Astyanax cocibolca
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Dejan Savićević Informasi pribadiTanggal lahir 15 September 1966 (umur 57)Tempat lahir Titograd, SFR YugoslaviaPosisi bermain Attacking Midfielder / WingerKarier junior1981–1983 OFK Titograd1983–1984 BudućnostKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1983–1988 Budućnost 130 (36)1988–1992 Red Star Belgrade 72 (23)1992–1998 AC Milan 97 (35)1999 Red Star Belgrade 3 (0)1999–2001 Rapid Wien 44 (18)Total 346 (135)Tim nasional1986–1999 Yugoslavia Kepelatihan2001–2003 Serbia dan M...

Kayu Darah Merah Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Angiosperma (tanpa takson): Eudicot (tanpa takson): Rosid Ordo: Myrtales Famili: Myrtaceae Genus: Corymbia Spesies: C. gummifera Nama binomial Corymbia gummifera(Gaertn.) K.D.Hill & L.A.S.Johnson Corymbia gummifera, yang umumnya dikenal sebagai Kayu Darah Merah,[1] adalah sebuah pohon kayu keras yang berasal dari timur Australia. Deskripsi Tumbuhan tersebut biasanya tumbuh sebagai sebuah pohon, namun dapat...

Consolidated Vultee XP-81 adalah pengembangan dari Consolidated Vultee Aircraft Corporation untuk membangun sebuah pesawat tempur kursi tunggal, pendamping jarak jauh yang menggunakan gabungan dari kedua turbojet dan mesin turboprop. Meskipun menjanjikan, kurangnya mesin cocok dipadukan dengan akhir Perang Dunia II. Referensi Ginter, Steve. Consolidated Vultee XP-81 (Air Force Legends Number 214). Simi Valley, California: Ginter Books, 2007. ISBN 0-942612-87-6. Green, William. War Planes of ...

Battle of the First World War Battle of Saint-MihielPart of the Western Front of World War IA Renault FT tank ploughing its way through a trench and starting toward the German line near Saint Michel, France.Date12–15 September 1918LocationSaint-Mihiel salient, France48°53′21″N 05°32′37″E / 48.88917°N 5.54361°E / 48.88917; 5.54361Result Allied victoryBelligerents United States France German Empire Austria-HungaryCommanders and leader...

Concours Eurovision de la chanson 1956 Dates Finale 24 mai 1956 Retransmission Lieu Teatro KursaalLugano, Suisse Présentateur(s) Lohengrin Filipello Directeur musical Fernando Paggi Télédiffuseur hôte RTSI Entracte Les Joyeux Rossignols & les Trois Ménestrels Participants Nombre de participants 7 Débuts Allemagne Belgique France Italie Luxembourg Pays-Bas Suisse Pays participants Résultat Chanson gagnante Refrain par Lys Assia Suisse Système de...

سيلفستر جيمس غيتس (بالإنجليزية: Sylvester James Gates) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 15 ديسمبر 1950 (74 سنة) تامبا مواطنة الولايات المتحدة العرق أمريكي أفريقي [1][2] عضو في الأكاديمية الأمريكية للفنون والعلوم، والأكاديمية الوطنية للعلوم الحياة العملية المدرس...
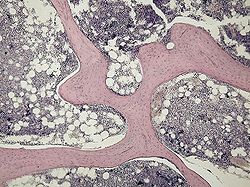
Tulang spongiosaIlustrasi tulang panjang yang menunjukkan lokasi tulang spongiosa ( di gambar disebut trabecular bone).RincianPengidentifikasiBahasa Latinsubstantia spongiosa ossiumMeSHD000071556TA98A02.0.00.004TA2380FMA24019Daftar istilah anatomi[sunting di Wikidata] Tulang spongiosa (atau juga disebut tulang spons) adalah salah satu dari dua jenis jaringan internal yang membentuk tulang. Jaringan yang lainnya disebut tulang kortikal. Tulang spongiosa memiliki rasio luas permukaan terhad...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

John Stafford John Stafford (24 novembre 1427 – 8 maggio 1473) è stato un nobile inglese ed ebbe il titolo di conte di Wiltshire. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Note 3 Bibliografia 4 Voci correlate Biografia Era figlio di Humphrey Stafford, I duca di Buckingham e della consorte Anne Neville, figlia di Ralph Neville, I conte di Westmorland. Nel 1461 venne creato cavaliere dell'ordine del bagno. Combatté come Yorkista nella battaglia di Hexham nel 1464. Nel 1469 venne fatto Steward del ducato di Corn...

