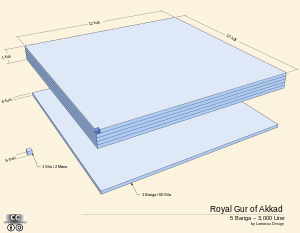
Ancient Mesopotamian units of measurement
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Pensiunan kapal selam anja modern Star III dari Scripps Institution of Oceanography Kapal selam anja adalah kapal bawah air yang perlu diangkut dan didukung oleh kapal permukaan atau sarana. Ini membedakan kapal selam anja dari kapal selam mandiri, yang mampu beroperasi secara mandiri.[1] Ada banyak jenis kapal selam anja, termasuk kendaraan tumpang manusia (HOV) dan kapal nirawak, [2] yang dikenal sebagai kendaraan kendali jarak jauh (ROV) atau kendaraan bawah air nirawak (UU...

Administrasi Pariwisata Nasional Tiongkok中华人民共和国国家旅游局Guójiā Lǚyóu JúLambang Nasional Republik Rakyat TiongkokInformasi lembagaDibentuk1982Dibubarkan19 Maret 2018Lembaga penggantiKementerian Kebudayaan dan Pariwisata TiongkokJenisNasionalWilayah hukum TiongkokKantor pusatBeijingPejabat eksekutifLi Jinzao (李金早), ChairmanLembaga indukDewan NegaraSitus webzh.travelchina.gov.cn Administrasi Pariwisata Nasional Tiongkok (APNT) (Hanzi sederhana: 国家旅�...

Puteri Indonesia 2022Tanggal27 Mei 2022TempatPlenary Hall, Jakarta Convention Center, Jakarta, IndonesiaTemaBorobudur: The Beauty and Uniqueness of Borobudur TemplePembawa acaraChoky SitohangPatricia GouwBubah Alfian (co-host)Anastasia Praditha (co-host)Pengisi acaraBunga Citra LestariMawar Eva de JonghVidi AldianoAndi RiantoMagenta OrchestraTamuHarnaaz SandhuSireethorn LeearamwatKarla GuilfúPenyiaranSCTVVidioPeserta44Finalis/Semifinalis11PemenangLaksmi De-Neefe Suardana Bali&...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Tamba (disambiguasi). Provinsi Tamba (丹波国code: ja is deprecated , tamba no kuni) adalah provinsi lama Jepang dengan wilayah yang sekarang menjadi bagian tengah prefektur Kyoto dan bagian timur prefektur Hyogo. Tamba berbatasan dengan provinsi Harima, Omi, Settsu, Tajima, Tango, Wakasa dan Yamashiro. Ibu kota diperkirakan berada di lokasi yang sekarang menjadi kota Kameoka. Tamba diperintah berbagai daimyo hingga ditaklukkan Oda Nobunaga yang kemudian memberika...

Radio station in Texas, United StatesKQBRLubbock, TexasUnited StatesBroadcast areaLubbock metropolitan areaFrequency99.5 MHzBrandingLonestar 99.5ProgrammingFormatCountryAffiliationsCompass Media NetworksPremiere NetworksOwnershipOwnerTownsquare Media(Townsquare License, LLC)Sister stationsKFMXKFYOKKAMKKCLKZIIHistoryFirst air date1964 (as KWGN-FM)Former call signsKFYO-FM (1948-1952)KWGN-FM (1964-1966)KWGO-FM (1966-1981)KRLB-FM (1981-1999)KCRM (1999)Call sign meaningreference to The Bear, the s...
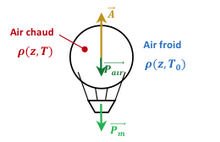
Ne doit pas être confondu avec Poussée (aérodynamique). La poussée d'Archimède permet de concevoir la balance hydrostatique utilisée par les orfèvres du Moyen Âge pour analyser la densité des alliages d'or et d'argent. Les montgolfières exploitent le principe de la poussée d'Archimède, en devenant plus légères que l’air ambiant[1]. La poussée d'Archimède est la force particulière que subit un corps placé entièrement ou partiellement dans un fluide (liquide ou gaz) et sou...

Liga Champions UEFA 2010–2011Wembley Stadium di London menjadi tuan rumah finalInformasi turnamenJadwalpenyelenggaraanKualifikasi:29 Juni – 25 Agustus 2010Kompetisi utama:14 September 2010 – 28 Mei 2011Jumlahtim pesertaKompetisi utama: 32Total: 76 (dari 52 asosiasi)Hasil turnamenJuara Barcelona (gelar ke-4)Tempat kedua Manchester UnitedStatistik turnamenJumlahpertandingan125Jumlah gol355 (2,84 per pertandingan)Pencetak golterbanyak Lionel Messi (12 gol)← 2009–2010 2011...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (mars 2014). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Comm...

Pangkalan Utama TNI Angkatan Laut IIILambang Lantamal IIIAktif4 Februari 1950Negara IndonesiaCabangTNI Angkatan LautTipe unitPangkalan Utama Angkatan LautBagian dariKomando Armada IMarkasJakarta Utara, Jakarta UtaraMotoBhakti Nala YudhaBaret BIRU LAUT Situs weblantamal3-koarmada1.tnial.mil.idTokohKomandanBrigadir Jenderal TNI (Mar) Harry IndartoWakil KomandanKolonel Laut (P) Whisnu Kusardianto, S.E., M.H., CRMP. Pangkalan Utama TNI Angkatan Laut III atau (Lantamal III) adalah pangka...

