Change of Habit
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

ANGI Homeservices, Inc.Berkas:Angi-logo.pngURLhttp://www.angieslist.com/ dan http://www.angieslist.com/ Tipeperusahaan bisnis dan Perusahaan publik PemilikIACService entry (en)1995 Lokasi kantor pusatIndianapolis dan Denver NegaraAmerika Serikat Total omset US$1.132 miliar (2018)[1] ANGI Homeservices Inc. adalah perusahaan layanan internet yang dibentuk pada tahun 2017 melalui penggabungan Angie's List dan HomeAdvisor.[2] Perusahaan ini pada awalnya berakar dari situs web...

العلاقات السويسرية القطرية سويسرا قطر سويسرا قطر تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات السويسرية القطرية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين سويسرا وقطر.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة سويسرا قطر ال�...

فوندابارينوكس تداخل دوائي دالتيبارين الصوديوم، وألتيبلاس، وتينيكتيبلاز، وستربتوكاينيز، وريفاروكسابان، وأبيكسابان، وأسبرين، ونابوميتون، ونابروكسين، وسيليكوكسيب، وديكلوفيناك، وبيروكسيكام، وميلوكسيكام، وفينوبروفين، وفل...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Trois-Novembre. Éphémérides Novembre 1er 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 3 octobre 3 décembre Chronologies thématiques Croisades Ferroviaires Sports Disney Anarchisme Catholicisme Abréviations / Voir aussi (° 1852) = né en 1852 († 1885) = mort en 1885 a.s. = calendrier julien n.s. = calendrier grégorien Calendrier Calendrier perpétuel Liste de calendriers Naissances...

Swiss waterfall For the place in Australia, see Rhine Falls, New South Wales. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Rhine Falls – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Rhine FallsGerman: RheinfallRhine Falls with Rheinfall Bridge and Lau...

Ancient city in Sicily Herbessos was an ancient city located at Montagna di Marzo, Sicily, a few kilometres north-west of Piazza Armerina.[1] It occupied an area of approximately 15 hectares and has been partially excavated. The first limited excavations were by Paolo Orsi in 1930 who described the riches that were illegally stolen over the years, feeding large collections. Subsequently in the 1950s Dinu Adamesteanu recognised, through aerial photography, part of the ancient access ro...

Iceberg that was struck by Titanic on April 14, 1912 'Iceberg' at the Titanic Museum in Branson, Missouri, whose building is modeled on the famous ship The passenger steamer Titanic collided with an iceberg and sank on the night of 14–15 April 1912 in the North Atlantic. Of the approximate 2,200 people on board, over 1,500 did not survive. After the disaster, there was interest in the iceberg itself to explain the circumstances of the collision and the resulting damage to the supposedly uns...

American politician (born 1963) Francis CooleyMember of the Connecticut House of Representativesfrom the 22nd districtIncumbentAssumed office January 4, 2023Preceded byWilliam Petit Personal detailsBornFrancis Rexford Cooley (1963-10-16) October 16, 1963 (age 60)Hartford, Connecticut, U.S.Political partyRepublicanResidence(s)Plainville, Connecticut, U.S.EducationUniversity of Colorado, University of Maine, University of Hartford Francis Rexford Cooley[1] (born Oct...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Insiden berbahaya (bahasa Inggris: critical incidents) adalah situasi yang dialami seseorang yang biasanya melibatkan diri dalam kejadian menegangkan. Seperti profesi pemadam kebakaran, penegak hukum, paramedis, dll. Profesi tersebut memiliki risik...

SMK Negeri 37 JakartaInformasiDidirikan1970AkreditasiANomor Pokok Sekolah Nasional20102601Kepala SekolahSiti Habibah, S.PdJurusan atau peminatanAkomodasi hotelJasa bogaTata busanaPatiseriRentang kelasX-XIIKurikulumKurikulum 2013 RevisiJumlah siswa838 siswaStatusSekolah Menengah Kejuruan NegeriAlamatLokasiJalan Pertanian III No.33, Pasar Minggu, Jakarta Selatan, DKI Jakarta, IndonesiaTel./Faks.(021) 7805787Situs [email protected] SMK Negeri...

American illustrator (1886–1944) Nell BrinkleyBorn(1886-09-05)September 5, 1886Denver, ColoradoDiedOctober 21, 1944(1944-10-21) (aged 58)Occupation(s)Illustrator and Comic artistSpouse Bruce McRae Jr. (m. 1920; div. 1937)ChildrenBruce McRae IIIParent(s)Robert Serrett Brinkley and May French BrinkleyAwardsWomen Cartoonists Hall of FameEisner Award Hall of Fame Nell Brinkley (September 5, 1886 – October 21, 1944) was an American i...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助�...
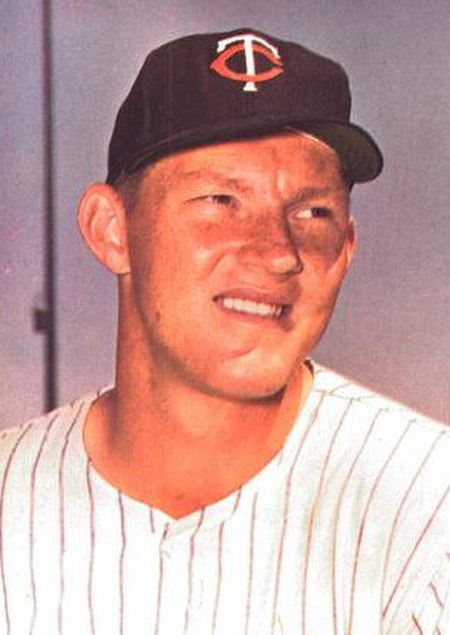

