Caleb Gardner
|
Read other articles:

Grant Holt Holt bermain untuk Norwich City pada tahun 2010Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Grant HoltTanggal lahir 12 April 1981 (umur 42)Tempat lahir Carlisle, InggrisTinggi 1,83 m (6 ft 0 in)Posisi bermain PenyerangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Wigan AthleticNomor 42Karier junior Carlisle UnitedKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1999 Workington ? (?)1999–2001 Halifax Town 6 (0)2001 → Sorrento (pinjaman) ? (?)2001 → Barrow (pinjaman) ? (?)2001 Sengkang Marine ? (?)2001...

Pakistani game show Jeeto PakistanAlso known asJeeto Pakistan Leagueجیتو پاکستانGenreFamily game show Reality ShowDirected byAsif Khan Khurram FaridPresented byFahad MustafaCountry of originPakistanOriginal languagesUrduEnglishNo. of seasons9No. of episodes Season 1: 760+ Season 2: 100+ Season 3: 97 ProductionProduction locationsKarachi, SindhCamera setupMulti-cameraRunning time130–152 minutesOriginal releaseNetworkARY DigitalRelease18 May 2014 (2014-05-18) –present&#...

Thor HushovdThor Hushovd lors du Tour du Haut-Var 2013InformationsSurnom Le Dieu du TonnerreLe bœuf de GrimstadLe VikingNaissance 18 janvier 1978 (46 ans)GrimstadNationalité norvégienneSpécialité sprinteur, classiques flandriennes, rouleur[1]Distinctions Liste détailléeFolkets idrettspris (2005)Prix de la culture du comté d'Aust-Agder (d) (2007)Sportif norvégien de l'année (2010)Médaille d'or Aftenposten (2010)Équipes professionnelles 09.1999-12.1999Crédit agricole (stagiair...

منتخب الغابون لكرة القدم معلومات عامة بلد الرياضة الغابون الفئة كرة القدم للرجال رمز الفيفا GAB الاتحاد اتحاد الغابون لكرة القدم كونفدرالية كاف (أفريقيا) الملعب الرئيسي ملعب عمر بونغو الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي الطاقم واللاعبون المدرب خوسيه أنتونيو كاماتشو ...

Medical campus in Perth, Western Australia This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Queen Elizabeth II Medical Centre – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2017) The Queen Elizabeth II Medical Centre (QEIIMC), commonly known as just QEII, is a medical campus in Perth, Western A...

Le province del Perù della Costa (giallo), Sierra (ocra) e Selva(verde) Le province del Perù (in spagnolo: provincias) costituiscono la suddivisione territoriale di secondo livello del Paese, dopo le regioni, e sono pari a 195; ciascuna di esse si suddivide a sua volta in distretti. La regione di Callao è formalmente definita come provincia costituzionale; la regione con il maggior numero di province è quella di Ancash, che ne conta 20. Le province dell'Amazzonia sono più estese e scarsa...
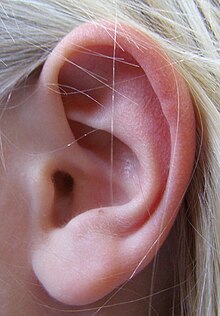
У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Ухо (значения). Анатомия уха. Наружное ухо: 1 — височная кость 2 — слуховой канал 3 — ушная раковина среднее ухо: 4 — барабанная перепонка 6 — молоточек 7 — наковальня 8 — стремечко внутре...

Music and musical traditions of Kazakhstan This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Music of Kazakhstan – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Music of Central Asia Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan Mongolia Tajikistan Turkmenistan Uzbekistan vte M...

Church in Canillo, Andorra Església de Sant Joan de Caselles Església de Sant Joan de Caselles is a church located in Canillo, Andorra. It is a heritage property registered in the Cultural Heritage of Andorra. It was built in the 11–12th century.[1] Art Inside the building different artistic pieces are preserved, the main one being a large stucco image of Christ in Majesty, as well as a mural with frescoes depicting scenes from Calvary with Saint Longinus and Stephaton, accompanie...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

日本におけるバーガーキングの事業については「バーガーキング (日本)」をご覧ください。 バーガーキングBurger King 2020年12月21日以後のロゴ 本部(マイアミ)種類 子会社業種 飲食店事業分野 ファストフード前身 インスタバーガーキング設立 インスタバーガーキング:1953年 (71年前) (1953)ジャクソンビル (フロリダ州)バーガーキング:1954年 (70年前) (1954) フ�...

هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (مارس 2023) بيريزني (بالأوكرانية: Березне) بيريزني بيريزني تقسيم إداري البلد أوكرا�...

Coast Salish people in western Washington (state) Ethnic group DuwamishdxʷdəwʔabšDuwamish territory shown highlighted in green. Orange blocks are current Indian reservationsTotal populationAbout 351 (1854),[1] unknown but more than 600 (2023)[2]Regions with significant populationsWestern Washington, United StatesLanguagesLushootseed (Southern), EnglishReligionIndigenous folk religion, Christianity, including syncretic formsRelated ethnic groupsOther Lushootseed-speaking pe...

Jalan Tol Kayu Agung-Palembang-BetungInformasi ruteBagian dari Jalan Tol Trans-SumateraDikelola oleh PT Waskita Sriwijaya TolPanjang:111.6 km (69,3 mi)Berdiri:1 April 2020 – sekarangPersimpangan besarUjung Selatan: Jalan Tol Terbanggi Besar-Pematang Panggang-Kayu Agung Simpang Susun Kayu AgungSimpang Susun JejawiSimpang Susun PalindraSimpang Susun KramasanUjung Utara: Jalan Tol Palembang-Indralaya Jalan Tol Betung-Jambi, Jalan Tol Jambi-Pekanbaru, Jalan Tol Jambi-Solok-P...

Pasto redirects here. For other uses, see Pasto (disambiguation). You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Spanish. (October 2012) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the Engl...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un canton français et la Manche. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Canton de Bréhal Situation du canton de Bréhal dans le département de la Manche. Administration Pays France Région Normandie Département Manche Arrondissement(s) Avranches (13)Coutances (14) Bureau centralisateur Bréhal Conseillersdépartementaux Mandat Valérie Coupel-BeaufilsAlain Nav...

Casciana Termefrazione Casciana Terme – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Toscana Provincia Pisa ComuneCasciana Terme Lari TerritorioCoordinate43°31′41″N 10°37′09″E43°31′41″N, 10°37′09″E (Casciana Terme) Altitudine130 m s.l.m. Superficie36,54 km² Abitanti2 499[2] (2001) Densità68,39 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale56034 Prefisso0587 Fuso orarioUTC+1 Codice ISTAT050007 Cod. catastaleA559 Nome abitanticascianese, ...

Analyst of business risk and uncertainty ActuaryDamage from Hurricane Katrina in 2005. Actuaries need to estimate long-term levels of such damage in order to accurately price property insurance, set appropriate reserves, and design appropriate reinsurance and capital management strategies.OccupationNamesActuaryOccupation typeProfessionstatisticianmathematicianActivity sectorsInsurancereinsurancepension planssocial welfare programsDescriptionCompetenciesMathematicsstatisticsfinanceanalytical s...

Former parliamentary constituency in the United Kingdom Brentford and ChiswickFormer borough constituencyfor the House of Commons1950–February 1974SeatsoneReplaced byBrentford and Isleworth (newly created seat) (to form eastern part of)1918–1950SeatsoneType of constituencyCounty constituencyCreated fromBrentfordReplaced byBrentford and Chiswick borough constituency, above Brentford and Chiswick was a constituency[n 1] 1918 – 1974 centred on the Brentford and Chiswick districts o...

Article principal : Maison de l'Empereur. Article connexe : Ordre de bataille de la Grande Armée pendant la campagne de Russie. Napoléon et le général de Lauriston — La paix à tout prix! Ici est détaillé l'ordre de bataille de la Maison de l'empereur Napoléon Ier telle qu'elle était à l'ouverture de la campagne de Russie (1812). La Maison de l'empereur est considérable pour cette campagne. La Maison civile Grand maréchal du palais: Duroc Grand écuyer: Caulaincour...