Questa voce sull'argomento cestisti statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Josh Hart Hart con la maglia di Villanova, il 13 febbraio 2017 Nazionalità Stati Uniti Altezza 196 cm Peso 97 kg Pallacanestro Ruolo Guardia/Ala piccola Squadra N.Y. Knicks Carriera Giovanili Sidwell Friends School2013-2017 Villanova Wildcats146 (1.927) Squadre di club 2017-2019 L.A. ...

Doa Santo FransiskusJudul asliBelle prière à faire pendant la MesseTerbit perdanaLa ClochetteNegaraPrancisBahasaBahasa PrancisPenerbitLa Ligue de la Sainte-Messe(ed. Romo Esther Bouquerel)TerbitDesember 1912 (1912-12) Doa Santo Fransiskus adalah sebuah doa Kristen yang dikenal luas untuk perdamaian. Doa ini sering diasosiasikan dengan Santo Fransiskus dari Asisi (c. 1182 – 1226), tapi tidak tercantum dalam tulisan-tulisannya. Bentuk saat ini dari doa tidak dapat dilacak lebih j...

This is the talk page for discussing improvements to the Anonymous and the Internet template. Put new text under old text. Click here to start a new topic. New to Wikipedia? Welcome! Learn to edit; get help. Assume good faith Be polite and avoid personal attacks Be welcoming to newcomers Seek dispute resolution if needed Archives: 1Auto-archiving period: 30 days Internet culture Template‑classThis template is within the scope of WikiProject Internet culture, a collaborative effort to im...

Voce principale: Società Sportiva Manfredonia Calcio. Società Sportiva Manfredonia CalcioStagione 2004-2005Sport calcio Squadra Manfredonia Allenatore Leonardo Bitetto Serie C21º (in Serie C1) Coppa Italia Serie COttavi di finale 2003-2004 2005-2006 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa pagina raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti la Società Sportiva Manfredonia Calcio nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione 2004-2005. Indice 1 Rosa 2 Risultati 2.1 Serie C2 2.1.1 Girone ...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

Region in CanadaInuvialuit Settlement Region Inuvialuit Nunangit SannaiqtuaqRegionInuvik, the largest community in the regionISR in Yukon and NWTCountryCanadaTerritoriesNorthwest TerritoriesYukonInuvialuit Final Agreement1984Subregions List Beaufort SeaMackenzie River deltaYukon coastNorthwest portion of Northwest TerritoriesWestern Arctic Archipelago Government • TypeBoard of Directors • Chair & CEODuane Ningaqsiq Smith[1]Area • Total435,000&#...
Area of a country where companies are very lightly taxed Free port redirects here. Not to be confused with various places named Freeport. Porto franco redirects here. Not to be confused with Brazilian city Porto Franco. This is currently being merged. After a discussion, consensus to merge this into Free-trade zone was found. You can help implement the merge by following the instructions at Help:Merging and the resolution on the discussion. Process started in May 2023. You can help expan...

52 relasi ekuivalensi pada himpunan 5-anggota yang digambarkan dengan matriks biner 5x5 (kotak yang berwarna, termasuk yang abu-abu, melambangkan 1; kotak putih melambangkan 0.) Indeks kolom dan baris dari kotak yang berwarna adalah anggota yang berkaitan, sementara warna yang dibedakan, selain abu-abu, mengindikasikan kelas ekuivalensi (masing-masing kotak abu-abu merupakan kelas ekuivalensinya sendiri). Dalam matematika, relasi ekuivalensi adalah relasi biner yang bersifat reflektif, simetr...

Эту статью предлагается разделить на Глитч и Сбой.Пояснение причин и обсуждение — на странице Википедия:К разделению/28 ноября 2021. Возможно, она слишком велика или её содержимое не имеет логической связности, и предлагается разнести статью в Глитч и Сбой. Не удаляйте ша...

Group of phyllosilicate minerals This article is about the mineral or gem. For other uses, see Mica (disambiguation). MicaGeneralCategoryPhyllosilicatesFormula(repeating unit)AB2–3(X, Si)4O10(O, F, OH)2IMA symbolMca[1]IdentificationColorpurple, rosy, silver, gray (lepidolite); dark green, brown, black (biotite); yellowish-brown, green-white (phlogopite); colorless, transparent (muscovite)CleavageAlmost perfectFractureflakyMohs scale hardness2.5–4 (lepidolite); 2.5–3 (biotite); 2...

この項目では、米を中心としたイネ科の穀物を炊いた食品について説明しています。 食事全般については「食事」をご覧ください。 新潟県中魚沼郡の食品メーカーについては「ごはん (食品メーカー)」をご覧ください。 2017年公開の日本映画については「ごはん (映画)」をご覧ください。 米飯 飯(めし)は、イネ科の穀物全般、とくに米へ水を加えて煮たり蒸したり�...