Bonding in solids
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Gereja Katolik Rusia. Gereja Katolik di RusiaRusia: Католическая церковь в россииcode: ru is deprecated Katedral MoskwaJenisKebijakan nasionalPenggolonganGereja Katolik RomaOrientasiKekristenan Slavia, LatinKitab suciAlkitabTeologiTeologi KatolikBadanpemerintahanECRPausPaus FransiskusKetua ECRClemens PickelNunsius ApostolikSede vacanteWilayahRussiaBahasaLatin, Slavia Gerejawi, RusiaDidirikanAbad ke-11PecahanGereja Ortodoks Rusia Bagian dari...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Bai' Najasy yaitu rekayasa pasar dalam ''demand'' atau permintaan yang terjadi apabila seorang produsen menciptakan permintaan palsu, sehingga seolah-olah ada banyak permintaan terhadap harga suatu produk yang menyebabkan harga jual produk tersebut nai...

Halaman ini memuat artikel tentang huruf M dalam alfabet Latin. Untuk penggunaan lainnya, lihat M (disambiguasi). Lihat entri m atau M di kamus bebas Wiktionary. Alfabet Latindasar ISO AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz lbs M adalah huruf Latin modern ke-13 yang dibaca [[Bantuan:Pengucapan|[ɛm]]]. Sejarah Hieroglif Mesirair →Proto-Semitikmem →Fenisiamem →Yunani Kunomu →Yunani Modernmu →EtruriaM →Latin KunoM →Latin Modern...

Farida JalalFarida JalalLahir14 Maret 1949 (umur 75)New Delhi, IndiaKebangsaanIndiaPekerjaanAktris, komedianTahun aktif1967 - sekarangSuami/istri Tabrez Barmavar (m. 1978; meninggal 2003) PenghargaanAktris Pendukung Terbaik: Paras (1972) Aktris Pendukung Terbaik: Henna (1992) Aktris Terbaik (Kritikus): Mammo (1995) Aktris Pendukung Terbaik: Dilwale Dulhania Le Jayenge (1996) Farida Jalal (lahir 14 Maret 1949) adalah seorang aktris...

Ishinomaki 石巻市KotaDari atas ke bawah, kiri ke kanan : Pulau Kinkasan, Ishinomori Manga Museum, Gereja Ortodoks Santo Yohanes Rasul, Taman Hiyoriyama, dan hidangan Sasa Kamaboko. BenderaEmblemLokasi Ishinomaki di Prefektur MiyagiIshinomakiLokasi di JepangKoordinat: 38°26′03″N 141°18′10″E / 38.43417°N 141.30278°E / 38.43417; 141.30278Koordinat: 38°26′03″N 141°18′10″E / 38.43417°N 141.30278°E / 38.43417; 141.30278...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento società calcistiche non è ancora formattata secondo gli standard. Commento: Voce da adeguare al modello di voce. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Viking F.K.Calcio Di mørkeblå (I blu scuro) Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Blu scuro Dati societari Città Stavanger Nazione Norvegia Confederazione UEFA Federazione NFF Campionato Eli...

Шалфей обыкновенный Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:РастенияКлада:Цветковые растенияКлада:ЭвдикотыКлада:СуперастеридыКлада:АстеридыКлада:ЛамиидыПорядок:ЯсноткоцветныеСемейство:ЯснотковыеРод:ШалфейВид:Шалфей обыкновенный Международное научное наз...
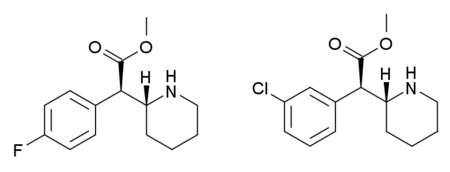
Stimulant drug 4-MethylmethylphenidateLegal statusLegal status CA: Schedule III DE: NpSG (Industrial and scientific use only) UK: Class B Identifiers IUPAC name methyl (2R)-2-(4-methylphenyl)-2-[(2R)-piperidin-2-yl]acetate CAS Number191790-79-1 Y 680996-70-7 (hydrochloride)PubChem CID44296147ChemSpider8281556 YUNII1Y11XUO4EYChemical and physical dataFormulaC15H21NO2Molar mass247.338 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Interactive image SMILES Cc2ccc(cc2)C(C(=O)OC)C1CCCCN1 ...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...

American TV series or program The Man Who Broke 1,000 ChainsVHS coverGenreBiographyDramaScreenplay byMichael CampusDirected byDaniel MannStarringVal KilmerCharles DurningSônia BragaKyra SedgwickJames KeachElisha Cook, Jr.Clancy BrownTheme music composerCharles BernsteinCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishProductionProducersYoram Ben-AmiMichael CampusProduction locationsJefferson, TexasMarshall, TexasCinematographyMikael SalomonEditorsDiana FriedbergWalter HannemannNoel Rog...
Burgau. Burgau adalah kota yang terletak di distrik Günzburg di Bavaria, Jerman. Kota Burgau memiliki luas sebesar 25.92 km² . Burgau pada tahun 2006, memiliki penduduk sebanyak 9.407 jiwa. lbsKota dan kotamadya di GünzburgAichen | Aletshausen | Balzhausen | Bibertal | Breitenthal | Bubesheim | Burgau | Burtenbach | Deisenhausen | Dürrlauingen | Ebershausen | Ellzee | Gundremmingen | Günzburg | Haldenwang | I...

