Anglo-Australian Telescope
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Hiasan keramik di Kubah Shakhrah, Yerusalem. Anikonisme dalam Islam adalah pelarangan dalam Islam terhadap penciptaan gambar makhluk hidup yang bernyawa. Pelarangan yang paling mutlak adalah gambar Allah, diikuti oleh penggambaran Nabi Muhammad, dan kemudian nabi-nabi Islam dan kerabat Nabi Muhammad, tetapi penggambaran semua manusia dan hewan tidak dianjurkan dalam hadis dan oleh tradisi lama para ulama, terutama Sunni. Hal ini telah menyebabkan seni Islam didominasi oleh pola geometris Isla...

خط عرض 38° شمالمعلومات عامةالكتابة بالحروف اللاتينية حسب ماكون-رايشور Samp'alsŏn الرومنة الكورية المنقحة Sampalseon البلد إيطاليااليونانتركيا الإحداثيات 38°N 0°E / 38°N 0°E / 38; 0 خط عرض 37° شمال خط عرض 39° شمال تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات 38° خط عرض 38 شمال خريطة لجميع �...

Temple Square Hospitality CorporationCompany typePrivateIndustryHospitalityFoundedSalt Lake City, Utah, United States (November 7, 1988 (1988-11-07))FounderPresiding Bishopric of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day SaintsHeadquartersSalt Lake City, Utah, United StatesArea servedSalt Lake City, Utah, United StatesKey peopleGary Porter (President / CEO)Clark Stenquist (VP / Controller)ServicesWeddingsFloristryBusiness gatheringsCateringRestaurantsTourismParentDeseret Managem...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

Musée ZadkineFaçade sur jardin du musée Zadkine, rue d'Assas à Paris.Informations généralesType Musée d'artOuverture 19 avril 1982Visiteurs par an 20 749 (2016)30 801 (2017)[réf. nécessaire]Site web zadkine.paris.frCollectionsCollections Ossip Zadkine et Valentine PraxNombre d'objets 400 sculptures500 œuvres sur papierLocalisationPays FranceCommune ParisAdresse 100 bis, rue d'AssasCoordonnées 48° 50′ 34″ N, 2° 20′ 01″ E...

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari Civil liberties di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan penerjem...

Church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach Erfreut euch, ihr HerzenBWV 66.266Church cantata by J. S. BachNikolaikirche, Leipzig, 1749 engravingRelatedbased on BWV 66.1OccasionSecond Day of EasterChoralepart of Christ ist erstandenPerformed10 April 1724 (1724-04-10): LeipzigMovements6Vocal SATB choir solo: alto, tenor and bass Instrumentaltrumpet2 oboesbassoon2 violinsviolacontinuo Erfreut euch, ihr Herzen (Rejoice, you hearts),[1] BWV 66.2, BWV 66, [2] is...

Athabaskan language of California, US Not to be confused with the Hup language. HupaNa꞉tinixwe Mixine꞉wheʼNative toUnited StatesRegionCalifornia (Hoopa Valley)Ethnicity2,000 Hupa (2007)Native speakers1 (2015)[1]RevivalL2 users: 30 (2007)Language familyDené–Yeniseian? Na-DenéAthabaskan–EyakAthabaskanPacific Coast AthabaskanHupaLanguage codesISO 639-2hupISO 639-3hupGlottologhupa1239ELPHupaHupa is classified as Critically Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's...

Bagian dari seriGereja Katolik menurut negara Afrika Afrika Selatan Afrika Tengah Aljazair Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi Chad Eritrea Eswatini Etiopia Gabon Gambia Ghana Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guinea Khatulistiwa Jibuti Kamerun Kenya Komoro Lesotho Liberia Libya Madagaskar Malawi Mali Maroko Mauritania Mauritius Mesir Mozambik Namibia Niger Nigeria Pantai Gading Republik Demokratik Kongo Republik Kongo Rwanda Sao Tome dan Principe Senegal Seychelles Sierra Leone Somalia Somaliland ...

Historic house in Vermont, United States United States historic placeFowler-Steele HouseU.S. National Register of Historic Places LocationN. Main St., Windsor, VermontCoordinates43°29′24″N 72°23′10″W / 43.49000°N 72.38611°W / 43.49000; -72.38611Area2 acres (0.81 ha)Built1805 (1805)Architectural styleGreek Revival, FederalNRHP reference No.82001710[1]Added to NRHPJune 17, 1982 The Fowler-Steele House, also known historically ...

Swedish opera singer Signe Rappe-Welden (1909) Signe Rappe-Welden née Rappe (24 September 1879 – 21 May 1974) was a Swedish operatic soprano and voice teacher. She made her dëbut in 1906 in Mannheim, acclaimed for both her voice and acting ability. She performed in Vienna from 1908 to 1911 and received the title of court singer in Sweden in 1909. Her most successful role was that of Salome in Covent Garden in 1910, which she later performed with Richard Strauss as conductor. After a short...

Presiden Menteri Thüringen sejak tahun 1920 antara lain sebagai berikut.[1] Daftar Partai Politik: SPD DDP DVP Landbund NSDAP SED CDU Kiri Militer Gambar Nama (Lahi...

