Alfred William Alcock
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

This is an overview of the regular, recurring, and other characters of the TV series The Last Ship. Overview Character Portrayed by Occupation Seasons 1 2 3 4 5 Tom Chandler Eric Dane Commanding Officer, USS Nathan James Chief of Naval Operations US Naval Academy Instructor Main Rachel Scott Rhona Mitra Paleomicrobiologist Main — Mike Slattery Adam Baldwin Executive Officer, USS Nathan James Commanding Officer, USS Nathan James Main Russ Jeter Charles Parnell Command Master Chief Petty Offi...

Pangkat militer Indonesia Angkatan Darat Angkatan Laut Angkatan Udara Perwira Jenderal Besar Laksamana Besar Marsekal Besar Jenderal Laksamana Marsekal Letnan Jenderal Laksamana Madya Marsekal Madya Mayor Jenderal Laksamana Muda Marsekal Muda Brigadir Jenderal Laksamana Pertama Marsekal Pertama Kolonel Kolonel Kolonel Letnan Kolonel Letnan Kolonel Letnan Kolonel Mayor Mayor Mayor Kapten Kapten Kapten Letnan Satu Letnan Satu Letnan Satu Letnan Dua Letnan Dua Letnan Dua Bintara Pembantu Letnan...

Perkiraan Konsumsi Energi dari tiga tipe peradaban yang didefinisikan oleh Skala Kardashev Proyeksi Skala Kardashev untuk peradaban manusia dari tahun 1900 hingga 2030 berdasarkan data dari International Energy Agency World Energy Outlook. Skala Kardashev (bahasa Rusia: Шкала Кардашева, Shkala Kardasheva) adalah metode untuk mengukur tingkat kemajuan teknologi suatu peradaban berdasarkan jumlah energi yang dapat digunakannya. Pengukuran tersebut diusulkan oleh astronom Soviet Ni...

Latvijas Radio Création 1er novembre 1925 Forme juridique Société anonyme à capitaux publics Siège social Rīga Lettonie Direction Aldis Pauliņš (président) Actionnaires État letton (60%) Activité Audiovisuel Produits Chaînes de radio, production radiophonique, publicité et internet Sociétés sœurs Latvijas Televīzija Effectif 292 (2022)[1] Site web www.latvijasradio.lsm.lv/lv/lr/ Chiffre d'affaires 12,8 M€ (2022)[1] Bilan comptable 7,8 M€ (2022)[1] Résultat net −2...

Questa voce sull'argomento diritto romano è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento diritto romano è priva o carente di note e riferimenti bibliografici puntuali. Sebbene vi siano una bibliografia e/o dei collegamenti esterni, manca la contestualizzazione delle fonti con note a piè di pagina o altri riferimenti precisi che indichino puntualmente la provenienza delle informazioni. Puoi migliorare questa...

Запрос «Пугачёва» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения. Алла Пугачёва На фестивале «Славянский базар в Витебске», 2016 год Основная информация Полное имя Алла Борисовна Пугачёва Дата рождения 15 апреля 1949(1949-04-15) (75 лет) Место рождения Москва, СССР[1]...

English football manager (born 1977) Sam Collins Collins as manager of York City in 2018Personal informationFull name Sam Jason Collins[1]Date of birth (1977-06-05) 5 June 1977 (age 46)[2]Place of birth Pontefract, EnglandHeight 6 ft 3 in (1.91 m)[3]Position(s) Centre backYouth career000–1994 Huddersfield TownSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1994–1999 Huddersfield Town 37 (0)1999–2002 Bury 82 (2)2002–2006 Port Vale 135 (11)2005–2006 → ...

American state election 1990 Michigan gubernatorial election ← 1986 November 6, 1990 1994 → Nominee John Engler James Blanchard Party Republican Democratic Running mate Connie Binsfeld Olivia Maynard Popular vote 1,276,134 1,258,539 Percentage 49.8% 49.1% County results Engler: 40-50% 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% Blanchard: &#...
Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Permainan daring – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (November 2013) Permainan daring (bahasa Inggris: online game) adalah jenis permainan komputer yang memanfaatkan jejaring komputer. Jej...

Not to be confused with Cash for access (disambiguation), Cash for Honours, or 2010 cash for influence scandal. The Palace of Westminster The 2009 cash for influence scandal (also cash for amendments or cash for laws) was a political scandal in the United Kingdom in 2009 concerning four Labour Party Life Peers offering to help make amendments to legislation for up to £120,000. The Lords Privileges Committee recommended the two men be suspended from the House for up to six months after an in...

In combinatorics, a Davenport–Schinzel sequence is a sequence of symbols in which the number of times any two symbols may appear in alternation is limited. The maximum possible length of a Davenport–Schinzel sequence is bounded by the number of its distinct symbols multiplied by a small but nonconstant factor that depends on the number of alternations that are allowed. Davenport–Schinzel sequences were first defined in 1965 by Harold Davenport and Andrzej Schinzel to analyze linear diff...

