfoundland)Show map of NewfoundlandCoordinates: 51°43′55″N 56°25′32″W / 51.73194°N 56.42556°W / 51.73194; -56.42556Country CanadaProvince Newfoundland and LabradorRegionNunatuKavut (unofficial)Government[1] • TypeMunicipal incorporationArea ...

Type of chemical substance For other uses, see Base (disambiguation).See also: Alkali Soaps are weak bases formed by the reaction of fatty acids with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. Acids and bases Acceptor number Acid Acid–base reaction Acid–base homeostasis Acid strength Acidity function Amphoterism Base Buffer solutions Dissociation constant Donor number Equilibrium chemistry Extraction Hammett acidity function pH Proton affinity Self-ionization of water Titration Lewis acid c...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori burkinabé è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Paul Koulibaly Nazionalità Burkina Faso Altezza 180 cm Calcio Ruolo Difensore Termine carriera 2018 CarrieraSquadre di club1 2005-2007 Étoile Ouagadougou? (?)2007 Al-Ittihad Tripoli2 (0)2008→ Al-Nasr Bengasi7 (1)2008-2009 União Leiria0 (0)2009 Al-Ittihad Tripoli? (?)2010-2011 Al-Shawehly? (?)2011-2012 Olympic ...

此條目可能包含不适用或被曲解的引用资料,部分内容的准确性无法被证實。 (2023年1月5日)请协助校核其中的错误以改善这篇条目。详情请参见条目的讨论页。 各国相关 主題列表 索引 国内生产总值 石油储量 国防预算 武装部队(军事) 官方语言 人口統計 人口密度 生育率 出生率 死亡率 自杀率 谋杀率 失业率 储蓄率 识字率 出口额 进口额 煤产量 发电量 监禁率 死刑 国债 ...

NGC 3803 الكوكبة الأسد[1] رمز الفهرس NGC 3803 (الفهرس العام الجديد)2MASX J11401725+1748044 (Two Micron All-Sky Survey, Extended source catalogue)PGC 36204 (فهرس المجرات الرئيسية)HIPASS J1140+17 (HIPASS)CAIRNS J114017.31+174805.0 (Cluster and Infall Region Nearby Survey)LEDA 36204 (ليون-ميودون قاعدة بيانات خارج المجرة) المكتشف ويليام بارسونز تاريخ �...

العلاقات النمساوية الناوروية النمسا ناورو النمسا ناورو تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات النمساوية الناوروية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين النمسا وناورو.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة ال�...

Chemical compound Magnesium pidolateClinical dataAHFS/Drugs.comConsumer Drug InformationATC codeA12CC08 (WHO) Identifiers IUPAC name Magnesium 5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxylate CAS Number135701-98-3PubChem CID9838620ChemSpider8014340 YUNIIV5PC588N7GCompTox Dashboard (EPA)DTXSID30905130 ECHA InfoCard100.080.955 Chemical and physical dataFormulaC10H12MgN2O6Molar mass280.519 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Interactive image SMILES [Mg+2].[O-]C(=O)C1NC(=O)CC1.[O-]C(=O)C1NC(=O)CC1 InChI...

Angsoka Sebatang angsoka (Pavetta indica) di Kebun Tropis Nong Nooch, Thailand Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Tracheophyta (tanpa takson): Angiospermae (tanpa takson): Eudikotil (tanpa takson): Asterid Ordo: Gentianales Famili: Rubiaceae Genus: Pavetta Spesies: P. indica Nama binomial Pavetta indicaLinnaeus Sinonim Referensi:[1][2] Ixora indica (L.) Baill. I. nunypapata Roxb. ex Wight & Arn. I. paniculata Lam. I. paveta Roxb. (nama tidak sah) I....

1942 film by Robert Emmett Tansey Texas to BataanDirected byRobert Emmett TanseyWritten byArthur HoerlProduced byDick Ross (associate producer)George W. Weeks (producer)StarringSee belowCinematographyRobert E. ClineEdited byS. Roy LubyMusic byFrank SanucciDistributed byMonogram PicturesRelease date 16 October 1942 (1942-10-16) Running time56 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglish Texas to Bataan is a 1942 American Western film directed by Robert Emmett Tansey. The film is t...

Questa voce sull'argomento politici italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Immacolata Zurzolo Deputata della Repubblica ItalianaIn caricaInizio mandato13 ottobre 2022 LegislaturaXIX GruppoparlamentareFratelli d'Italia CircoscrizionePiemonte 1 CollegioPiemonte 1 - 02 Sito istituzionale Dati generaliPartito politicoFratelli d'Italia Titolo di studioDiploma di ragione...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع هيلسبورو (توضيح). هيلسبورو الإحداثيات 45°55′20″N 64°38′43″W / 45.922222222222°N 64.645277777778°W / 45.922222222222; -64.645277777778 تقسيم إداري البلد كندا[1] تاريخ الإلغاء 1 يناير 2023 معلومات أخرى رمز جيونيمز 5975301 الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي تع...

Award 1995 Nobel Prize in LiteratureSeamus Heaneyfor works of lyrical beauty and ethical depth, which exalt everyday miracles and the living past.Date 5 October 1995 (1995-10-05) (announcement) 10 December 1995 (ceremony) LocationStockholm, SwedenPresented bySwedish AcademyFirst awarded1901WebsiteOfficial website ← 1994 · Nobel Prize in Literature · 1996 → The 1995 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Irish poet Seamus Heaney (1939–20...
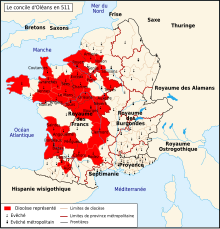
Saint Aubin assistant au IIIe concile d'Orléans en 538 La page concile d'Orléans répertorie les conciles et synodes diocésains qui se tiennent dans la ville française d'Orléans au Moyen Âge et à l'Époque moderne. Il semble que six conciles d'envergure nationale se soient tenus à Orléans entre 511 et 634 ou 645. Haut Moyen Âge Participation des évêques au concile d'Orléans en 511. Époque mérovingienne (481-751) Article détaillé : Concile mérovingien. Plusieurs conciles...

2002 single by Anastacia Why'd You Lie to MeSingle by Anastaciafrom the album Freak of Nature ReleasedSeptember 9, 2002 (2002-09-09)Studio The Dream Factory (New York City) Cove City Sound (Glen Cove, New York) Encore (Burbank, California) Genre Dance-pop R&B Length3:43Label Epic Daylight Songwriter(s) Anastacia Damon Sharpe Greg Lawson Trey Parker Damon Butler Canela Cox Producer(s)Ric WakeAnastacia singles chronology Boom (2002) Why'd You Lie to Me (2002) You'll Never Be ...