Alexander McDougall
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Federal government of Lincoln's North U.S United States of America Union 1861–1865 Top: 1861–1863Bottom: 1863–1865 Coat of arms 'Motto: 'E pluribus unumOut of many, oneAnthem: Hail, Columbia (de facto)My Country, 'Tis of Thee (de facto)Map of the division of the states in the American Civil War (1861–1865). Northern and Western free states loyal to the United States Southern slave states which seceded and formed the Confederacy Southern sla...
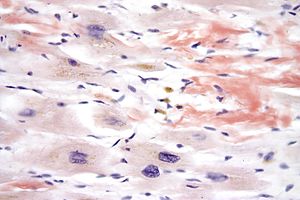
Artikel ini memberikan informasi dasar tentang topik kesehatan. Informasi dalam artikel ini hanya boleh digunakan untuk penjelasan ilmiah; bukan untuk diagnosis diri dan tidak dapat menggantikan diagnosis medis. Wikipedia tidak memberikan konsultasi medis. Jika Anda perlu bantuan atau hendak berobat, berkonsultasilah dengan tenaga kesehatan profesional. Kardiomiopati restriktifGambaran histologi amyloidosis jantung, penyebab kardiomiopati restriktif.Informasi umumNama lainKardiomiopati oblite...

Koordinat: 27°S 103°E / 27°S 103°E / -27; 103 Cekungan Wharton Cekungan Wharton adalah wilayah laut di Samudra Hindia timur laut. Namanya diambil dari William Wharton (1843-1905), ahli hidrografi dari Angkatan Laut Britania Raya. Nama lainnya adalah Cekungan Cocos (diambil dari Kepulauan Cocos) dan Cekungan Australia Barat.[1] Cekungan ini terletak di sebelah timur Punggung Ninety East dan sebelah barat Australia Barat. Cekungan Wharton memiliki kaitan deng...

Jan Hendrik Weissenbruch, karya Jozef Israëls (1882) Jan Hendrik Weissenbruch, juga dikenal sebagai Hendrik Johannes Weissenbruch (19 Juni 1824 – 24 Maret 1903) adalah seorang pelukis Belanda dari Aliran Den Haag. Ia dikenal karena karya-karya warna cairnya. Daftar pustaka Sillevis, John & Tabak, Anne. The Hague School Book, Waanders Uitgegevers, Zwolle (2004), pp. 229–237 Leeuw, Ronald de; Sillervis, John and Dumas, Charles (1983): The Hague School: Dutch Masters ...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Parson's Cause – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 1760s political dispute in British Virginia George Cooke's 1834 depiction of Patrick Henry arguing the Parson's Cause case at the Ha...

Jamur merang Volvariella volvaceae Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Fungi Divisi: Basidiomycota Kelas: Homobasidiomycetes Ordo: Agaricales Famili: Pluteaceae Genus: Volvariella Spesies: V. volvacea Nama binomial Volvariella volvacea(Bulliard ex Fries) Singer Jamur merang (Volvariella volvacea, sinonim: Volvaria volvacea, Agaricus volvaceus, Amanita virgata atau Vaginata virgata) adalah spesies jamur pangan yang biasa tumbuh di Asia Timur dan Tenggara yang beriklim tropis atau subtropis. Ist...

كارلتون سكينر معلومات شخصية الميلاد 8 أبريل 1913 بالو ألتو الوفاة 22 يونيو 2004 (91 سنة) بوسطن مواطنة الولايات المتحدة مناصب حاكم غوام في المنصب17 سبتمبر 1949 – 22 أبريل 1953 الحياة العملية المدرسة الأم جامعة ويسليان المهنة سياسي، وضابط الحزب �...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat BTV. Artikel ini bukan mengenai B-Channel atau Biznet Home. BeritaSatu beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk media lain bermerek sama yang segrup, lihat B Universe § Media. BTVNama sebelumnyaQ Channel (1998-2005)QTV (2005-2011)BeritaSatu (2011-2022)JenisJaringan televisiSloganBersatu MenginspirasiNegaraIndonesiaBahasaBahasa IndonesiaPendiriPeter F. GonthaTanggal siaran perdana1 Mei 1998 (siaran percobaan)Tanggal peluncuran29 Mei 1998 (sebagai Q Channel)15 Septem...