German mathematician (1845–1918) Georg CantorCantor, c. 1910BornGeorg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor(1845-03-03)3 March 1845Saint Petersburg, Russian EmpireDied6 January 1918(1918-01-06) (aged 72)Halle, Province of Saxony, German EmpireNationalityGerman-RussianAlma mater Swiss Federal Polytechnic University of Berlin University of Göttingen Known forSet theorySpouse Vally Guttmann (m. 1874)AwardsSylvester Medal (1904)Scientific careerFie...
Protected area in New South Wales, AustraliaBiamanga National ParkNew South WalesIUCN category II (national park) Mumbulla Mountain from the Princes Highway, AustraliaBiamanga National ParkNearest town or cityBegaCoordinates36°27′04″S 149°56′31″E / 36.45111°S 149.94194°E / -36.45111; 149.94194Established1994Area137.49 km2 (53.1 sq mi)[1]Managing authoritiesNSW National Parks and Wildlife ServiceWebsiteBiamanga National ParkSee alsoPr...

British soup Windsor soupTypeSoupPlace of originGreat BritainMain ingredientsCalf's feet, bouquet garni, Madeira wineVariationsWhite and brown soups Windsor soup or Brown Windsor soup is a British soup.[1][2][3] While commonly associated with the Victorian and Edwardian eras, the practice of calling it 'Brown Windsor' did not emerge until at least the 1920s, and the name was usually associated with low-quality brown soup of uncertain ingredients. Although Windsor soup ...

Radio station in Rock Hill, South CarolinaWYTX-LPRock Hill, South CarolinaBroadcast areaMetro Rock HillFrequency98.5 FM MHzBranding98-5 YTXProgrammingFormatVariety[1]OwnershipOwnerYork Technical CollegeHistoryFirst air dateJuly 9, 2015Former call signsWYTX-LP (2014–Present)[2]Call sign meaningW York Technical (College) XTechnical informationFacility ID196642ClassL1Power88.4 WattsHAAT31.7 meters (104 ft)Transmitter coordinates34°56′9.0″N 80°59′37.0″W / ...

Ruggero da FioreRuggero da Fiore in una stampa ottocentescaNascitaBrindisi, 1267 MorteAdrianopoli, 30 aprile 1305 Cause della morteOmicidio Dati militariPaese servito Impero bizantino Forza armata Ordine dei Templari Esercito bizantino UnitàCompagnia Catalana GradoMegadux Guerre Crociate Guerra del Vespro Guerre bizantino-ottomane BattaglieAssedio di San Giovanni d'Acri voci di militari presenti su Wikipedia Manuale Ruggero Flores, o Roger de Flor (nei documenti frater Rogerius ...

Amazing KissSingel oleh BoAdari album LISTEN TO MY HEARTDirilis25 Juli 2001FormatCDDirekam?GenrePopLabelAvex TraxProduser? Amazing Kiss adalah singel ke-2 BoA di Jepang. Lagu Amazing Kiss Someday, Somewhere Amazing Kiss (English Version) Amazing Kiss (Instrumental) Someday, Somewhere (Instrumental) lbsBoAKoreaAlbum Studio ID; Peace B • No.1 • Atlantis Princess • My Name • Girls on Top • Hurricane Venus R...

ヨハネス12世 第130代 ローマ教皇 教皇就任 955年12月16日教皇離任 964年5月14日先代 アガペトゥス2世次代 レオ8世個人情報出生 937年スポレート公国(中部イタリア)スポレート死去 964年5月14日 教皇領、ローマ原国籍 スポレート公国親 父アルベリーコ2世(スポレート公)、母アルダその他のヨハネステンプレートを表示 ヨハネス12世(Ioannes XII、937年 - 964年5月14日)は、ロ...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. SD Permata NusantaraInformasiJenisSekolah SwastaAlamatLokasi, Batam, Kepri, IndonesiaMoto SD Permata Nusantara, merupakan salah satu Sekolah Dasar swasta yang ada di Batam, Provinsi Kepulauan Riau. Sama dengan SD pada umumnya di Indonesia masa p...

عنتمنظمة الأمم والشعوب غير الممثلةإفريقيا أفريقان بروتسلاند Bellah people [لغات أخرى] بيافرا حراطين منطقة القبائل أوغادين شعب أوغوني أوروميا باستر صوماليلاند توغولاند الغربية يوروبا Zambesia آسيا حركة آتشيه الحرة آشوريون/سريان/كلدان بلوشستان، باكستان تلال جاتجام تركست�...

Municipality in Catalonia, SpainCalafellMunicipalityCalafell beach Coat of armsCalafellLocation in CataloniaCoordinates: 41°12′07″N 1°34′12″E / 41.202°N 1.57°E / 41.202; 1.57Country SpainCommunity CataloniaProvince TarragonaComarcaBaix PenedèsGovernment • MayorRamon Ferré Solé (2015)[1]Area[2] • Total20.4 km2 (7.9 sq mi)Population (2018)[3] • Total25,444 �...

For the private company, see Australian Election Company. Australian Electoral CommissionAgency overviewFormed21 February 1984JurisdictionCommonwealth of AustraliaHeadquartersCanberraEmployees3,478 (as at 31 December 2023)[1]Minister responsibleSpecial Minister of StateAgency executivesMr Tom Rogers, Electoral CommissionerThe Hon. Justice Susan Kenny, ChairpersonDr David Gruen, Non-judicial memberParent agencyDepartment of FinanceWebsitewww.aec.gov.au Entrance to polling station run ...

