2 Kings 4
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

American politician and diplomat Harold Marsh Sewall (January 3, 1860 – October 28, 1924) was an American politician and diplomat. Harold M. SewallUnited States Minister to HawaiiIn office1897 – August 12, 1898PresidentWilliam McKinleyPreceded byAlbert Sydney Willis Personal detailsBorn(1860-01-03)January 3, 1860Bath, Maine, U.S.DiedOctober 28, 1924(1924-10-28) (aged 64)New York City, New York, U.S.Resting placeOak Grove CemeteryBath, Maine, U.S. Sewall was born in Bath,...

Stasiun Itaya板谷駅Stasiun kecilTampak peron Stasiun Itaya dari kejauhan (September 2012)Lokasi582 Itaya, Yonezawa-shi, Yamagata-ken 992-1331JepangKoordinat37°48′42″N 140°16′07″E / 37.811594°N 140.268631°E / 37.811594; 140.268631Koordinat: 37°48′42″N 140°16′07″E / 37.811594°N 140.268631°E / 37.811594; 140.268631Operator JR EastJalur■ Jalur Utama ŌuLetak21.2 km dari FukushimaJumlah peron2 peron sisi rendahLayanan Tid...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Arbel. Lucy Arbell Lucy Arbell par Paul Nadar. Données clés Nom de naissance Georgette GallGeorgette Wallace (à partir de 1884, après avoir été reconnue) Naissance 8 juin 1878 Vésinet Décès 21 mai 1947 (à 68 ans) Bougival Nationalité Française Activité principale Cantatrice, artiste lyriquemezzo-soprano Lieux d'activité Paris modifier Lucy Arbell, nom de scène de Georgette Wallace, née Georgette Gall au Vésinet le 8 juin 1878 et m...

Vanilla SkyPoster rilis teatrikalSutradaraCameron CroweProduserCameron CroweTom CruisePaula WagnerSkenarioCameron CroweBerdasarkanOpen Your Eyesoleh Alejandro AmenábarMateo GilPemeranTom CruisePenélope CruzKurt RussellJason LeeNoah TaylorCameron DiazPenata musikNancy WilsonSinematograferJohn TollPenyuntingJoe HutshingMark LivolsiPerusahaanproduksiVinyl FilmsWingNut FilmsCruise/Wagner ProductionsDistributorParamount PicturesTanggal rilis 14 Desember 2001 (2001-12-14) Durasi137 men...

追晉陸軍二級上將趙家驤將軍个人资料出生1910年 大清河南省衛輝府汲縣逝世1958年8月23日(1958歲—08—23)(47—48歲) † 中華民國福建省金門縣国籍 中華民國政党 中國國民黨获奖 青天白日勳章(追贈)军事背景效忠 中華民國服役 國民革命軍 中華民國陸軍服役时间1924年-1958年军衔 二級上將 (追晉)部队四十七師指挥東北剿匪總司令部參謀長陸軍�...
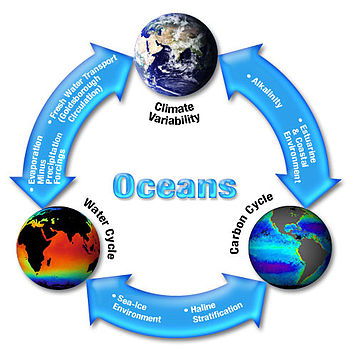
Scientific study of the Earth's spheres and their natural integrated systems An ecological analysis of CO2 in an ecosystem. As systems biology, systems ecology seeks a holistic view of the interactions and transactions within and between biological and ecological systems. Earth system science (ESS) is the application of systems science to the Earth.[1][2][3][4] In particular, it considers interactions and 'feedbacks', through material and energy fluxes, between...

American biblical scholar (1794-1863) Edward RobinsonBornApril 10, 1794Southington, Connecticut, U.S.DiedJanuary 27, 1863 (1863-01-28) (aged 68)New York City, U.S. Edward Robinson (April 10, 1794 – January 27, 1863) was an American biblical scholar known for his magnum opus, Biblical Researches in Palestine, the first major work in Biblical Geography and Biblical Archaeology, which earned him the epithets Father of Biblical Geography and Founder of Modern Palestinology.[1]...

15th-century dynasty based in Sindh For other uses, see Samma. 24°44′46.02″N 67°55′27.61″E / 24.7461167°N 67.9243361°E / 24.7461167; 67.9243361 Samma dynasty(Sindh Sultanate)سما راڄ1351–1524South Asia1400 CEDELHISULTANATE(TUGHLAQS)TIMURIDEMPIRESHAH MIRSULTANATEPHAGMODRUPASSAMMASMARYULGUGEKUMAONKANGRAKALMATGUJARATGOVERNORATEBAHMANISULTANATEKHANDESHSULTANATETOMARASTWIPRAEASTERNGANGASSUGAUNASMALLACHEROSNAGVANSISAHOMKAMATASCHUTIABENGALSULTANATEVI...

Japanese video game designer (born 1952) Miyamoto redirects here. For the Japanese surname, see Miyamoto (surname). For the crater, see Miyamoto (crater). The native form of this personal name is Miyamoto Shigeru. This article uses Western name order when mentioning individuals. Shigeru Miyamoto宮本 茂Miyamoto in 2015Born (1952-11-16) November 16, 1952 (age 71)Sonobe, Kyoto, JapanAlma materKanazawa College of ArtOccupations Game designer game producer game director EmployerN...
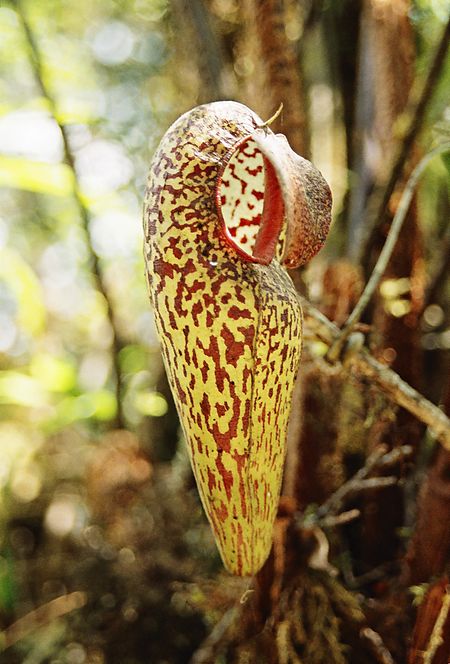

Nepenthes aristolochioides Kantong atas N. aristolochioides Status konservasi Kritis (IUCN 2.3) Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Tracheophyta (tanpa takson): Angiospermae (tanpa takson): Eudikotil (tanpa takson): Inti eudikotil Ordo: Caryophyllales Famili: Nepenthaceae Genus: Nepenthes Spesies: N. aristolochioides Nama binomial Nepenthes aristolochioidesJebb & Cheek (1997)[1] Nepenthes aristolochioides (/[invalid input: 'icon']n[invalid input: 'ɨ']...

Italian actress (1931–2011) Dorian GrayGray in 1958BornMaria Luisa Mangini(1931-02-02)2 February 1931Bolzano, Kingdom of ItalyDied15 February 2011(2011-02-15) (aged 80)Torcegno, Trentino, ItalyOccupationActressYears active1951–1965 Dorian Gray (born Maria Luisa Mangini; 2 February 1931 – 15 February 2011) was an Italian actress. Biography Gray made her stage debut in 1950. After five years she left the world of the theater and devoted herself to cinema. Dorian Gray in Totò, P...

莎拉·阿什頓-西里洛2023年8月,阿什頓-西里洛穿著軍服出生 (1977-07-09) 1977年7月9日(46歲) 美國佛羅里達州国籍 美國别名莎拉·阿什頓(Sarah Ashton)莎拉·西里洛(Sarah Cirillo)金髮女郎(Blonde)职业記者、活動家、政治活動家和候選人、軍醫活跃时期2020年—雇主內華達州共和黨候選人(2020年)《Political.tips》(2020年—)《LGBTQ國度》(2022年3月—2022年10月)烏克蘭媒�...