1965 Major League Baseball championship series 1965 World Series Team (Wins) Manager(s) Season Los Angeles Dodgers (4) Walter Alston 97–65, .599, GA: 2 Minnesota Twins (3) Sam Mele 102–60, .630, GA: 7DatesOctober 6–14VenueMetropolitan Stadium (Minnesota)Dodger Stadium (Los Angeles)MVPSandy Koufax (Los Angeles)UmpiresEddie Hurley (AL), Tony Venzon (NL), Red Flaherty (AL), Ed Sudol (NL), Bob Stewart (AL), Ed Vargo (NL)Hall of FamersDodgers: Walt Alston (manager) Don DrysdaleSandy KoufaxTw...

Parigné-le-Pôlin Administration Pays France Région Pays de la Loire Département Sarthe Arrondissement La Flèche Intercommunalité Communauté de communes du Val de Sarthe Maire Mandat Joël Leproux 2020-2026 Code postal 72330 Code commune 72230 Démographie Gentilé Parignéens Populationmunicipale 1 051 hab. (2021 ) Densité 76 hab./km2 Géographie Coordonnées 47° 51′ 02″ nord, 0° 06′ 29″ est Altitude Min. 37 mMax. 113 m...

Untuk nama festival Tahun Baru Hawaii kuno, lihat Makahiki. Matariki, nama Māori untuk Pleiades (foto). Gambar inframerah yang menampakkan rincian antarbintang. Dalam bahasa Māori, Matariki merupakan nama gugus bintang Pleiades sekaligus nama musim waktu terbit pertamanya[1] pada akhir Mei atau awal Juni. Matariki menjadi penanda awal tahun baru. Beberapa orang merayakan Matariki pada waktu yang berbeda; ada yang pada saat gugus bintang ini terbit pada akhir Mei atau awal Juni, ada ...

Yehu BiografiKelahiran9 abad SM Kematian9 abad SM KegiatanPekerjaannabi KeluargaAyahHanani (en) Yehu (UK /ˈdʒiːhjuː/, US /ˈdʒiːhuː/;[1] Ibrani: יהוא, Yêhū Dialah Yahweh)[2] bin Hanani adalah seorang nabi yang disebutkan dalam Perjanjian Lama, yang hidup pada abad ke-9 SM. Catatan Alkitab Menurut Alkitab, Yehu mengutuk Baesa, raja Israel, dan keluarga Baesa (1 Raja–Raja 16:7), menuduhnya membuat orang-orang jatuh ke dalam dosa penyembahan berhala seperti pendahu...
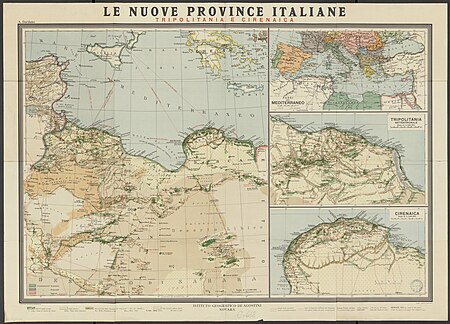
Semi-autonomous state affiliated with the Ottoman Empire (1551–1912) Not to be confused with Tripoli Eyalet. Ottoman Tripolitaniaایالت طرابلس غرب(1551–1864)Eyālet-i Trâblus Gârbولايت طرابلس غرب(1864–1912)Vilâyet-i Trâblus GârbEyalet and Vilayet of Ottoman Empire1551–1912 Flag Lesser coat of arms (1856) The Tripolitania Eyalet in 1795CapitalTripoliHistory • Siege of Tripoli 1551• Karamanli dynasty rises to power 1711• First Ba...

British professor of international relations This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages) This article is an autobiography or has been extensively edited by the subject or by someone connected to the subject. It may need editing to conform to Wikipedia's neutral point of view policy. There may be relevant discussion on the talk page. (July 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This ...

3. Armee3rd ArmyFlag of the Staff of an Armee Oberkommando (1871–1918)Active2 August 1914 – 30 January 1919Country German EmpireTypeArmyEngagementsWorld War I Western Front Battle of the Frontiers Battle of Charleroi First Battle of the Marne First Battle of the Aisne Second Battle of the Aisne Nivelle Offensive Meuse-Argonne Offensive InsigniaAbbreviationA.O.K. 3Military unit The 3rd Army (‹See Tfd›German: 3. Armee / Armeeoberkommando 3 / A.O.K. 3) was an army level command of ...