Representing 43.6% of the Welsh population in 2021, Christianity is the largest religion in Wales. Wales has a strong tradition of nonconformism, particularly Methodism. From 1534 until 1920 the established church was the Church of England, but this was disestablished in Wales in 1920, becoming the still Anglican but self-governing Church in Wales. Most adherents to organised religion in Wales follow the Anglican Church in Wales, Presbyterian Church of Wales, Baptist Union of Wales, Union of...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع بلدة غرينوود (توضيح). بلدة غرينوود الإحداثيات 44°28′06″N 85°31′37″W / 44.468333333333°N 85.526944444444°W / 44.468333333333; -85.526944444444 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة ويكسفورد خصائص جغرافية المساحة 35.4 ميل مرب�...

BovinaeRentang fosil: Miosen - Sekarang Bison Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Mamalia Ordo: Artiodactyla (Tidak termasuk) Ruminantiamorpha Subordo: Ruminansia Infraordo: Pecora Famili: Bovidae Subfamili: BovinaeGray, 1821 Suku Bovini Boselaphini Strepsicerotini Bovinae adalah sebuah subfamili yang tergolong familia Bovidae yang mencakup berbagai kelompok tersebar di 10 genus hewan berkuku jari berukuran medium hingga besar, termasuk sapi domestik, bison, kerbau a...

2022 film directed by Nelson BeastTheatrical release posterDirected byNelson DilipkumarWritten byNelson DilipkumarProduced byKalanithi MaranStarringVijayPooja HegdeSelvaraghavanCinematographyManoj ParamahamsaEdited byR. NirmalMusic byAnirudh RavichanderProductioncompanySun PicturesDistributed byRed Giant MoviesRelease date 13 April 2022 (2022-04-13) Running time158 minutes[1]CountryIndiaLanguageTamilBudgetest. ₹130–150 crore[a]Box officeest. ₹217–300 cro...

Legislative Assembly constituency in Karnataka, India KudachiConstituency No. 5 for the Karnataka Legislative AssemblyConstituency detailsCountryIndiaRegionSouth IndiaStateKarnatakaDistrictBelagaviLS constituencyChikkodiEstablished2008Total electors193,564 (2023)[1]ReservationSCMember of Legislative Assembly16th Karnataka Legislative AssemblyIncumbent Mahendra Kallappa Tammannavar PartyINCElected year2023Preceded byP. Rajeev Kudachi Assembly constituency is one of the 224 constituenci...

Peace TVDiluncurkan21 Januari 2006PemilikZakir Naik (pendiri dan presiden) Shariful Islam Naik (CEO) Lords Production Ltd, anak usaha dari Universal Broadcasting Corporation Ltd [1]Slogan The solution for Humanity NegaraUni Emirat ArabSaluran seindukPeace TV Urdu, Peace TV Bangla, Peace TV Albanian, Peace TV Chinese Peace TV adalah satu jaringan televisi satelit berbasis Islam yang disiarkan secara global 24/7 dari Dubai, Uni Emirat Arab. Sekitar 75% program Peace TV disiarkan dalam B...

Internationaux de France de tennis 1981 Édition Roland-Garros Date Du 25 mai au 7 juin 1981 Lieu Stade Roland-Garros Paris Catégorie Grand Chelem Surface Terre (ext.) Dotation 300 000 $ Tableaux de simple Dames 7 tours (96 joueuses) Hana Mandlíková Messieurs 7 tours (128 joueurs) Björn Borg Tableaux de double Dames 6 tours (48 équipes) Rosalyn Fairbank Tanya Harford Messieurs 6 tours (64 équipes) Heinz Günthardt Balázs Taróczy Mixte 5 tours (32 équipes) Andrea Jaeger Jim...

花瓶(かびん)は切花を挿す目的で用いられる容器(花器)である。一般には置物であるが、壁に掛けて用いるものは掛け花瓶という[1]。なお、花器の花篭には花瓶と一体になっているものと分離しており内部に花瓶を収めるものとがある[1]。 中国の花瓶 概要 花瓶の色、形、模様、材質、および大きさは多様性に富む。多くの花瓶は、挿された花をより良�...

Medieval Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta This article is about a historical term for various groups of Muslims. For other uses, see Moor. Castillian ambassadors attempting to convince Moorish Almohad king Abu Hafs Umar al-Murtada to join their alliance (contemporary depiction from the Cantigas de Santa María) Christian and Moor playing chess, from The Book of Games of Alfonso X, c. 1285 The term Moor is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans ...