Abattoir Blues / The Lyre of Orpheus
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

PT Sasa IntiJenisAnak perusahaanIndustriBahan makananDidirikan28 November 1972; 51 tahun lalu (1972-11-28)PendiriTan Kang SoTan Siong KieKantorpusatJl. Letjen S. Parman Kav. 32-34, Jakarta Barat 11480, Jakarta, IndonesiaWilayah operasiSeluruh duniaTokohkunciRudolf Tjandra (CEO)ProdukPenyedap rasaBumbuSambalSantanSausIndukRodamasSitus webwww.sasa.co.id PT Sasa Inti (Sasa) merupakan perusahaan makanan dan bumbu masak terkemuka dari Indonesia yang didirikan oleh Rodamas pada tahun 1972. Sej...
Artikel ini bukan mengenai Dewan Legislatif Palestina, badan legislatif Otoritas Nasional Palestina sampai 2006. Negara Palestina Artikel ini adalah bagian dari seri Politik dan KetatanegaraanPalestina Jabatan yang statusnya disengketakan ditunjukkan dengan huruf miring Negara Anggota Liga Arab Pemerintahan Pemerintah Negara Palestina (Ramallah) Presiden: Mahmoud Abbasa Perdana Menteri: Mohammad Shtayyeh Pemerintah Hamas (Gaza) Simbol nasional Bendera Lagu kebangsaan Lambang Dewan Legislatif ...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (يوليو 2019) منتخب الهند لكرة اليد البلد ؟؟ الزي الأساسي الزي الإحتياطي بطولة آسيا لكرة اليد للرجال الظهور 3 (أول مرة في...

Katedral San Jose de Nueva EcijaKatedral Paroki Santo Yosef PekerjaFilipina: Parokyang Katedral ni San Jose ManggagawaSpanyol: Catedral Parroquia de San José ObreroKatedral San Jose de Nueva EcijaKatedral San Jose de Nueva EcijaLokasi katedral di Filipina15°47′32″N 120°59′22″E / 15.792167°N 120.989528°E / 15.792167; 120.989528Koordinat: 15°47′32″N 120°59′22″E / 15.792167°N 120.989528°E / 15.792167; 120.989528Loka...

American baseball player (born 1988) Baseball player Danny DuffyDuffy with the Kansas City Royals in 2011Texas Rangers – No. 24PitcherBorn: (1988-12-21) December 21, 1988 (age 35)Goleta, California, U.S.Bats: LeftThrows: LeftMLB debutMay 18, 2011, for the Kansas City RoyalsMLB statistics (through 2021 season)Win–loss record68–68Earned run average3.95Strikeouts1,048 Teams Kansas City Royals (2011–2021) Career highlights and awards World Series champion (2015) Medals...
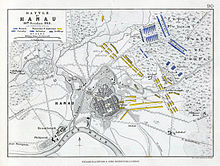
1813 battle during the War of the Sixth Coalition Battle of HanauPart of the German campaign of the Sixth CoalitionBattle of Hanau, Horace VernetDate30–31 October 1813LocationHanau, Duchy of Frankfurt50°07′59″N 8°55′01″E / 50.1331°N 8.9169°E / 50.1331; 8.9169Result French victoryBelligerents France Bavaria AustriaCommanders and leaders Napoleon Bonaparte Karl von WredeStrength 17,000-30,000 43,000Casualties and losses 4,500[1]-5,0...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Consistoire. Cet article est une ébauche concernant le protestantisme. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Le consistoire était, dans les régions protestantes, un organe judiciaire mi-laïc, mi-ecclésiastique, formé des pasteurs et des anciens de l'Église, laïcs élus. Ils avaient pour but de diriger l'église locale et de contrôler les mœurs des citoyens[1]...
Ribellione dei BoxerTruppe statunitensi scalano il muro di PechinoData2 novembre 1899 - 7 settembre 1901 LuogoCina settentrionale CausaTrattati ineguali, ingerenze occidentali e giapponesi in Cina EsitoVittoria dell'Alleanza delle otto nazioni Modifiche territorialiConcessioni territoriali accordate dalla Cina alle potenze europee SchieramentiAlleanza delle otto nazioni (ordine di contribuzione): Giappone Impero russo Impero britannico Francia Stati Uniti Germania Italia&#...

Luca Nizzetto Luca Nizzetto in azione con la maglia del Modena Nazionalità Italia Altezza 176 cm Peso 70 kg Calcio Ruolo Centrocampista Squadra Belfiorese CarrieraGiovanili 2005 VeronaSquadre di club1 2005-2006→ Feralpisalò12 (3)2006→ Olbia13 (1)2006-2007→ Castelnuovo31 (3)2007-2008 Mezzocorona30 (9)[1]2008-2009 Legnano33 (8)2009-2013 Cremonese112 (11)[2]2013-2014 Trapani39 (4)2014-2016 Modena49 (0)[3]2016-...

