Bilche-Zolote
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Eighth race of the 2013 NASCAR Nationwide Series 2013 Aaron's 312 Race details Race 8 of 33 of the 2013 NASCAR Nationwide SeriesDate May 4, 2013Official name 22nd Annual Aaron's 312Location Lincoln, Alabama, Talladega SuperspeedwayCourse Permanent racing facility2.66 mi (4.28 km)Distance 110 laps, 292.6 mi (470.894 km)Scheduled Distance 117 laps, 311.22 mi (500.86 km)Average speed 133.269 miles per hour (214.476 km/h)Pole positionDriver Travis Pastrana Roush Fenway RacingTime 54.255Most ...
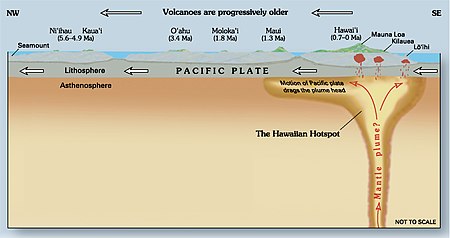
У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Горячая точка. Положение на карте Строение Гавайской горячей точки Гавайская горячая точка (Гавайское горячее пятно) — вулканическая горячая точка, расположенная вблизи острова Гавайи, в северной части Тихого океана. �...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Generale (disambigua). Generale (più formalmente ufficiale generale) è un grado militare che indica una persona appartenente alla più elevata categoria degli ufficiali. All'interno di questa categoria possono esserci più gradi, uno dei quali, in molte forze armate, è denominato generale, senza ulteriori specificazioni: si tratta di uno dei ranghi più elevati, se non il più elevato, superiore al generale di corpo d'armata o t...

Bahasa Albania Shqipgjuha shqipeӘлбания тілі Dituturkan diAlbania dan KosovoWilayahEropa Tenggara (Balkan)Penutur6.169.000 jiwa (Ethnologue, 2000) Rumpun bahasaIndo-Eropa Albania Bentuk awalProto-Albania Albania Status resmiBahasa resmi di Albania Kosovo[a]Diakui sebagaibahasa minoritas di Kroasia Makedonia Utara Montenegro Italia Rumania SerbiaDiatur olehAkademi Ilmu Pengetahuan Albania Akademi Ilmu Pengetahuan da...

此條目可能包含不适用或被曲解的引用资料,部分内容的准确性无法被证實。 (2023年1月5日)请协助校核其中的错误以改善这篇条目。详情请参见条目的讨论页。 各国相关 主題列表 索引 国内生产总值 石油储量 国防预算 武装部队(军事) 官方语言 人口統計 人口密度 生育率 出生率 死亡率 自杀率 谋杀率 失业率 储蓄率 识字率 出口额 进口额 煤产量 发电量 监禁率 死刑 国债 ...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

Italian automobile manufacturer AutobianchiIndustryAutomotiveFounded11 January 1955Defunct1995; 29 years ago (1995)FateMerged into LanciaSuccessorLanciaHeadquartersDesio, ItalyProductsAutomobilesRevenueU$1.7 billion dollars (1967)Number of employees4,500 (1967)ParentFiat S.p.A. Autobianchi (Italian: [autoˈbjaŋki]) was an Italian automobile manufacturer, created jointly by Bianchi, Pirelli and Fiat in 1955. Autobianchi produced only a handful of models during its li...

الماليزية-المغربية ماليزيا المغرب الماليزية-المغربية تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الماليزية المغربية تشير إلى العلاقات الثنائية بين ماليزيا والمغرب. ماليزيا لديها سفارة في الرباط،[1] والمغرب له السفارة في كوالالمبور.[2] التاريخ تشكلت العلا...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Monuments of Mars – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 1991 video gameMonuments of MarsEpisode 2, level 4Developer(s)Scenario SoftwarePublisher(s)Apogee SoftwareDesigner(s)Todd ReplogleProgramm...

American theoretical ecologist This biography of a living person relies too much on references to primary sources. Please help by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately, especially if potentially libelous or harmful.Find sources: Alan Hastings – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Alan ...

