Bible Fellowship Church
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Peta Uriménil. Uriménil merupakan sebuah komune di departemen Vosges yang terletak pada sebelah timur laut Prancis. Lihat pula Komune di departemen Vosges Referensi INSEE lbsKomune di departemen Vosges Les Ableuvenettes Ahéville Aingeville Ainvelle Allarmont Ambacourt Ameuvelle Anglemont Anould Aouze Arches Archettes Aroffe Arrentès-de-Corcieux Attignéville Attigny Aulnois Aumontzey Autigny-la-Tour Autreville Autrey Auzainvilliers Avillers Avrainville Avranville Aydoilles Badménil-aux-B...

حرب الاستقلال الإيطالية الأولى جزء من حروب توحيد إيطاليا معركة نوفارا 1849 معلومات عامة التاريخ 23 مارس 1848 – 24 مارس 1849 الموقع لومبارديا فينيشيا وبييمونتي النتيجة نصر نمساوي تغييراتحدودية لا تغيير المتحاربون مملكة سردينيا دوقية توسكانا الكبرىبتحالف مؤقت مع: الدولة البابوي�...

Japanese idol group HKT48Official logoBackground informationOriginFukuoka, JapanGenresPop, J-pop, Teen pop, Bubblegum popYears active2011 (2011)–presentLabelsEMI (UMG)Member ofAKB48 GroupMembersTeam H detailsTeam KIV detailsTeam TII detailsWebsitewww.hkt48.jp HKT48 (read H.K.T. Forty-eight) is a Japanese idol group produced by Yasushi Akimoto. HKT48 is named after the Hakata-ku, Fukuoka city of Fukuoka Prefecture, where Akimoto originally intended to base the group.[1] The grou...

كأس اليونان 1991–92 تفاصيل الموسم كأس اليونان النسخة 50 البلد اليونان المنظم الاتحاد الإغريقي لكرة القدم البطل نادي أولمبياكوس عدد المشاركين 72 كأس اليونان 1990–91 كأس اليونان 1992–93 تعديل مصدري - تعديل كأس اليونان 1991–92 (باليونانية: Κύπελλο Ελλάδος...

Colombian football referee (born 1980) In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Roldán and the second or maternal family name is Pérez. Wilmar Roldán Roldán refereeing at the 2018 FIFA World CupFull name Wilmar Alexander Roldán Pérez[1]Born (1980-01-24) 24 January 1980 (age 44)[2]Remedios, ColombiaDomesticYears League Role2003- Categoría Primera A RefereeInternationalYears League Role2008– FIFA Referee CONMEBOL Referee Wilmar Alexander ...

Governorate of Lebanon This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Beqaa Governorate – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Governorate of LebanonBeqaa Governorate مقاطعة البقاعGovernorate of LebanonMap of Lebanon wi...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Les Têtes brûlées. Têtes brûlées Lili Damita et Victor McLaglen Données clés Titre original The Cock-Eyed World Réalisation Raoul Walsh Scénario Raoul Walsh Acteurs principaux Victor McLaglenEdmund LoweLili Damita Sociétés de production Fox Film Corp. Pays de production États-Unis Genre Comédie dramatique Durée 115 minutes Sortie 1929 Pour plus de détails, voir Fiche technique et Distribution. modifier Têtes brûlées (The Cock-Eyed World) e...

Role-playing in Self-portrait as an Oriental Potentate with a Kris, etching, 1634. B18 Royal Collection, 1642 The dozens of self-portraits by Rembrandt were an important part of his oeuvre. Rembrandt created approaching one hundred self-portraits including over forty paintings, thirty-one etchings and about seven drawings; some remain uncertain as to the identity of either the subject (mostly etchings) or the artist (mostly paintings), or the definition of a portrait.[1] This was an ...

博里萨夫·约维奇攝於2009年 南斯拉夫社會主義聯邦共和國第12任總統任期1990年5月15日—1991年5月15日总理安特·马尔科维奇前任亚内兹·德尔诺夫舍克继任塞吉多·巴伊拉莫维奇(英语:Sejdo Bajramović) (代任)第12任不结盟运动秘书长任期1990年5月15日—1991年5月15日前任亚内兹·德尔诺夫舍克继任斯捷潘·梅西奇第3任塞尔维亚常驻南斯拉夫社会主义联邦共和国主席团代表任�...

Universitas ManilaSegel universitasNama sebelumnyaInstituto de Manila (1913-1921)MotoPatria Scientia et VirtusJenisSwastaDidirikan5 Oktober 1913 40386PresidenEmily Dodson de Leon, Ed. D.Staf akademik800, termasuk pegawai yang tidak mengajarJumlah mahasiswalebih dari 9.000LokasiManila, FilipinaKampusSampaloc, ManilaLagu AlmamaterUM ForeverWarna Hijau EmasAtletikNAASCUNama julukanHawksAfiliasiASAIHL PACUOlahragaBola basketMaskotElangSitus webwww.um.edu.ph Universitas Manila (UM) (Fil...