May Wallace MaddoxLahir(1877-08-23)23 Agustus 1877Russiaville, Indiana, Amerika SerikatMeninggal11 Desember 1938(1938-12-11) (umur 61)Los Angeles, California, Amerika SerikatPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1914-1938Suami/istriThomas W. Maddox (?-1938) (kematiannya) (2 anak) May Wallace (23 Agustus 1877 – 11 Desember 1938) adalah seorang pemeran film perempuan Amerika Serikat.[1] Ia tampil dalam 63 film antara 1914 dan 1939. Filmografi pilihan The Cup of Life (192...

Questa voce sugli argomenti allenatori di calcio portoghesi e calciatori portoghesi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti dei progetti di riferimento 1, 2. Jorge Humberto Raggi Nazionalità Portogallo Altezza 173 cm Calcio Ruolo Attaccante Termine carriera 1966 - giocatore1972 - allenatore Carriera Squadre di club1 1957-1961 Académica69 (20)1961-1962 Inter2 (0)1962-1964 L.R. Vicenza25 (5)1964-1966&#...
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發...

Curious George 2: Follow That Monkey!SutradaraNorton VirgienProduserRon HowardBrian GrazerShare StallingsPemeranMartin BrygmannHenning MortzenKaya BruelLaus HoyerAnne HoyerKristian BolandPaul HuttelJens Matt Lauer Jacob TychsenPerusahaanproduksiUniversal Animation StudiosDistributorUniversal Home EntertainmentImagine EntertainmentTanggal rilis10 Juli 2009 (Denmark)7 Agustus 2009 (Swedia) 2010 (Amerika Serikat)Durasi77 menitBahasaInggris Curious George 2: Follow That Monkey! adalah film animas...

County in Texas, United States County in TexasDelta CountyCountyDelta County Courthouse in CooperLocation within the U.S. state of TexasTexas's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 33°23′N 95°40′W / 33.39°N 95.67°W / 33.39; -95.67Country United StatesState TexasFounded1870SeatCooperLargest cityCooperArea • Total278 sq mi (720 km2) • Land257 sq mi (670 km2) • Water21 sq mi (50&...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Antonio Re Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Difensore CarrieraSquadre di club1 1922-1927 Derthona46+ (0+)1927-1928 Vogherese? (?) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo → indica un trasferimento in prestito. Modifica dati su...

† Палеопропитеки Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:СинапсидыКласс:�...

جبهة التحرير العربية البلد دولة فلسطين تاريخ التأسيس 1969 المقر الرئيسي رام الله الأيديولوجيا بعثية الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل شعار جبهة التحرير العربية جزء من سلسلة عنالفكر البعثي المنظمات الأم حركة البعث العربي (1940–1947)حزب البعث ا...

British politician (1847-1934) The Most HonourableThe Marquess of Aberdeen and TemairKT KP GCMG GCVO PCLord Lieutenant of IrelandIn office11 December 1905 – 17 February 1915MonarchsEdward VII George VPrime MinisterSir Henry Campbell-Bannerman H. H. Asquith David Lloyd GeorgePreceded byThe Earl of DudleySucceeded byLord WimborneIn office8 February 1886 – 20 July 1886MonarchVictoriaPrime MinisterWilliam Ewart GladstonePreceded byThe Earl of CarnarvonSucceeded byThe Marques...

Samir Kuntarسمير القنطارSamir Kuntar saat mengunjungi Makam Hafez di Shiraz, Iran.Lahir(1962-07-20)20 Juli 1962[1]LebanonMeninggal19 Desember 2015(2015-12-19) (umur 53)SuriahSebab meninggalTewas karena ledakanKebangsaanLebanonPekerjaanMilitanDikenal atasSerangan Nahariya 1979Gerakan politikFront Pembebasan Palestina dan HizbullahGugatan kejahatanPembunuhanHukuman kriminalLima hukuman seumur hidupKarier militerPengabdianHizbullahLama dinas1978–2015Perang/pe...

Green copper-based pigment This article is about copper(II) acetate, used as a pigment. For other uses, see Verdigris (disambiguation). Verdigris Color coordinatesHex triplet#43B3AEsRGBB (r, g, b)(67, 179, 174)HSV (h, s, v)(177°, 63%, 70%)CIELChuv (L, C, h)(67, 45, 187°)Source[1]ISCC–NBS descriptorBrilliant bluish greenB: Normalized to [0–255] (byte) The Statue of Liberty, showing advanced patination; verdigris is responsible for the statue's iconic green colour....

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها...
