Aragarças Revolt
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Strada statale 483TermoleseLocalizzazioneStato Italia Regioni Molise Province Campobasso DatiClassificazioneStrada statale InizioPalata FineTermoli Lunghezza31,825[1] km Provvedimento di istituzioneD.M. 22/12/1964 - G.U. 48 del 24/02/1965[2] GestoreTratte ANAS: nessuna (dal 2001 la gestione è passata alla Provincia di Campobasso) Percorso Manuale La ex strada statale 483 Termolese (SS 483), ora strada provinciale 168 Termolese (SP 168)[3], è una strada...

Akademi Militer IndiaMotoवीरता और विवेक - Veerata or Vivek (Berani dan Bijak)JenisAkademi militerDidirikan1 Oktober 1932KomandanLetnan JenderalLokasiDehradun, Uttarakhand, IndiaWarnaMerah darah dan Abu-abu baja Pada saat upacara wisuda taruna Akmil India Akademi Militer India (Bahasa Hindi: भारतीय सैन्य अकादमी - Bharatiya Sena Akaadamiy), (Bahasa Inggris: Indian Military Academy) disingkat IMA adalah akademi pembentukan da...

Bahasa Tamil KunoWilayahTamiḻakam, India KunoEraBerkembang menjadi Bahasa Tamil Pertengahan pada abad ke-7 Masehi Rumpun bahasaDravida Proto-Dravida-SelatanTamil–KannadaTamil–KodaguPra–TamilTamil Kuno Sistem penulisanBrahmi Tamil, kemudian Vaṭṭeḻuttu, dan PallawaKode bahasaISO 639-3otyLINGUIST Listoty Bahasa Tamil KunoGlottologoldt1248 (Bahasa Tamil Kuno)[1]QIDQ20987452 Status konservasi Punah EXSingkatan dari Extinct (Punah)Terancam CRSingkatan dari Critically end...

Species of flowering plant Senecio pulcher Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Clade: Asterids Order: Asterales Family: Asteraceae Genus: Senecio Species: S. pulcher Binomial name Senecio pulcherHook. & Arn.[1] Range of Senecio pulcher. Senecio pulcher is an ornamental plant native to the wet valleys & slopes and flooded rocky[2] habitats in Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay. Cited in Flora Brasiliensis&#...

Roy Makaay Makaay dengan Feyenoord saat 2007Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Rudolphus Antonius MakaayTanggal lahir 9 Maret 1975 (umur 49)[1]Tempat lahir Wijchen, Belanda[1]Tinggi 188 m (616 ft 9+1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain PenyerangKarier junior SC Woezik DIOSA Blauw Wit NijmegenKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1993–1997 Vitesse 109 (42)1997–1999 Tenerife 72 (21)1999–2003 Deportivo La Coruña 133 (79)2003–2007 Bayern Munich 129 (78)2007–2010 Fey...

Australian cricketer George GiffenGiffen in about 1895Personal informationFull nameGeorge GiffenBorn(1859-03-27)27 March 1859Adelaide, South Australia, AustraliaDied29 November 1927(1927-11-29) (aged 68)Adelaide, South Australia, AustraliaHeight1.80 m (5 ft 11 in)BattingRight-handedBowlingRight-arm off spinRoleAll-rounderRelationsWalter Giffen (brother)International information National sideAustraliaTest debut (cap 27)31 December 1881 v EnglandLast ...

Religious symbol representing a ring of light For other uses, see Halo (disambiguation). Standing Buddha with a halo, 1st–2nd century AD (or earlier), Greco-Buddhist art of Gandhara Jesus and nine of the Twelve Apostles depicted with Floating disk haloes in perspective (detail from The Tribute Money, illustrating Matthew 17:24–27, by Masaccio, 1424, Brancacci Chapel) A halo (from Ancient Greek ἅλως (hálōs) 'threshing floor, disk';[1][2] also called a n...

Annual Australian event on 26 May National Sorry Day2016 National Sorry Day event in BrisbaneAlso calledNational Day of HealingObserved by AustraliaTypeCulturalSignificanceCommemoration of the Stolen GenerationsDate26 MayNext time26 May 2024 (2024-05-26)FrequencyAnnuallyFirst time26 May 1998 (1998-05-26) National Sorry Day, officially the National Day of Healing, is an event held annually in Australia on 26 May commemorating the Stolen Generations. It i...
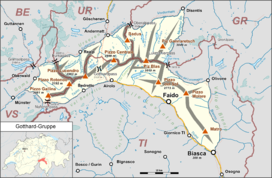
For the larger, underlying geological structure, see Gotthard nappe. You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (June 2016) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the German article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than s...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Leavitt. Sam Leavitt En chapeau blanc, sur le tournage de Sursis pour une nuit (1966), avec les acteurs Eleanor Parker et Stuart Whitman(au sol) et le réalisateur Robert Gist (derrière eux) Données clés Nom de naissance Samuel E. Leavitt Naissance 6 février 1904New YorkÉtat de New York, États-Unis Nationalité Américaine Décès 21 mars 1984 (à 80 ans)Los Angeles (Woodland Hills)Californie, États-Unis Profession Directeur de la photographie Fi...