1999 book by Roberto Mangabeira Unger and Cornel West The Future of American Progressivism: An Initiative for Political and Economic Reform AuthorRoberto Mangabeira UngerCornel WestCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishGenrePolitical theoryPublisher1999 (Beacon Press)Pages104ISBN0807043273OCLC20613970LC ClassJK271.U533 1998Preceded byDemocracy Realized: The Progressive Alternative Followed byWhat Should the Left Propose? The Future of American Progressivism: An Initiati...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Nida Ria – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Nida Ria GroupGenreQasidahTahun aktif1980 - sekarang Nida Ria Group adalah sebuah group Qasidah Modern yang didirikan oleh anak pendiri Nasida...

Peer-to-peer ridesharing, food delivery This article may have been created or edited in return for undisclosed payments, a violation of Wikipedia's terms of use. It may require cleanup to comply with Wikipedia's content policies, particularly neutral point of view. (June 2020) BoltFormerlymTakso, TaxifyIndustryTransportationMobility as a serviceFoundedAugust 2013; 10 years ago (2013-08)FounderMarkus VilligHeadquartersTallinn, EstoniaArea served45 countries in Europe, Af...

Takayuki YamadaNYAFF 2011 Star Asia Awards - TAKAYUKI YAMADA - 18Nama asal山田 孝之Lahir20 Oktober 1983 (umur 40)Satsumasendai, Kagoshima, JepangPekerjaanAktor, penyanyiTahun aktif1998–sekarangAgenStardust Promotion Takayuki Yamada (山田孝之code: ja is deprecated , Yamada Takayuki, lahir 20 Oktober 1983) adalah aktor dan penyanyi Jepang. Dia memainkan peran utama dalam film tahun 2005, Densha Otoko.[1] Dia juga muncul di film-film seperti Vengeance Can Wait,&...

Local government area in Victoria, AustraliaShire of CorioVictoriaLocation in VictoriaPopulation57,720 (1992)[1] • Density81.912/km2 (212.151/sq mi)Established1861Area704.66 km2 (272.1 sq mi)Council seatGeelong NorthRegionBarwon South WestCountyGrant LGAs around Shire of Corio: Ballan Bacchus Marsh Werribee Bannockburn Shire of Corio Werribee Bannockburn Geelong Corio Bay The Shire of Corio was a local government area located between Geelong and Werrib...

New Zealand-Samoan actress Frankie AdamsFrankie Adams at WonderCon 2018Born (1994-01-03) 3 January 1994 (age 30)Savaiʻi, SamoaNationalitySamoa and New Zealand[1]OccupationActressHeight180 cm (5 ft 11 in) Frankie Adams (born 3 January 1994) is a Samoan New Zealand actress, best known for her roles as Bobbie Draper in the science fiction television series The Expanse and as Ula Levi in the prime-time soap opera Shortland Street.[2] Early life and education A...

A questa voce o sezione va aggiunto il template sinottico {{Emittente TV}} Puoi aggiungere e riempire il template secondo le istruzioni e poi rimuovere questo avviso. Se non sei in grado di riempirlo in buona parte, non fare nulla; non inserire template vuoti. La Südwestfunk (SWF in sigla) era l'emittente pubblica regionale tedesca della Renania-Palatinato e del Baden-Württemberg meridionale. Il confine preciso con il bacino della Süddeutscher Rundfunk (SDR) nel Baden-...
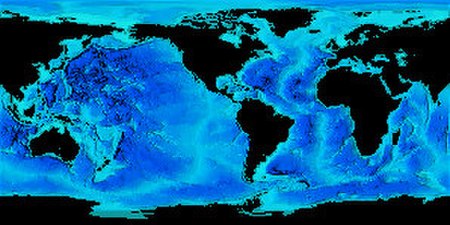
Peta dasar laut Dasar laut adalah bagian terbawah dari permukaan laut. Bentuk dasar laut mirip dengan di daratan. Isi dari dasar laut diketahui melalui eksplorasi dan survei hidrografi. Di dalam dasar laut terdapat terumbu karang, padang lamun dan tambang yang bervariasi. Konfigurasi dasar laut menggunakan peta batimetri. Kajian mengenai dasar laut menjadi bagian dari oseanografi. Pencitraan Dugaan dan fakta tentang bentuk Awalnya, ilmuwan mengira bahwa bentuk dasar laut hanya datar dan tidak...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Easy jet. easyJet Codes IATAOACIIndicatif d'appel U2/EC EZY/EJU EASY/ALPINE Repères historiques Date de création mars 1995 Généralités Basée à Londres-Luton Autres bases Liste Berlin-BrandebourgBarcelone-El PratPalma de Majorque Bordeaux-MérignacLyon-Saint-ExupéryNice-Côte d'AzurParis-Charles de GaulleParis-Orly Toulouse-BlagnacNantes-AtlantiqueMilan-MalpensaNaples-CapodichinoVenise - Marco Polo AmsterdamLisbonne-H. DelgadoPorto-F. Sá-CarneiroBelf...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant la Lituanie, l’Union européenne et une élection ou un référendum. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. 2004 2014 Élections européennes de 2009 en Lituanie 7 juin 2009 Postes à élire 12 députés européens pour la Lituanie Union de la patrie 25,69 % Sièges obtenus 4 Parti social-démocrate 19,06 % Sièges obtenus 3 ...