Agathoxylon
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Untuk stasiun kereta cepat dengan nama yang sama, lihat Stasiun Karawang (KCIC). Stasiun Karawang LW04LJ04 Stasiun Karawang, September 2022Tampak proyek pembangunan kanopi stasiun yang sedang berlangsungLokasi Jalan Arif Rahman HakimNagasari, Karawang Barat, Karawang, Jawa Barat 41312IndonesiaKoordinat6°18′30″S 107°17′49″E / 6.30833°S 107.29694°E / -6.30833; 107.29694Koordinat: 6°18′30″S 107°17′49″E / 6.30833°S 107.29694°E...
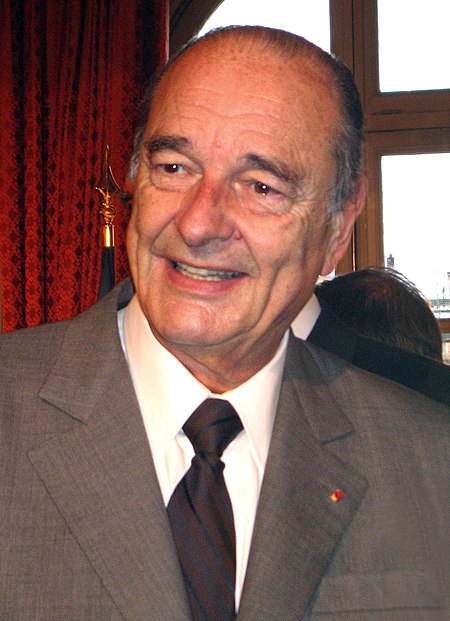

1992 2005 Référendum sur le quinquennat présidentiel Méthode de vote 24 septembre 2000 Type d’élection Référendum Corps électoral et résultats Inscrits 39 941 192 Votants 12 058 688 30,19 % Votes exprimés 10 118 348 Blancs et nuls 1 940 340 Oui (+ de 75 %) Oui (entre 72,5 et 75 %) Oui (entre 70 et 72,5 %) Oui (entre 50 et 70 %) Approuvez-vous le projet de loi constitutionnelle fixant la durée du manda...

العلاقات البوسنية الجامايكية البوسنة والهرسك جامايكا البوسنة والهرسك جامايكا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات البوسنية الجامايكية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين البوسنة والهرسك وجامايكا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة...

Mateus Uribe Piala Dunia FIFA 2018, Kolombia vs. Inggris.Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Mateus UribeTanggal lahir 21 Maret 1991 (umur 33)Tempat lahir Medellín, KolombiaTinggi 182 cm (6 ft 0 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini AméricaNomor 8Karier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2017 – América 30 (11)Tim nasional2017 – Kolombia 10 (0) * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya dihitung dari liga domestik Mateus Uribe (lahir 21 Maret 1991) adalah seoran...

NeverwasSutradaraJoshua Michael SternProduser Sidney Kimmel Greg Shapiro Ditulis olehJoshua Michael SternPemeran Ian McKellen Aaron Eckhart Brittany Murphy Nick Nolte William Hurt Jessica Lange Penata musikPhilip GlassSinematograferMichael GradyPenyuntingSteven KemperPerusahaanproduksi Kingsgate Films Legacy Filmworks Sidney Kimmel Entertainment DistributorNeverwas ProductionsTanggal rilis 09 September 2005 (2005-09-09) (Toronto) Durasi108 menitNegara Amerika Serikat Kanada Bah...

This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (March 2024) Ice hockey team in Rouen, FranceDragons de RouenNicknameDragonsCityRouen, FranceLeagueLigue Magnus1985-PresentFounded1982Home arenaCentre sportif Guy-Boissière(capacity: 2747)Colours PresidentThierry ChaixGeneral managerGuy FournierHead coachFabrice LhenryAsst. coachAri SaloCaptainMathieu RoyAffiliateDragons de Rouen IIWebsiteLes DragonsFran...

Artistic swimming has been contested at the Asian Games since the 1994 Games. The current Asiad program has competition in duet and team events,[1] but in past games, solo and combination events were also contested. Editions Games Year Host city Best nation XII 1994 Hiroshima, Japan Japan XIII 1998 Bangkok, Thailand Japan XIV 2002 Busan, South Korea Japan XV 2006 Doha, Qatar China XVI 2010 Guangzhou, China China XVII 2014 Incheon, South Korea China...

Election for governor of Maryland, U.S. 1919 Maryland gubernatorial election ← 1915 November 4, 1919 1923 → Nominee Albert Ritchie Harry Nice Party Democratic Republican Popular vote 112,240 112,075 Percentage 49.06% 48.99% County results Ritchie: 40–50% 50–60% Nice: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Governor befor...

International cricket tour Bangladeshi cricket team in the West Indies in 2022 West Indies BangladeshDates 16 June – 16 July 2022Captains Kraigg Brathwaite (Tests) Nicholas Pooran (ODIs & T20Is) Shakib Al Hasan (Tests)Tamim Iqbal (ODIs)Mahmudullah (T20Is)Test seriesResult West Indies won the 2-match series 2–0Most runs Kyle Mayers (153) Shakib Al Hasan (138)Most wickets Alzarri Joseph (12) Khaled Ahmed (10)Player of the series Kyle Mayers (WI)One Day International se...