Югославская армия на родинесерб. Југословенска војска у отаџбини Довоенное полковое знамя Югославской королевской армии, используемое в ЮВуО[1] Основание 1941 (начало формирования) Роспуск 1946 (завершение организованной деятельности) Командование Начальник штаба Вер�...

Ordinance applying to a municipality or other locality Town Law redirects here. For other uses, see town privileges. A local ordinance is a law issued by a local government such as a municipality, county, parish, prefecture, or the like.[1] Drug use forbidden by local ordinance in Rotterdam, Netherlands Hong Kong In Hong Kong, all laws enacted by the territory's Legislative Council remain to be known as Ordinances (Chinese: 條例; Jyutping: tiu4lai6) after the transfer of the...

2013 animated film by Ben Stassen The House of MagicDirected by Jeremy Degruson Ben Stassen Screenplay by James Flynn Dominic Paris Ben Stassen Story byBen StassenProduced by Nadia Khamlichi Adrian Politowski Ben Stassen Caroline Van Iseghem Gilles Waterkeyn Starring Cinda Adams George Babbit Murray Blue Kathleen Browers Joey Camen Grant George Shanelle Gray Nina Grillo Kyle Hebert Goldie Jonsie Kendra Leif Joey Lotsko Millie Mup Will Parks Sage Sommer Michael Sorich Doug Stone Joseph W. Terr...

「SINE」重定向至此。關於SINE的其他意思,請見「SINE (消歧义) 」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是弦函數。 由於受到破坏,依據方針,本条目页已獲半保護。 請参閱保护方针及保护日志以获取更多信息。如果您不能修改此条目页,您可以请求修改、在讨论页提出修改提议、申请解除保护、登录或创建账号。 正弦 性質 奇偶性 奇 定義域 (-∞,∞) 到達域 [-1,1] 周...

Motorola Star TAC Производитель Motorola Размеры 94 мм х 55 мм х 19 мм Масса 88г Motorola MicroTAC[вд]Motorola RAZR[вд] Медиафайлы на Викискладе Motorola StarTAC — мобильный телефон, первая[1] «раскладушка» (флип-телефон) на рынке мобильных телефонов. Телефон выпущен 3 января 1996 года. StarTAC — преемник ...

市镇详图 艾扬(法語:Ayen)是法国科雷兹省的一个市镇,位于该省西部,属于布里夫拉盖拉尔德区。该市镇总面积13.16平方公里,2009年时的人口为714人。[1] 人口 艾扬(Ayen)人口变化图示 参见 科雷兹省市镇列表 参考文献 ^ 法国INSEE人口数据-2009年. [2012-10-15]. (原始内容存档于2012-01-08). 查论编 科雷兹省市镇省会 蒂勒 副省会 布里夫拉盖亚尔德 于塞勒 �...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un producteur de cinéma et un scénariste. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les conventions filmographiques. James SchamusJames Schamus lors de la Berlinale 2014.BiographieNaissance 7 septembre 1959 (64 ans)DétroitNationalité américaineFormation Université de Californie à BerkeleyActivités Scénariste, réalisateur, producteur de cinéma, producteur de télévisionConjoint Nancy Kricorian (en)...

Cầu Nhật Tân là cầu dây văng lớn nhất Việt Nam nằm tại Hà Nội Cầu dây văng là một loại cầu bao gồm một hoặc nhiều trụ (thường được gọi là tháp), với dây cáp neo chịu đỡ toàn bộ hệ mặt cầu và các dầm cầu. Có ba loại cầu dây văng chủ yếu, được phân biệt theo cách nối cáp vào trụ cầu. Theo kiểu thiết kế đàn hạc, các dây cáp được bố trí gần như song song nhau bằng cá...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento calciatori italiani non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Ettore Banchero...

山野ホールYAMANO HALL 2007年に竣工したMYタワー(東京・代々木)。地下3階に新たな山野ホールが設置された。 情報正式名称 山野ホール開館 2007年3月客席数 800席(固定276席 可動524席)延床面積 33,878.03m²設備 ロールバックチェアスタンド、主舞台、迫り舞台、ホワイエ、控室用途 ファッションショー、セミナー、スクール、講演会、エキシビジョンなど運営 学校法�...