1059 papal bull regarding papal election In nomine Domini (Latin: In the name of the Lord) is a papal bull written by Pope Nicholas II. The bull was issued on 13 April 1059[note 1] and caused major reforms in the system of papal election, most notably establishing the cardinal-bishops as the sole electors of the pope, with the consent of minor clergy. Background Until the publication of the bull, the election of the pope was often decided by a puppet electoral process.[2] The ...

Batalla de Bibracte Parte de Guerra de las Galias Mapa de BibracteFecha 29 de junio de 58 a. C.[1][2]Lugar Cercanías de Bibracte, cerca de la actual Autun, Francia[3]Coordenadas 46°55′00″N 4°02′00″E / 46.916667, 4.033333Resultado Victoria romana decisivaConsecuencias Fin de la migración helvéticaBeligerantes República romana Eduos Helvecios[4][5] Boyos[4] Tulingos[4] Rauracos[4] Latobrigos[4]...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: 1993 in India – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) List of events ← 1992 1991 1990 1993 in India → 1994 1995 1996 Centuries: 18th 19th 20th 21st Decades: 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s ...
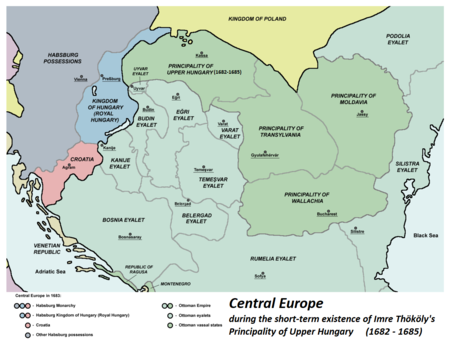
Military conflicts between Ottomans and Holy League (1683–1699) Great Turkish WarPart of the Ottoman–Habsburg wars, the Russo-Ottoman wars and the Polish–Ottoman warsFrom top left: The Battle of Vienna, the Siege of Buda, the Azov campaigns, the Battle of ZentaDate14 July 1683 – 26 January 1699(15 years, 6 months, 1 week and 5 days)Location Central Europe Eastern Europe Balkans Result Holy League victoryTerritorialchanges The Habsburg monarchy wins lands in Hungary...

Species of butterfly Cambridge vagrant male N. t. thalassinaBobiri Forest, Ghana Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Lepidoptera Family: Pieridae Genus: Nepheronia Species: N. thalassina Binomial name Nepheronia thalassina(Boisduval, 1836) Synonyms Pieris thalassina Boisduval, 1836 Eronia thalassina sinalata Suffert, 1904 Eronia thalassina f. hesione Stoneham, 1957 Eronia thalassina f. proserpina Stoneham, 1957 Eronia ver...
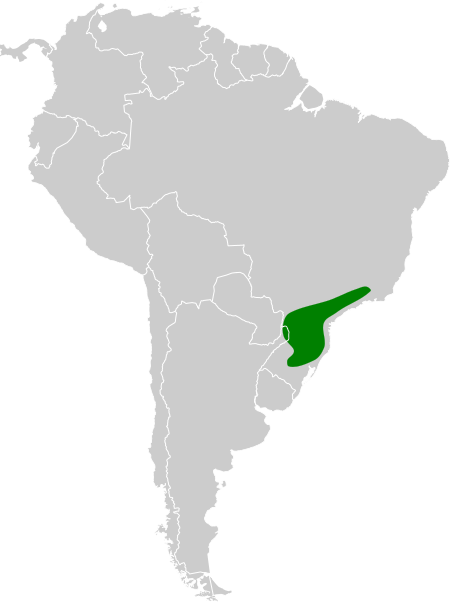
Species of bird Araucaria tit-spinetail Conservation status Near Threatened (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Aves Order: Passeriformes Family: Furnariidae Genus: Leptasthenura Species: L. setaria Binomial name Leptasthenura setaria(Temminck, 1824) The Araucaria tit-spinetail (Leptasthenura setaria) is a Near Threatened species of bird in the Furnariinae subfamily of the ovenbird family Furnariidae. It is fou...

3e cérémonie des Oscars L'hôtel Ambassador, qui a accueilli la 3e cérémonie des Oscars Oscars du cinéma Organisée par l'Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences Détails Date 5 novembre 1930 Lieu Ambassador HotelHollywood États-Unis Présentateur Conrad Nagel Site web http://oscar.go.com/ Résumé Meilleur film À l'Ouest, rien de nouveau Films les plus nommés Parade d'amour (6) Chronologie 2e cérémonie des Oscars 4e cérémonie des Oscars modifier La ...

Manzanilla de Castilla TaxonomíaReino: PlantaeSubreino: TracheobiontaDivisión: MagnoliophytaClase: MagnoliopsidaSubclase: AsteridaeOrden: AsteralesFamilia: AsteraceaeSubfamilia: AsteroideaeTribu: AnthemideaeGénero: MatricariaEspecie: M. chamomillaL., 1753[editar datos en Wikidata] La manzanilla de Castilla, manzanilla alemana, dulce o cimarrona (Matricaria chamomilla) es una especie de planta herbácea anual de la familia de las asteráceas. Nativa de Europa y las regiones...