Ancient script of Central and South Asia Brahmi redirects here. For other uses, see Brahmi (disambiguation). For later scripts derived from Brahmi, see Brahmic scripts. BrahmiBrāhmīBrahmi script on Ashoka Pillar in Sarnath (c. 250 BCE)Script type Abugida Time periodAt least by the 3rd century BCE[1] to 5th century CEDirectionLeft-to-right LanguagesSanskrit, Pali, Prakrit, Tamil, Saka, Tocharian, Telugu, EluRelated scriptsParent systemsEgyptian hieroglyphsProto-Sinaitic sc...

Rancho Monte del Diablo was granted in 1834 to Salvio Pacheco, a noted Californio ranchero. Rancho Monte del Diablo (Devil's Mount Ranch in Spanish) was a 17,921-acre (72.52 km2) Mexican land grant in present-day Contra Costa County, California given in 1834 by Governor José Figueroa to Salvio Pacheco.[1] The name Monte del Diablo means thicket of the devil in Spanish. The name was later incorrectly translated as Mount Diablo. The grant covered the area from the Walnut Creek cha...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) لويس مرسيدس (بالإسبانية: Luis Mercedes) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 15 فبراير 1968 سان بيدرو دي ماكوريس الوفاة 30 يونيو 2019 (51 سنة) [1] سان بيدرو دي ماكوريس ...
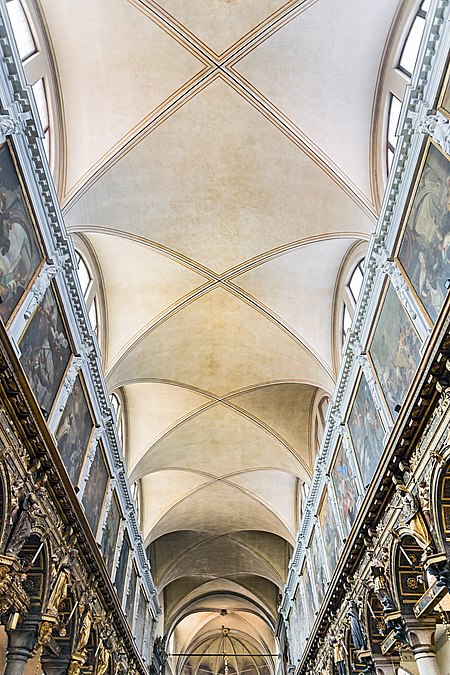

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento elementi architettonici non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Schema che illustra come si ottiene una volta a crociera La volta a crociera è un tipo di copertura architettonica formata dall'intersezione longitudinale di due volte a botte. Indice 1 Storia 2 Descrizione 2.1 Struttura 3 Volta esapartita 4 Esem...

العلاقات الإيطالية المالاوية إيطاليا مالاوي إيطاليا مالاوي تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الإيطالية المالاوية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين إيطاليا ومالاوي.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقا...

أنثيا تقسيم إداري البلد اليونان [1] إحداثيات 40°52′17″N 25°59′25″E / 40.871388888889°N 25.990277777778°E / 40.871388888889; 25.990277777778 السكان التعداد السكاني 747 (resident population of Greece) (2021)801 (resident population of Greece) (2001)744 (resident population of Greece) (1991)781 (resident population of Greece) (2011) الرمز الجغرافي 736778 تع�...

Departemen San José BenderaLambang kebesaranNegara UruguayIbu kota DepartemenSan José de MayoPemerintahan • IntendanJosé Luis Falero • Partai berkuasaPartido NacionalLuas • Total4,992 km2 (1,927 sq mi)Populasi (2011 census) • Total108.309 • Kepadatan22,000/km2 (56,000/sq mi)DemonimMaragatoZona waktuUTC-3 (UYT)Kode ISO 3166UY-SJSitus webimsj.gub.uy Map of San José Department Departemen San José ...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Сердце пармы (значения). Сердце пармы Жанры историческая драма с элементами фэнтези Режиссёр Антон Мегердичев Продюсеры Влад РяшинИгорь ТолстуновДарья ЛавроваАнтон Златопольский На основе романа«Сердце пармы»Алексея И...







