Bochnia
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Delegate Joseph Marion Hernández of the Florida Territory, elected in 1822, the first Hispanic or Latino American to serve in the United States Congress in any capacity. Hispanic and Latino Americans have served in the United States Congress since the early 19th century. The first group elected to serve in the Congress were incorporated as part of the United States territorial expansion into previous Spanish territories of the North American mainland as part of American campaigns of Manifes...

For other people named George Hyde, see George Hyde (disambiguation). George J. HydeBorn(1888-01-04)January 4, 1888Äpfingen, Baden-Württemberg, German EmpireDiedDecember 2, 1963(1963-12-02) (aged 75)Brooklyn, New York, U.S.NationalityGerman-AmericanOccupation(s)Machinist, gunsmith and gun designerKnown forDesigning the M3 grease gun, designing the FP-45 Liberator pistol George J. Hyde Sr. (born Heide; January 4, 1888 – December 2, 1963) was a German-born American machinist, guns...

ilustrasi sosok Sazae-oni (栄螺鬼) dalam Gazu Hyakki Tsurezure Bukuro (百器徒然袋) Sazae-oni (栄螺鬼) adalah makhluk meyerupai moluska raksasa yang ada dalam cerita rakyat Jepang.[1] Wujudnya dideskripsikan sebagai jenis dari obake yang terbentuk ketika seekor siput laut dari jenis Turbo cornutus mencapai usia 30 tahun. Menurut legenda, Sazae-oni merupakan makhluk mengerikan dan mematikan yang biasanya muncul dari laut pada malam hari. Ia mengubah bentuk menjadi wanita untu...

Vous lisez un « bon article » labellisé en 2008. « Un nouveau superbe clipper partant pour San Francisco », publicité pour le voyage vers la Californie publiée à New York dans les années 1850. La ruée vers l’or en Californie (California gold rush) est une période d'environ huit ans (1848-1856) qui commence en janvier 1848 par suite de la découverte d'or à Sutter's Mill, une scierie appartenant au Suisse Johann August Sutter, près de Coloma, à l'est de Sac...

American military officer (1887–1971) Benjamin Berl LipsnerLipsner (c. 1940)Personal detailsBorn(1887-09-15)September 15, 1887Chicago, Illinois, U.S.DiedDecember 24, 1971(1971-12-24) (aged 84)Chicago, Illinois, U.S.Resting placeRosehill CemeteryChicago, Illinois, U.S.SpouseRose E.Children4Alma materArmour Institute Benjamin Berl Lipsner (September 15, 1887 – December 24, 1971) was an American military officer and civil servant. He served as the first supervisor of the Post Offi...

American college football season 2021 VMI Keydets footballConferenceSouthern ConferenceRecord6–5 (4–4 SoCon)Head coachScott Wachenheim (7th season)Offensive coordinatorBilly Cosh (2nd season)Defensive coordinatorTom Clark (7th season)Home stadiumAlumni Memorial FieldSeasons← 20202022 → 2021 Southern Conference football standings vte Conf Overall Team W L W L No. 9 East Tennessee State $^ 7 – 1...

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі ор...

Questa voce sull'argomento film drammatici è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Lupi nell'abissoUna scena del filmPaese di produzioneItalia Anno1959 Durata90 min Dati tecniciB/N Generedrammatico RegiaSilvio Amadio SoggettoSilvio Amadio, Luciano Vincenzoni SceneggiaturaGino De Santis, Carlo Romano, Silvio Amadio ProduttoreItalo Zingarelli Casa di produzioneCompagnie Industrielle et Commerciale Cinématographique (CICC), Films Borderie, Radiu...

Polymer of glucose and structural component of cell wall of plants and green algae Cellulose[1] Identifiers CAS Number 9004-34-6 Y ChEMBL ChEMBL2109009 N ChemSpider None ECHA InfoCard 100.029.692 EC Number 232-674-9 E number E460 (thickeners, ...) KEGG C00760 PubChem CID 14055602 UNII SMD1X3XO9M Y CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID3050492 Properties Chemical formula (C12H20O10)n Molar mass 162.1406 g/mol per glucose unit Appearance white powder Density 1....