Peta lokasi Munisipalitas Ringkøbing-Skjern Munisipalitas Ringkøbing-Skjern adalah sebuah kawasan pemukiman (Denmark: kommune) di Region Midtjylland di semenanjung Jutlandia di Denmark tengah. Munisipalitas Ringkøbing-Skjern memiliki luas sebesar 1.485 km² dan memiliki populasi sebesar 58.368 jiwa. Referensi Municipal statistics: NetBorger Kommunefakta Diarsipkan 2007-08-12 di Wayback Machine., delivered from KMD aka Kommunedata (Municipal Data) Municipal merges and neighbors: Eniro ...

2003 live album by Grateful DeadDick's Picks Volume 27Live album by Grateful DeadReleasedJanuary 17, 2003RecordedDecember 16, 1992GenreJam Folk rock Psychedelic rockLength196:21LabelGrateful Dead RecordsGrateful Dead chronology Go to Nassau(2002) Dick's Picks Volume 27(2003) Birth of the Dead(2003) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllmusic[1]The Music Box[2]Rolling Stone [3] Dick's Picks Volume 27 is an album by the Grateful Dead, the 27th installme...

Bessye J. BeardenBornBessye BanksNovember 1893Atlantic City, New Jersey, U.S.DiedSeptember 16, 1943(1943-09-16) (aged 49)Harlem, New York, U.S.NationalityAmericanEducationVirginia Normal and Industrial InstituteOccupationJournalistSpouseRichard Howard Bearden Bessye Johnson Bearden (November 1893 – September 16, 1943)[1][2] was an American journalist and civic activist, who was the mother of artist Romare Bearden. Biography Born in Atlantic City, New Jers...

Not to be confused with Bellingham North Tyne railway station. Railway station in County Durham, England BillinghamGeneral informationLocationBillingham, Borough of Stockton-on-TeesEnglandCoordinates54°36′21″N 1°16′46″W / 54.6057149°N 1.2795366°W / 54.6057149; -1.2795366Grid referenceNZ466236Owned byNetwork RailManaged byNorthern TrainsPlatforms2Tracks2Other informationStation codeBILClassificationDfT category F2HistoryOriginal companyStockton and Hartlepoo...

1929 film Les Nouveaux MessieursTheatrical release posterDirected byJacques FeyderWritten by Charles Spaak Jacques Feyder Based onLes Nouveaux Messieursby Robert de Flers (play)Francis de Croisset (play)Starring Gaby Morlay Albert Préjean Henry Roussell Cinematography Georges Périnal Maurice Desfassiaux Productioncompanies Films Albatros Sequana Films Distributed byArmor FilmsRelease date 5 April 1929 (1929-04-05) Running time135 minutesCountryFranceLanguageSilent (French int...

Refusal to pay taxes in the U.S. Tax resistance in the United States has been practiced at least since colonial times, and has played important parts in American history. Tax resistance is the refusal to pay a tax, usually by means that bypass established legal norms, as a means of protest, nonviolent resistance, or conscientious objection. It was a core tactic of the American Revolution and has played a role in many struggles in America from colonial times to the present day. In addition, th...

The national symbols of Kuwait are official and unofficial flags, icons or cultural expressions that are emblematic, representative or otherwise characteristic of Kuwait and of its culture. Symbol Title Name of Symbol Picture National flag Flag of Kuwait Coat of arms Coat of arms of Kuwait National anthem an-Nashīd al-Waṭani National anthem of Kuwait Problems playing this file? See media help. National flower Arfaj flower[1] National bird Falcon[2] National animal Arabian c...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Cultural depictions of Ronald Reagan – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article is part of a series aboutRonald Reagan Personal life Filmography Bibliography Death Residences Birthplace o...

Clear fluid emitted from the urethra of the penis during arousal Not to be confused with Premature ejaculation. Pre-ejaculate on the glans of the penisPre-ejaculate (also known as pre-ejaculatory fluid, pre-seminal fluid or Cowper's fluid, and colloquially as pre-cum) is a clear, colorless, viscous fluid that is emitted from the urethra of the penis during sexual arousal. It is similar in composition to semen but has distinct chemical differences. The presence of sperm in the fluid is variabl...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Hoz et Jaca (homonymie). Cet article est une ébauche concernant une localité d'Aragon. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Hoz de Jaca Héraldique Drapeau Église des saints rois et de Saint Laurent Administration Pays Espagne Statut Municipio Communauté autonome Aragon Province Province de Huesca Comarque Alto Gállego Maire Mandat Esperanza López Sanz (PAR) 200...