184th Paratroopers Division NemboActive1942-1944Country Kingdom of ItalyBranch Royal Italian ArmyTypeInfantryRoleAirborneSizeDivisionEngagementsWorld War II: Italian campaign InsigniaIdentificationsymbol Nembo Division gorget patchesMilitary unit The 184th Paratroopers Division Nembo (Italian: 184ª Divisione paracadutisti Nembo) was an airborne division of the Royal Italian Army during World War II. After the Armistice of Cassibile the division joined the Italian Co-belligerent Arm...

Nahason BiografiKelahiranMesir Kematian1312 SM KeluargaAnakSalmon, Elimelekh AyahAminadab SaudaraEliseba Nahason dalam kitab Kejadian dari Kitab Suci Ibrani dan Alkitab, adalah salah satu anak dari Aminadab dan isterinya yang tidak diketahui namanya. Ia mempunyai saudari yang bernama Eliseba, istri Harun.[1] Ia mempunyai seorang putra bernama Salma (Salmon).[2] Nahason adalah seorang pemimpin (jenderal) suku Yehuda.[3] Melalui keturunan Nahason dilahirkanlah Daud h...
この存命人物の記事には検証可能な出典が不足しています。 信頼できる情報源の提供に協力をお願いします。存命人物に関する出典の無い、もしくは不完全な情報に基づいた論争の材料、特に潜在的に中傷・誹謗・名誉毀損あるいは有害となるものはすぐに除去する必要があります。出典検索?: 浜亮太 – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · ...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع القصبة (توضيح). قرية القصبة - قرية - تقسيم إداري البلد اليمن المحافظة محافظة صنعاء المديرية مديرية أرحب العزلة عزلة شعب السكان التعداد السكاني 2004 السكان 831 • الذكور 409 • الإناث 422 • عدد الأسر 74 • عدد المساكن 69 معلومات أخ�...

Ghost town in Indiana, United StatesBlack Rock, IndianaGhost townBlack RockLocation in Warren CountyCoordinates: 40°22′04″N 87°05′49″W / 40.36778°N 87.09694°W / 40.36778; -87.09694CountryUnited StatesStateIndianaCountyWarrenTownshipWarrenElevation[1]525 ft (160 m)Time zoneUTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) • Summer (DST)UTC-4 (EDT)ZIP code47970Area code765GNIS feature ID431141[1] Black Rock is an extinct community located in Warren...

Piotrków TrybunalskiNight view of Old Town, Słowacki Street, Piotrkowska Manufaktura, street in Old Town, Royal Castle, Market Square Hiệu kỳHuy hiệuTập tin:Piotrkow Trybunalski logo 2018.jpgBiểu trưngLỗi Lua trong Mô_đun:Location_map tại dòng 583: Không tìm thấy trang định rõ bản đồ định vị. "Mô đun:Location map/data/Łódź Voivodeship", "Bản mẫu:Bản đồ định vị Łódź Voivodeship", và "Bản mẫu:Location map ...
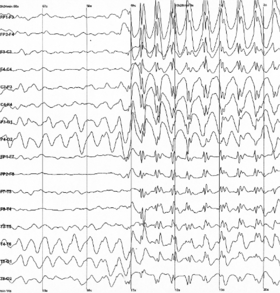
Electrophysiological monitoring method to record electrical activity of the brain Not to be confused with other types of electrography. EEG redirects here. For other uses, see EEG (disambiguation). ElectroencephalographyEpileptic spike and wave discharges monitored EEG[edit on Wikidata] Electroencephalography (EEG)[1] is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynapti...

Human settlement in EnglandGodwickThe church tower at the site of Godwick villageGodwickLocation within NorfolkCivil parishTittleshallDistrictBrecklandShire countyNorfolkRegionEastCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited Kingdom List of places UK England Norfolk 52°45′45″N 0°49′52″E / 52.762436°N 0.831°E / 52.762436; 0.831 Godwick is a deserted village in the county of Norfolk. Its location was south of Fakenham between the villages of Tittleshall and...

Railway line in Chiba Prefecture, Japan Kururi LineKururi Line E130 series DMUsOverviewNative name久留里線StatusIn operationOwnerJR EastLocaleChiba PrefectureTerminiKisarazuKazusa-KameyamaStations14ServiceOperator(s)JR EastDepot(s)KisarazuRolling stockKiHa E130 series DMUHistoryOpened1912TechnicalLine length32.2 km (20.0 mi)Number of tracksEntire line single trackedCharacterRuralTrack gauge1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in)ElectrificationNoneOperating speed65 km/h (40 mph)...