1804–1813 war between the Persian Empire and Imperial Russia This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Russo-Persian War 1804–1813 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Russo-Persian War (1804–1813)Part of the Russo-Persian W...

Involvement of Luxembourg in World War II Heinrich Himmler, saluted by a Luxembourg policeman, during his visit to Luxembourg in October 1940, several months after the invasion. The involvement of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg in World War II began with its invasion by German forces on 10 May 1940 and lasted beyond its liberation by Allied forces in late 1944 and early 1945. Luxembourg was placed under occupation and was annexed into Germany in 1942. During the occupation, the German authorit...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (نوفمبر 2020) مؤتمر أساقفة منطقة شمال إفريقيا الاختصار CERNA البلد الجزائر ليبيا المغرب تونسالصحراء الغربية المقر الرئيسي الرباط تاريخ التأسيس 1966 تعديل مصدري - ت...

Azerbaijani political party New Azerbaijan Party Yeni Azərbaycan PartiyasıAbbreviationYAPPresidentIlham AliyevVice PresidentMehriban AliyevaFounderHeydar AliyevFounded21 November 1992 (1992-11-21)Registered18 December 1992 (1992-12-18)HeadquartersSergey Senyuşkin küç. 26, Baku, AzerbaijanYouth wingYeni Azərbaycan Partiyası Gənclər Birliyi [az]Women's wingQadınlar ŞurasıMembership 773,770 (2022 est.)[1]Ideology Conservatism[2&#...

This article is about the youth team that started competing in competitions in 2010. For other Singapore-related national football teams, see Singapore national football team. Singapore U15/16/17sNickname(s)The CubsThe Young LionsThe SchoolboysAssociationFootball Association of SingaporeConfederationAFC (Asia)Sub-confederationAFF (Southeast Asia)Head coachÁngel ToledanoCaptainKeegan PhangHome stadiumJalan Besar Stadium (temporarily shared with the senior team)FIFA codeSIN First colours Seco...

Person who does not take a direct part in hostilities during war For the corps of the British Army that was active from 1916 to 1920 and again from 1940 to 1963, see Non-Combatant Corps. A Swedish Army medic wearing a Red Cross treats an Afghan civilian in 2006, during the War in Afghanistan. They would be considered non-combatants in the war. Non-combatant is a term of art in the law of war and international humanitarian law to refer to civilians who are not taking a direct part in hostiliti...

Italian directory of nobles For other uses, see Golden Book.See also: Libro d'Oro della Nobiltà italiana (official register) and Libro d'Oro della Nobiltà italiana (private publication) Il Libro d'Oro della Nobiltà Italiana It has been suggested that this article should be split into articles titled Libro d'Oro della Nobiltà italiana (official register) and Libro d'Oro della Nobiltà italiana (private publication). (discuss) (July 2024) This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's...

English footballer Adam Watts Personal informationFull name Adam James Watts[1]Date of birth (1988-03-04) 4 March 1988 (age 36)[1]Place of birth Hackney, EnglandHeight 6 ft 2 in (1.88 m)[1]Position(s) DefenderYouth career000?–2007 FulhamSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2007–2010 Fulham 0 (0)2007 → Milton Keynes Dons (loan) 2 (0)2009 → Northampton Town (loan) 5 (0)2009 → Lincoln City (loan) 10 (0)2010–2011 Lincoln City 59 (1)2012 Gainsb...

American television executive (1901–1990) This article is about the broadcasting executive. For the philosopher, see William Paley. For the filmmaker, see William C. Paley. William S. PaleyPaley in 1939BornWilliam Samuel Paley(1901-09-28)September 28, 1901Chicago, Illinois, U.S.DiedOctober 26, 1990(1990-10-26) (aged 89)New York City, U.S.Resting placeMemorial Cemetery of Saint John's ChurchAlma materUniversity of PennsylvaniaOccupationTelevision executiveKnown forPresident of...

1865 battle of the American Civil War Battle of BentonvillePart of the Campaign of the CarolinasFrank Leslie's Illustrated Newspaper April 22, 1865 issue, showing union troops routing the rebel left flankDateMarch 19–21, 1865LocationBentonville, North Carolina35°18′23″N 78°19′26″W / 35.30639°N 78.32389°W / 35.30639; -78.32389Result Union victoryBelligerents United States (Union) Confederate StatesCommanders and leaders William T. Sherman Josep...

Former train station in New York City Pennsylvania StationView from the northeast in the 1910sGeneral informationLocationNew York CityU.S.Coordinates40°45′01″N 73°59′35″W / 40.7503°N 73.9931°W / 40.7503; -73.9931Owned byPennsylvania RailroadPenn CentralConstructionArchitectMcKim, Mead, and White[1][2]Architectural styleBeaux-ArtsOther informationStatusDemolished (above ground)HistoryOpenedSeptember 8, 1910 (LIRR)November 27, 1910 (...
