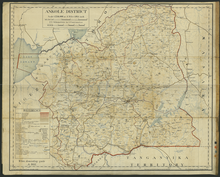
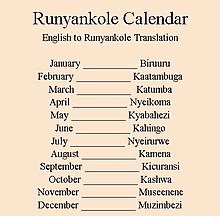
Ankole
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
Star AllianceDidirikan14 Mei 1997Armada5.033Tujuan1.294 bandara195 negaraSloganThe Way the Earth Connects.Kantor pusatFrankfurt am Main, JermanSitus webstaralliance.comStar Alliance, diluncurkan pada 14 Mei 1997, adalah sebuah aliansi maskapai penerbangan pertama di dunia, dan yang terbesar sampai saat ini dengan berbagai bentuk kerjasama.[1] Per April 2018, Star Alliance adalah aliansi maskapai penerbangan terbesar berdasarkan jumlah penumpang dengan 762,27 juta penumpang, mengunggul...

Joshua AngristBiographieNaissance 18 septembre 1960 (63 ans)ColumbusNom dans la langue maternelle Joshua David AngristNationalités israélienneaméricaineFormation Université de Princeton (doctorat)Oberlin CollegeActivités Économiste, économètre, professeur d'universitéEnfant Noam Angrist (d)Autres informationsA travaillé pour Université HarvardMassachusetts Institute of TechnologyMembre de Société d'économétrie (1998)Académie américaine des arts et des sciencesDirecteurs ...

Fujiwara no Hirotsugu digambarkan oleh Kikuchi Yōsai Pemberontakan Fujiwara no Hirotsugu (藤原広嗣の乱code: ja is deprecated ) (藤原広嗣の乱, Fujiwara no Hirotsugu no ran) merupakan sebuah pemberontakan gagal pada zaman Nara yang dipimpin oleh Fujiwara no Hirotsugu (藤原広嗣) di Kepulauan Jepang, pada tahun 740. Hirotsugu, tidak puas dengan kekuatan politik, mengangkat tentara di Dazaifu, Kyushu, tetapi dikalahkan oleh pasukan pemerintah. Sumber sejarah Pemberontakan Fujiwara...

République de Floride occidentaleen Republic of West Florida 1810–1810le Bonnie Blue Flag La Floride-Occidentale, aujourd'hui partagée entre la Louisiane, le Mississippi et l'AlabamaInformations générales Statut République Capitale St. Francisville Histoire et événements 23 septembre 1810 Création 27 octobre 1810 Annexion par les États-Unis Entités précédentes : Nouvelle-Espagne Entités suivantes : Floride modifier - modifier le code - voir Wikidata (aide) La r�...

H.Dahlan JamaluddinS.I.P. Ketua DPRA ke-16Masa jabatan15 November 2019 – 21 Maret 2022PresidenJoko WidodoPendahuluSulaiman, S.E, M.SMPenggantiPetahanaAnggota DPRAMasa jabatan13 November 2017 – 30 September 2019PendahuluMakhrum TahirPenggantiPetahanaDaerah pemilihanACEH 2(Pidie, Pidie Jaya)PetahanaMulai menjabat 30 September 2019Mayoritas12.291 suara Informasi pribadiLahir26 Agustus 1980 (umur 43)Meuko Kuthang, Bandar Dua, Pidie Jaya, Daerah Istimewa AcehKeba...

23°34′N 120°21′E / 23.56°N 120.35°E / 23.56; 120.35 Rural townshipXingang Township新港鄉 Singang, SinkangRural townshipFengtian TempleXingang Township in Chiayi CountyLocationChiayi County, TaiwanArea • Total66.05 km2 (25.50 sq mi)Population (May 2022) • Total30,543 Xingang Township Government Office Xingang Township or Singang Township (Chinese: 新港鄉; pinyin: Xīngǎng Xiāng) is a rural township in C...

Taman Peringatan SandakanHalaman utama taman tersebut.Koordinat5°53′19″N 118°2′50″E / 5.88861°N 118.04722°E / 5.88861; 118.04722Koordinat: 5°53′19″N 118°2′50″E / 5.88861°N 118.04722°E / 5.88861; 118.04722LokasiSandakanTipePrasastiDidedikasikan kepadaMengenang seluruh tahanan perang yang kehilangan nyawa mereka saat Pawai Kematian Sandakan Taman Peringatan Sandakan adalah sebuah situs peringatan yang dibangun di bekas hala...

Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens ADGRL4IdentifiersAliasesADGRL4, ETL, KPG_003, ELTD1, adhesion G protein-coupled receptor L4External IDsOMIM: 616419 MGI: 2655562 HomoloGene: 11170 GeneCards: ADGRL4 Gene location (Human)Chr.Chromosome 1 (human)[1]Band1p31.1Start78,889,764 bp[1]End79,282,124 bp[1]Gene location (Mouse)Chr.Chromosome 3 (mouse)[2]Band3|3 H3Start151,143,524 bp[2]End151,250,723 bp[2]RNA expression patternBgeeHumanMo...