Instrumental blues standard first recorded by Freddie King For other uses, see Hideaway (disambiguation). Hide AwaySingle by Freddie KingB-sideI Love the Woman (initially A-side)Released1960 (1960)–1961RecordedAugust 26, 1960StudioKing, Cincinnati, OhioGenreBluesLength2:36LabelFederalSongwriter(s)Freddie King, Sonny ThompsonProducer(s)Sonny ThompsonFreddie King singles chronology You've Got to Love Her with a Feeling (1960) Hide Away (1960) Lonesome Whistle Blues (1961) Hide Away or Hi...

Family of 32-bit microprocessors This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: I486 OverDrive – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) An Intel DX2-66 MHz OverDrive An Intel i486SX2-50 MHz OverDrive processor installed next to the original i486S...

Conflict over water rights in California between 1902 and 2006 The Los Angeles Aqueduct in the Owens Valley The California Water Wars were a series of political conflicts between the city of Los Angeles and farmers and ranchers in the Owens Valley of Eastern California over water rights. As Los Angeles expanded during the late 19th century, it began outgrowing its water supply. Fred Eaton, mayor of Los Angeles, promoted a plan to take water from Owens Valley to Los Angeles via an aqueduct. Th...

Italo-cileniLuogo d'origine Italia Popolazione52.006 cittadini italiani.[1]ca. discendenti:300.000 (1989)[2]150.000 (2004)[3]600.000 (2014)[4] Linguaitaliano, spagnolo ReligioneCattolicesimo Distribuzione Cile52.006 cittadini italiani.[1]ca. discendenti:300.000 (1989)[2]150.000 (2004)[3]600.000 (2014)[4] Manuale La famiglia Alessandri nel 1920, dalla quale vengono due Presidenti del Cile: Arturo Alessandri (al cen...

Cet article recense les sites inscrits au patrimoine mondial en Ouzbékistan. Statistiques L'Union soviétique ratifie la Convention pour la protection du patrimoine mondial, culturel et naturel le 12 octobre 1988 ; la république socialiste soviétique d'Ouzbékistan fait alors partie de l'union et le premier bien ouzbek est inscrit au patrimoine mondial en 1990[1]. Lors de la dislocation de l'Union soviétique, l'Ouzbékistan devient indépendant le 1er septembre 1991. Le pays notifie ...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يونيو 2018) اضغط هنا للاطلاع على كيفية قراءة التصنيف أسد شرق إفريقيا المرتبة التصنيفية نويع[1] التصنيف العلمي فوق النطاق حيويات مملكة عليا أبواكيات...
هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. محمية بركة الطيور أو محمية الجهراء محمية طبيعية كويتية، تقع ضمن منطقة التحريج في شرق مدينة الجهراء، تبلغ مساحة المحمية 2.5 كم2، وهي عبارة عن منطقة ساحلية مالجة، تتجمع فيها ميا�...

People from the UK and its territories Britons redirects here. For other uses, see Britons (disambiguation). Ethnic group British peopleUnion FlagTotal population British c. 72 million British diaspora c. 200 million[1] Regions with significant populationsUnited Kingdom57,678,000[A][2]United States109,531,643[B][3][4]678,000[C][5]Australia19,301,379[B][6][7]1,300,000[D][8]Canada...
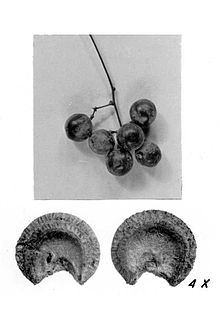
Genus of flowering plants Menispermum Fruit and seed of Menispermum canadense Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Order: Ranunculales Family: Menispermaceae Subfamily: Menispermoideae Genus: MenispermumL. Species See text Menispermum (moonseed) is a small genus of deciduous climbing woody vines in the moonseed family (Menispermaceae). Plants in this genus have small dioecious flowers, and clusters of small grape-like drupes.[1...

Questa voce sull'argomento centri abitati della Romania è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. SpinenicomuneSpineni – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Romania RegioneMuntenia Distretto Olt TerritorioCoordinate44°45′N 24°33′E44°45′N, 24°33′E (Spineni) Superficie73,98 km² Abitanti2 025 (2007) Densità27,37 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale237415 Fuso orarioUTC...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (سبتمبر 2018) هما شاه سلطان معلومات شخصية مكان الميلاد جورجيا الوفاة 1672 بإسطنبولإسطنبول مواطنة الدولة العثمانية الديانة الإسلام الزوج إبراهيم الأول سلطان الد...