Graphic IRC client by Microsoft Microsoft Comic ChatMicrosoft Chat version 2.5Original author(s)MicrosoftDeveloper(s)David Kurlander, Microsoft Research Virtual Worlds GroupInitial releaseAugust 13, 1996; 27 years ago (1996-08-13)Final release2.5 / March 1999; 25 years ago (1999-03) Written inC++Operating systemMicrosoft WindowsPlatformIBM PCAvailable inMultiple languages [1]TypeIRC clientsLicenseProprietaryNot to be confused with Windows Chat....

Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’art et une chronologie ou une date. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Chronologies Données clés 1612 1613 1614 1615 1616 1617 1618Décennies :1580 1590 1600 1610 1620 1630 1640Siècles :XVe XVIe XVIIe XVIIIe XIXeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies thématiques Art Architecture, Arts...

Angola 23.er puesto Titular Alternativo Datos generales Asociación Federación Angoleña de Fútbol Confederación CAF Seudónimo Las palancas negras Ranking FIFA 57.mo lugar (mayo de 2006) Participación 1.ª Mejor resultado Debutante Entrenador Luís Oliveira Estadísticas Partidos 3 Goles anotados 1 (0.33 por partido) Goles recibidos 2 (0.67 por partido) Goleador Flávio (Un gol) Cronología Anterior — Siguiente Por definir La selección de Angola fue uno de los 32 países participante...

Canadian civil servant (1905–2000) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Bent Gestur Sivertz – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Bent Gestur Sivertz's Order of the British Empire Medal, University of King's College, Halifax, Nov...

1960 film Under Ten FlagsItalian film posterDirected byDuilio ColettiWritten byVittoriano PetrilliDuilio ColettiUlrich MöhrProduced byDino De LaurentiisStarringVan HeflinCharles LaughtonMylène DemongeotCinematographyAldo TontiEdited byJerry WebbMusic byNino RotaProductioncompanyDino de Laurentiis CinematograficaDistributed byParamount Pictures (US)Release dates 15 September 1960 (1960-09-15) (US) 21 September 1960 (1960-09-21) (Italy) Running time92 min...
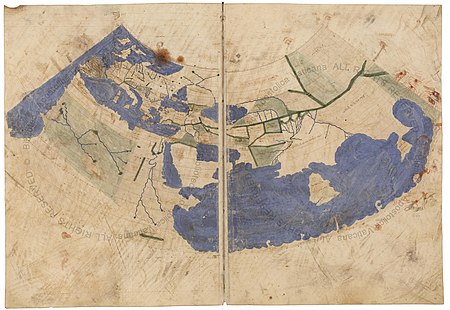
Treatise on cartography by Claudius Ptolemaeus The Geography of Ptolemy in a c. 1411 Latin translation by Jacobus Angelus with 27 maps by Claus Swart. The Geography (Ancient Greek: Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis, lit. Geographical Guidance), also known by its Latin names as the Geographia and the Cosmographia, is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, compiling the geographical knowledge of the 2nd-century Roman Empire. Original...

Seán Patrick O'MalleyGCIH OFM CapKardinal, Uskup Agung BostonKeuskupan agungBostonPenunjukan1 Juli 2003Awal masa jabatan30 Juli 2003PendahuluBernard Francis LawJabatan lainKardinal-Imam S. Maria della VittoriaAnggota Dewan Penasehat KardinalPresiden Komisi Kepausan bagi Perlindungan MinorAnggota Kongregasi bagi Doktrin ImanImamatTahbisan imam29 Agustus 1970oleh John Bernard McDowellTahbisan uskup2 Agustus 1984oleh Edward John Harper, James Aloysius Hickey, dan Eugene Antonio Marino...

العلاقات الهندية التوفالية الهند توفالو الهند توفالو تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الهندية التوفالية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين الهند وتوفالو.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة الهند ت...

138th final of the FA Cup For the women's event, see 2019 FA Women's Cup final. Football match2019 FA Cup finalWembley Stadium, the venue of the matchEvent2018–19 FA Cup Manchester City Watford 6 0 Date18 May 2019 (2019-05-18)VenueWembley Stadium, LondonMan of the MatchKevin De Bruyne (Manchester City)RefereeKevin Friend (Leicestershire)Attendance85,854← 2018 2020 → The 2019 FA Cup final was an association football match between Manchester City and Watford on 18 M...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant la Région flamande et le bois et la forêt. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. La forêt flamande couvre approximativement 1 500 km2, ce qui représente 11 % de son territoire. On y trouve une petite majorité de feuillus. L'essence feuillue la plus courante est le Peuplier, devant le Chêne et le Hêtre commun. Les essences résineuses les plu...

Las referencias de este artículo no tienen un formato correcto. Puedes colaborar editándolas como se indica en esta página.También puedes avisar en su página de discusión a quien las añadió pegando lo siguiente: {{subst:Aviso formato de referencias|Yihadismo}} ~~~~Este aviso fue puesto el 14 de noviembre de 2015. Para el concepto original islámico, véase Yihad. Las Torres Gemelas pertenecientes al World Trade Center en Nueva York ardiendo en llamas el 11 de septiembre de 2001. El a...