For the Winter Olympics, there are three venues starting with the letter 'N', 16 starting with the letter 'O', 14 starting with the letter 'P', none starting with the letter 'Q', and eight starting with the letter 'R'. N Norefjell hosted the downhill and giant slalom alpine skiing events for the 1952 Winter Olympics in Oslo. Venue Games Sports Capacity Ref. Nakiska 1988 Calgary Alpine skiing, Freestyle skiing (demonstration) Not listed. [1] Norefjell 1952 Oslo Alpine skiing (downhill...

سعادة (لقب) لودافايك أشر لودافايك أشر عام 2015 نائب رئيس وزراء هولندا تولى المنصب5 نوفمبر 2012 رئيس الوزراء مارك روته Maxime Verhagen Minister of Social Affairs and Employment of the Netherlands تولى المنصب5 نوفمبر 2012 رئيس الوزراء مارك روته Henk Kamp Acting Mayor of Amsterdam في المنصب12 مارس 2010 – 7 يوليو 2010 جوب كوهن Eberhard ...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助�...

أشرف بن شرقي بن شرقي مع الزمالك المصري عام 2020 معلومات شخصية الاسم الكامل أشرف بن شرقي[1] الميلاد 24 سبتمبر 1994 (العمر 29 سنة)[1]أولاد زباير، المغرب الطول 1.76 م (5 قدم 9 1⁄2 بوصة)[2] مركز اللعب الجناح / وسط هجومي الجنسية المغرب معلومات النادي النادي الحالي �...

Дунгане в Казахстане в первые десятилетия XXI века превратились в крупнейшую дунганскую общину в центральноазиатском регионе (62 тыс. чел), опередив дунган Киргизии (60 тысяч) и Узбекистана. 3 000[1] дунганских беженцев поселились на территории Российской империи одной �...

Tasso di natalità per paese (2023) Il tasso di natalità è il rapporto tra il numero delle nascite in una comunità o in un popolo durante un periodo di tempo e la quantità della popolazione media dello stesso periodo[1]. Il tasso di natalità misura la frequenza delle nascite di una popolazione in un arco di tempo (normalmente un anno) ed è calcolato come rapporto tra il numero dei nati in quel periodo e la popolazione media. Indice 1 Descrizione 2 In politica 3 Controllo della p...

Manado United 9Nama lengkapManado United 9JulukanPaus BiruBerdiri2010StadionStadion Klabat Kota Manado, Provinsi Sulawesi Utara(Kapasitas: 30.000)Ketua Umum Harley Benfica Mangindaan (pendiri)Pelatih Muhammad Zein Al HadadLigaLiga Primer Indonesia2011Peringkat 17 Kostum kandang Kostum tandang Manado United 9 adalah sebuah tim sepak bola Indonesia yang berbasis di Kota Manado. Klub yang didirikan tahun 2010 ini bermain di Liga Primer Indonesia musim 2011. Klub ini dilatih oleh Muhammad Zein Al...

Basic method for pseudo-random number sampling Inverse transform sampling (also known as inversion sampling, the inverse probability integral transform, the inverse transformation method, or the Smirnov transform) is a basic method for pseudo-random number sampling, i.e., for generating sample numbers at random from any probability distribution given its cumulative distribution function. Inverse transformation sampling takes uniform samples of a number u {\displaystyle u} between 0 and 1, int...

この記事の主題はウィキペディアにおける独立記事作成の目安を満たしていないおそれがあります。目安に適合することを証明するために、記事の主題についての信頼できる二次資料を求めています。なお、適合することが証明できない場合には、記事は統合されるか、リダイレクトに置き換えられるか、さもなくば削除される可能性があります。出典検索?: 世界痛...

Il testamentoTitolo originaleThe Testament AutoreJohn Grisham 1ª ed. originale1999 1ª ed. italiana1999 GenereRomanzo SottogenereLegal thriller Lingua originaleinglese Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Il testamento (The Testament) è un romanzo di John Grisham, pubblicato nel 1999. Il libro è stato tradotto in trentadue lingue.[1] Nel 2000, Il testamento (secondo un'indagine della Publishing Trends, rivista anglosassone) ha raggiunto il record mondiale delle vendite, risult...

Classique de Saint-Sébastien 1988GénéralitésCourse 8e Classique de Saint-SébastienDate 13 août 1988Distance 244 kmPays traversé(s) EspagneLieu de départ Saint-SébastienLieu d'arrivée Saint-SébastienPartants 171Vitesse moyenne 39,610 km/hRésultatsVainqueur Gert-Jan TheunisseDeuxième Enrique AjaTroisième Steven RooksClassique de Saint-Sébastien 1987Classique de Saint-Sébastien 1989modifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata La 8e édition de la Classique de Saint-S...

Quirin de NeussFonctionTribunBiographieNaissance RomeDécès 30 mars 116RomeÉpoque Haut Empire romainEnfant Balbine de RomeGens InconnuAutres informationsÉtape de canonisation SaintFête 30 avrilmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Statue de saint Quirin (XVIIIe siècle) vénérée à Houtaing, Ath, Belgique. Châsse de saint Quirin à Neuss. Saint Quirin de Rome est un saint martyr de l'Église catholique. Sa fête est célébrée le 30 avril[1],[2]. Introduction Il existe ...